Effective Strategies for Managing Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Learn about Hashimoto's thyroiditis, its symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and effective management strategies. This article emphasizes hormone replacement therapy and the importance of regular monitoring for optimal health. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment.

Effective Strategies for Managing Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing swelling often visible as a goiter. This condition affects hormone production, leading to symptoms such as exhaustion, weight gain, mood changes, and muscle discomfort. Factors contributing to the disease include genetics, hormonal imbalances, high iodine levels, and radiation exposure.
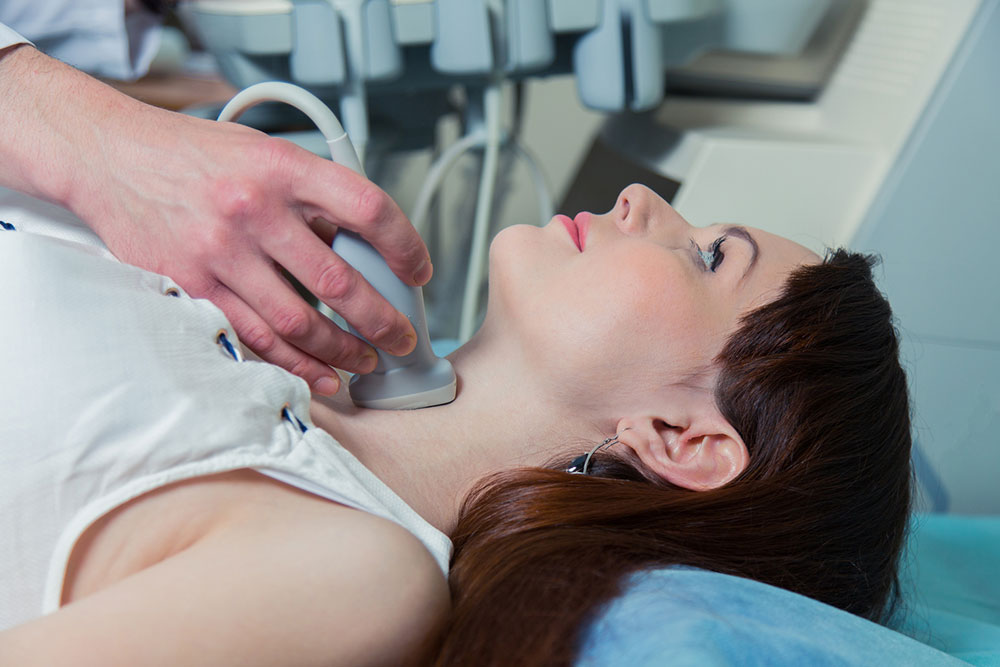
Diagnosis involves blood tests that check thyroid hormone and antibody levels. Treatment primarily includes hormone replacement therapy with synthetic levothyroxine, carefully managed by your healthcare provider to maintain balanced hormone levels and avoid complications.
Diagnosis Techniques
Doctors may suspect Hashimoto's if you present symptoms like fatigue, dry skin, or throat issues, especially with a history of thyroid problems. Blood tests measure TSH and detect specific antibodies, with low thyroid hormones and high TSH indicating Hashimoto's disease.
Treatment Approach
If your hormone levels are stable, monitoring may suffice. When intervention is needed, daily doses of synthetic hormones like levothyroxine are commonly prescribed. Regular check-ups ensure appropriate dosing, minimizing risks of over or under-treatment, which can cause additional health issues.
Important Reminder:
This article provides general information about Hashimoto's disease. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment options. The content is for informational purposes and may not reflect all current medical practices or advancements.