Proven Methods for Combating and Managing Toenail Fungal Infections
Discover effective methods to treat and manage toenail fungal infections. This guide covers symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle tips to achieve healthy nails. Early intervention and consistent care are key to preventing recurrence and promoting nail recovery. Consult healthcare professionals for tailored advice and effective solutions.
Proven Methods for Combating and Managing Toenail Fungal Infections
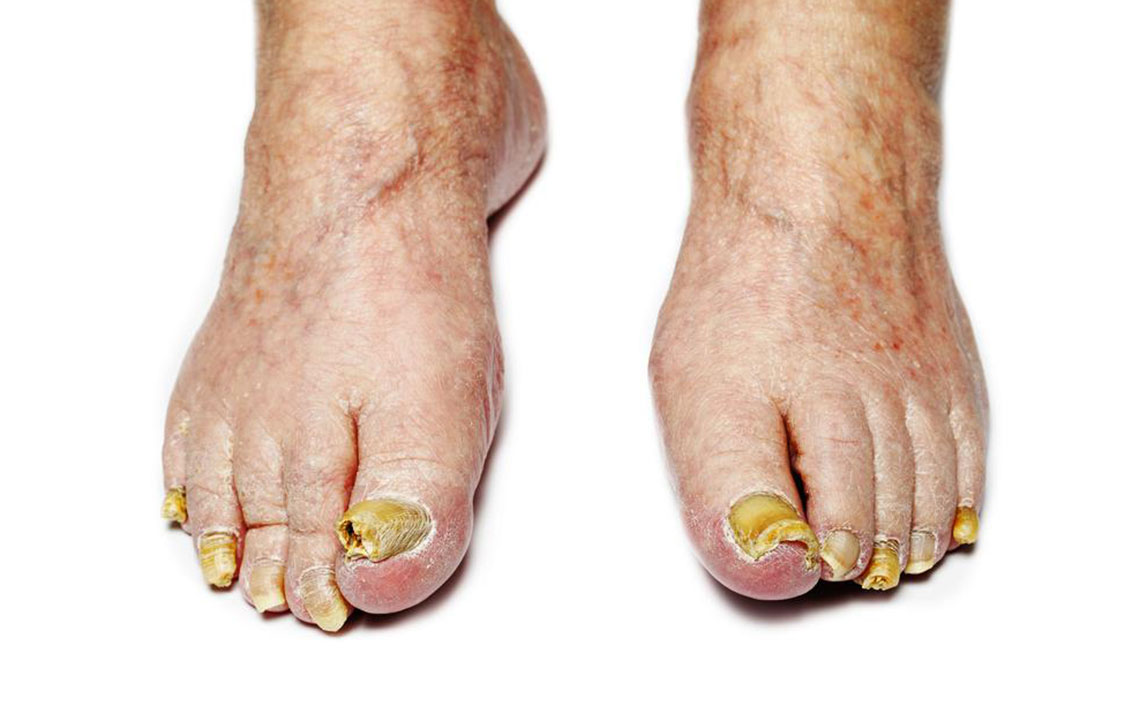
Toenail fungal infections are common, often starting as small white or yellow spots under the nail tip. As the infection progresses, the nail may become discolored, thickened, or crumbly at the edges. Mild infections might not need treatment, but more severe cases causing discomfort or thickening require remedies or medications. Fungal infections tend to recur despite treatment efforts. Keep reading to learn about symptoms and effective strategies to eliminate toenail fungus:
Signs and Symptoms
While toenails are most frequently affected, fingernails can also develop fungal infections. When addressed properly, these infections usually don't lead to lasting issues. Individuals with diabetes or weakened immune systems may face more serious complications. Common signs include yellow or brown nails, thickening, brittleness, crumbling edges, and dark debris beneath the nail. A foul odor might be present, and while pain is rare, noticeable changes indicate infection.
Treatment Strategies
Antifungal Drugs
Doctors often recommend oral or topical antifungal medications for toenail infections. Using both can increase success rates.
Systemic Antifungal Treatments
Oral antifungals tend to be highly effective and promote the growth of healthy nails within 6 to 12 weeks, with full recovery taking several months. They may cause side effects like skin rash or liver issues, so regular monitoring is advised, especially for those with liver or heart conditions.
Medicated Nail Polish
Applying antifungal nail lacquer daily is a common approach. This involves coating the nail and surrounding area, then removing and reapplying weekly. Consistent use over nearly a year provides the best results.
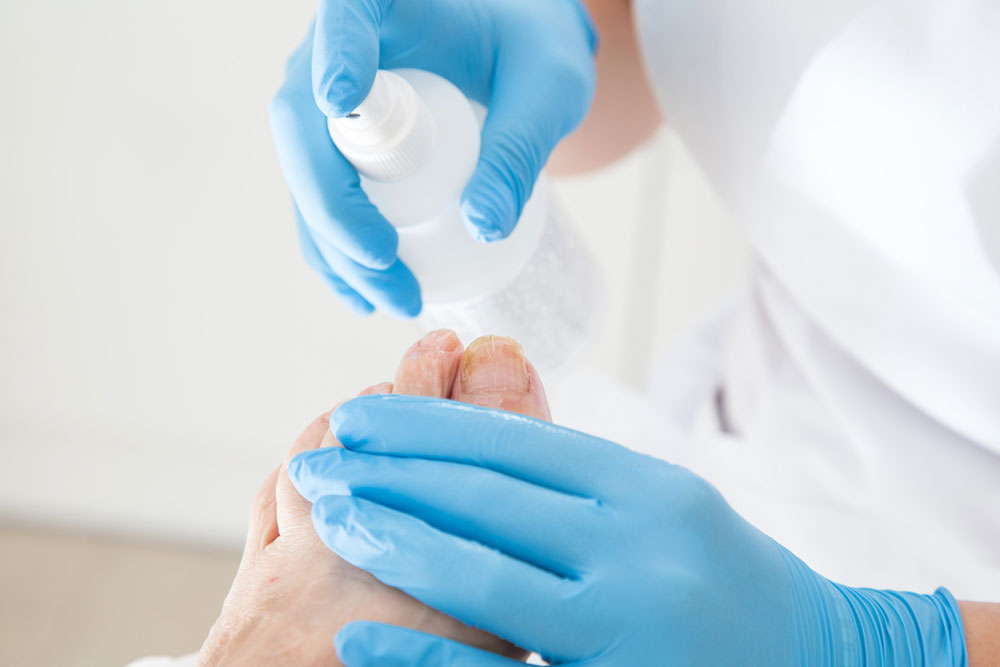
Topical Antifungal Creams
Prescription creams are used after soaking the affected nails. Thinning thickened nails enhances medication absorption. Non-prescription urea-based lotions can soften nails for easier application.
Surgical Options
If infections resist medications, nail removal—either temporary or permanent—may be performed to allow direct treatment or relieve discomfort.
Home and Lifestyle Tips
Apply over-the-counter antifungal creams or ointments on affected nails. Carefully file away white patches and soak nails in water before applying medication after drying.
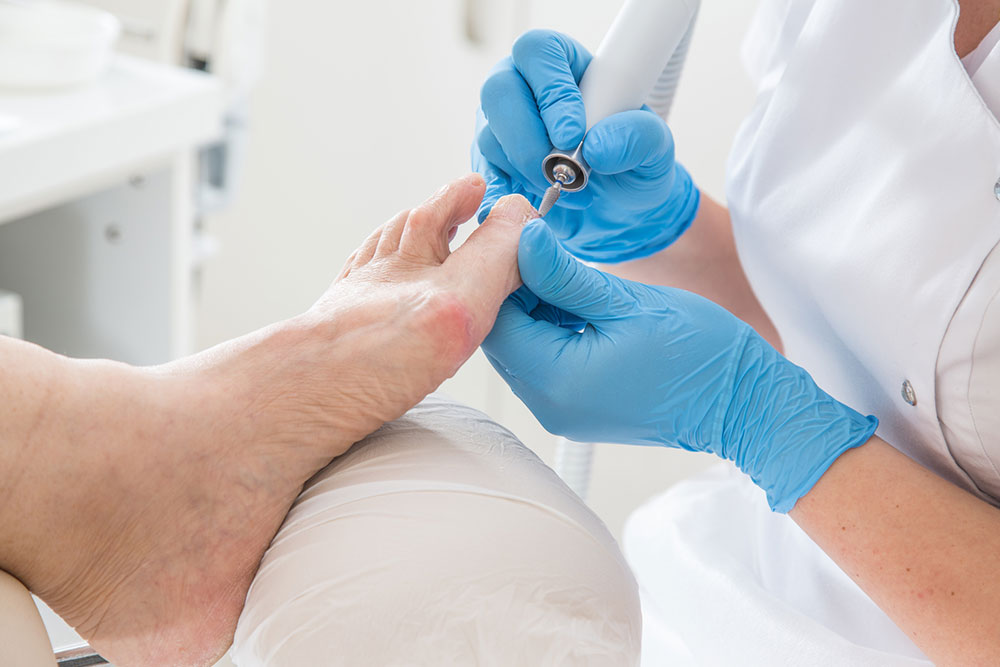
Keep nails trimmed and filed to reduce discomfort and improve treatment absorption. Use creams containing urea or seek professional help for trimming, especially if blood circulation issues exist.
Early treatment enhances the chances of curing toenail fungus and restoring healthy nails. Prompt action prevents the infection from spreading to other areas or people. Treatment duration varies based on severity and often takes several months. Due to common relapses, consistent care is essential.
Note:
Our blog provides helpful information but does not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. This information serves as a guide and may not reflect all current options or updates.