Proven Approaches to Mitigate Viral Illness Symptoms
Discover effective strategies to relieve viral infection symptoms, including early diagnosis, vaccination, and antiviral treatments. Understanding symptoms and proper medical intervention can significantly improve recovery and prevent severe complications. This guide emphasizes prompt healthcare advice and testing methods for accurate diagnosis and management of viral illnesses across different types.
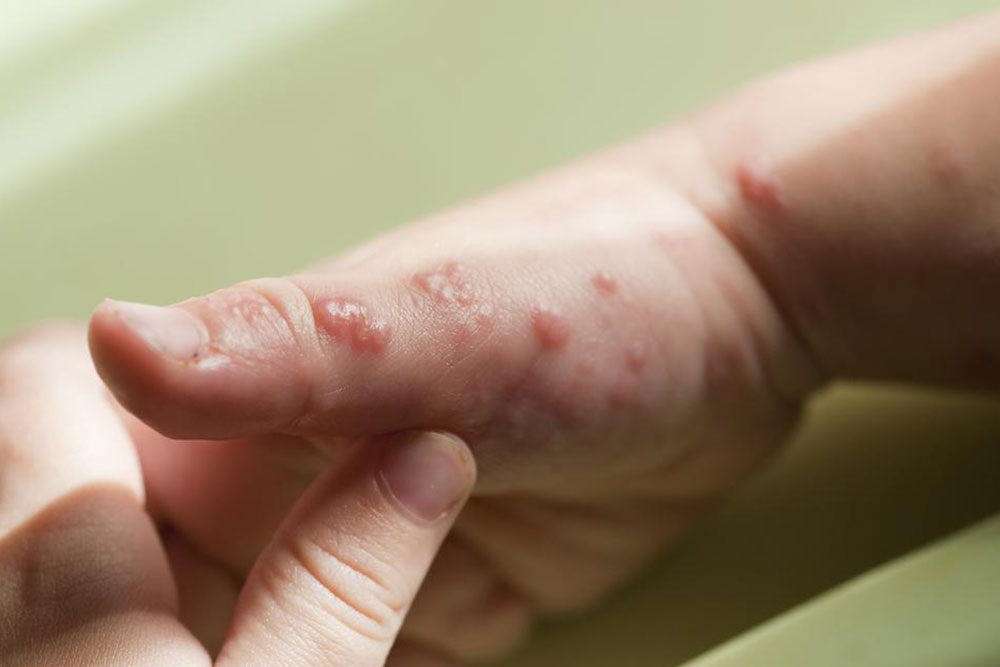
Methods to Reduce Viral Infection Discomforts
Viral illnesses stem from various viruses present in our surroundings and can spread rapidly depending on the specific virus. Airborne viruses cause respiratory infections, while viruses transmitted through contaminated food and drinks spread via ingestion. Some viruses also transfer through sexual contact or kissing, entering the body through saliva.
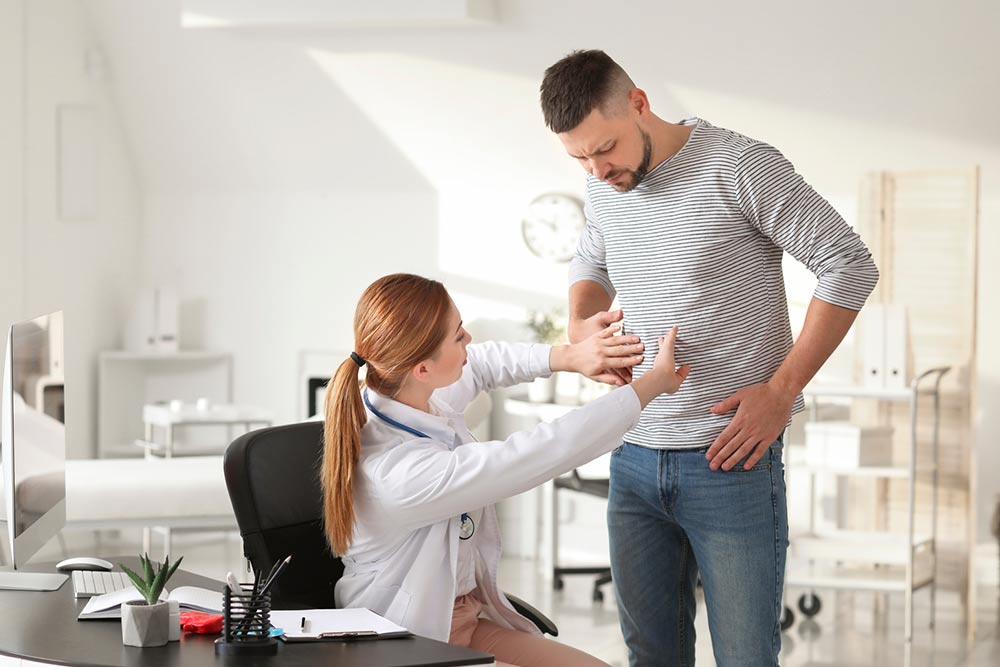
Common signs of viral infections include fever, fatigue, muscle ache, skin rashes, coughing, vomiting, sneezing, diarrhea, nasal blockage, chills, and headaches.
More severe symptoms may involve personality shifts, neck stiffness, extreme drowsiness, urinary problems, bowel irregularities, dehydration, seizures, back pain, confusion, and limb paralysis.
Detecting viral infection symptoms can be difficult, highlighting the need for prompt medical consultation. Early diagnosis is especially vital for children.
Healthcare professionals must identify the specific virus to determine the best treatment.
Diagnostic techniques include:
Blood tests to detect the virus, antibodies, or antigens responsible for the illness.
Laboratory tests such as blood and fluid cultures to isolate and identify virus strains.
For viral skin infections, samples are taken from affected areas for analysis. A spinal tap may be necessary to examine cerebrospinal fluid, and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is used to replicate viral DNA for precise identification.
Available treatment approaches include:
Vaccination is the most effective preventive method, boosting immunity to prevent viral infections. Regular immunization is highly encouraged.
Antiviral drugs can lessen symptoms by interfering with viral proteins, though they are less effective than vaccines. These medications aim to inhibit viral activity and help manage symptoms, with vaccines providing longer-lasting protection.


