Essential Strategies for Managing Atrial Fibrillation
This comprehensive guide explores effective management options for atrial fibrillation, including rhythm restoration techniques like cardioversion and medication strategies to control heart rate and reduce stroke risks. Understanding these approaches helps patients and healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to individual needs, improving outcomes and quality of life.
Approaches to Managing Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation, known as AFib, is a heart rhythm disorder marked by irregular and rapid beats, leading to sensations like fluttering or quivering. About 27% of Americans are affected by AFib, contributing to nearly one-fifth of strokes. The condition often stems from blood thickening and clot formation, commonly associated with high cholesterol or blood sugar levels, which elevate blood pressure.
Management strategies depend on the duration, symptom severity, and underlying causes. The goal is to restore normal heart rhythm and diminish stroke risk through medical intervention.
Key treatments focus on restoring the heart's normal rhythm, often via procedures like cardioversion. Techniques include electrical cardioversion and medication-assisted approaches.
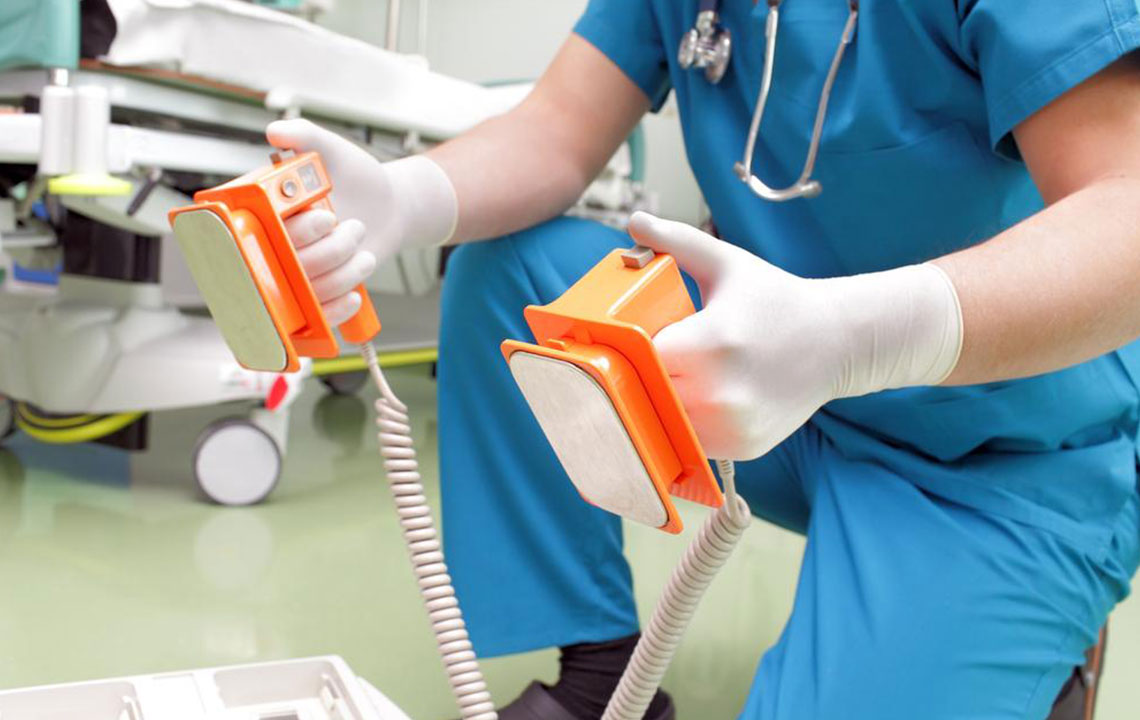
Electrical Cardioversion: This method involves delivering a timed electric shock to the chest with paddles, temporarily stopping the heart’s electrical signals to reset its rhythm.
Medication Therapy: Anti-arrhythmic drugs are given through IV or orally to restore rhythm. Patients typically receive blood thinners beforehand to reduce clotting risks, with careful monitoring during treatment.
Following cardioversion, drugs are often prescribed to prevent recurrence, though side effects such as fatigue, nausea, or dizziness may occur. Despite therapy, AFib can return, and medications also help reduce stroke risk.
Heart rate control is achievable with medications like beta blockers or calcium channel blockers. While effective at rest, their effectiveness during activity may decrease, necessitating combination therapy. Some drugs may cause side effects like hypotension or worsened heart function.