Complete Overview of Managing Genital Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores genital psoriasis, covering its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of professional diagnosis, effective management strategies, and emotional support to improve quality of life. The article aims to inform individuals about this chronic condition with sensitivity and expertise.

Understanding Genital Psoriasis: Signs, Causes, and Care
Genital psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects sensitive areas, causing discomfort and emotional challenges. Although psoriasis mainly affects the skin, when it appears in intimate regions, it presents specific considerations. This article provides an in-depth look at genital psoriasis, including its symptoms, underlying causes, and management options, presented professionally and with sensitivity.
What Is Genital Psoriasis?
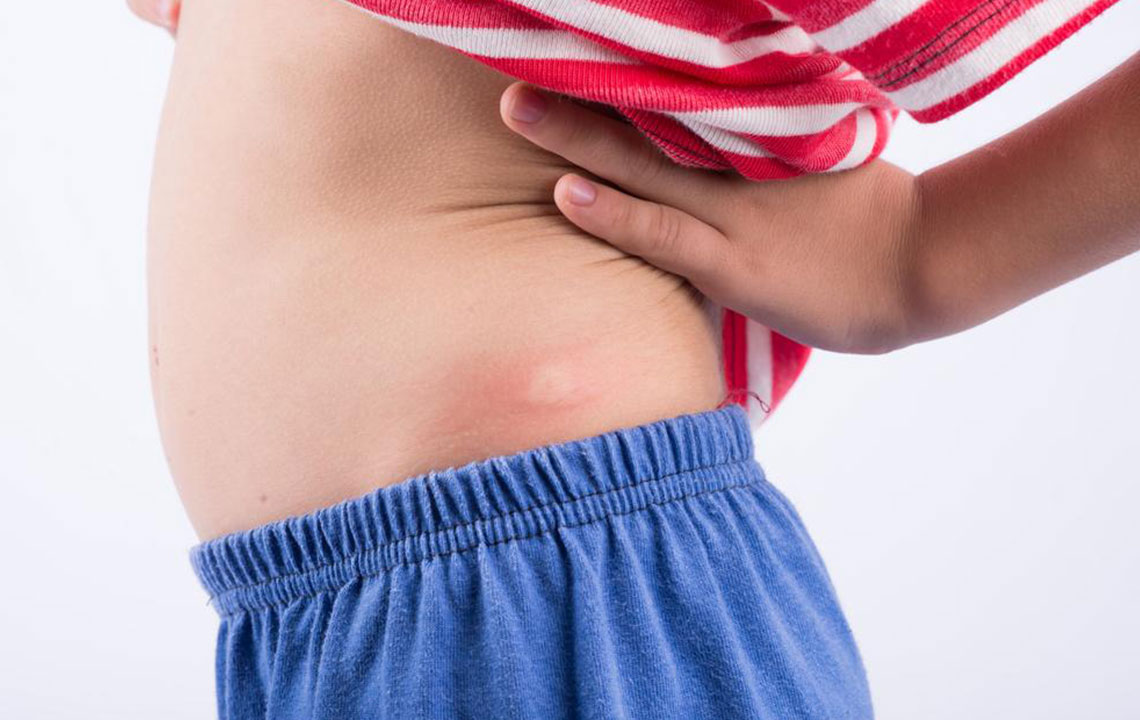
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease leading to accelerated skin cell production, resulting in red, scaly patches. When these occur in the genital region, it is known as genital psoriasis. It affects both genders, usually involving the groin, inner thighs, and surrounding areas. Unlike other psoriasis patches, these areas tend to have smoother, less flaky skin because of moisture.
Symptoms of Genital Psoriasis:
Typical signs include:
Red patches: Usually smooth and less scaled compared to other psoriasis spots.
Itching and irritation: The sensitive skin can lead to significant discomfort.
Burning sensations: Some may experience burning, especially during physical activity or intimacy.
Dryness and cracking: Skin can become dry, resulting in cracks and irritation.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of psoriasis remains unknown; however, genetic, immune, and environmental factors play roles. Common triggers include:
Stress: Emotional strain can exacerbate symptoms.
Infections: Infections like strep throat may induce flare-ups.
Skin injuries: Cuts or abrasions can prompt outbreaks.
Diagnosis and Management
Healthcare providers diagnose genital psoriasis through physical examination, sometimes supported by a biopsy to rule out similar conditions. Treatment approaches include:
Topical treatments: Corticosteroid creams and medicated ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
Moisturizers: Fragrance-free, gentle lotions to keep skin hydrated.
Trigger management: Stress reduction and avoiding harsh soaps can minimize flare-ups.
Light therapy: Phototherapy may help in certain cases.
Healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet and regular exercise promote overall skin health.
Mental and Emotional Impact:
Dealing with genital psoriasis can affect mental well-being and intimate relationships. Support from healthcare professionals, counselors, or support groups can provide valuable assistance, improving overall quality of life. Proper understanding, effective management, and open communication with medical experts empower individuals to handle this condition confidently, leading to better health outcomes.