Key Attributes for Successful Live-In Caregivers
Discover the essential qualities of successful live-in caregivers, including compassion, reliability, and adaptability. This guide highlights key skills and personal traits needed to provide exceptional care for clients with health challenges or disabilities. Developing these attributes ensures compassionate, effective, and personalized support, making a positive impact on clients' lives and fostering trust with families. Perfect for aspiring caregivers, this article emphasizes professional conduct and emotional resilience vital for a rewarding caregiving career.

Key Attributes for Successful Live-In Caregivers
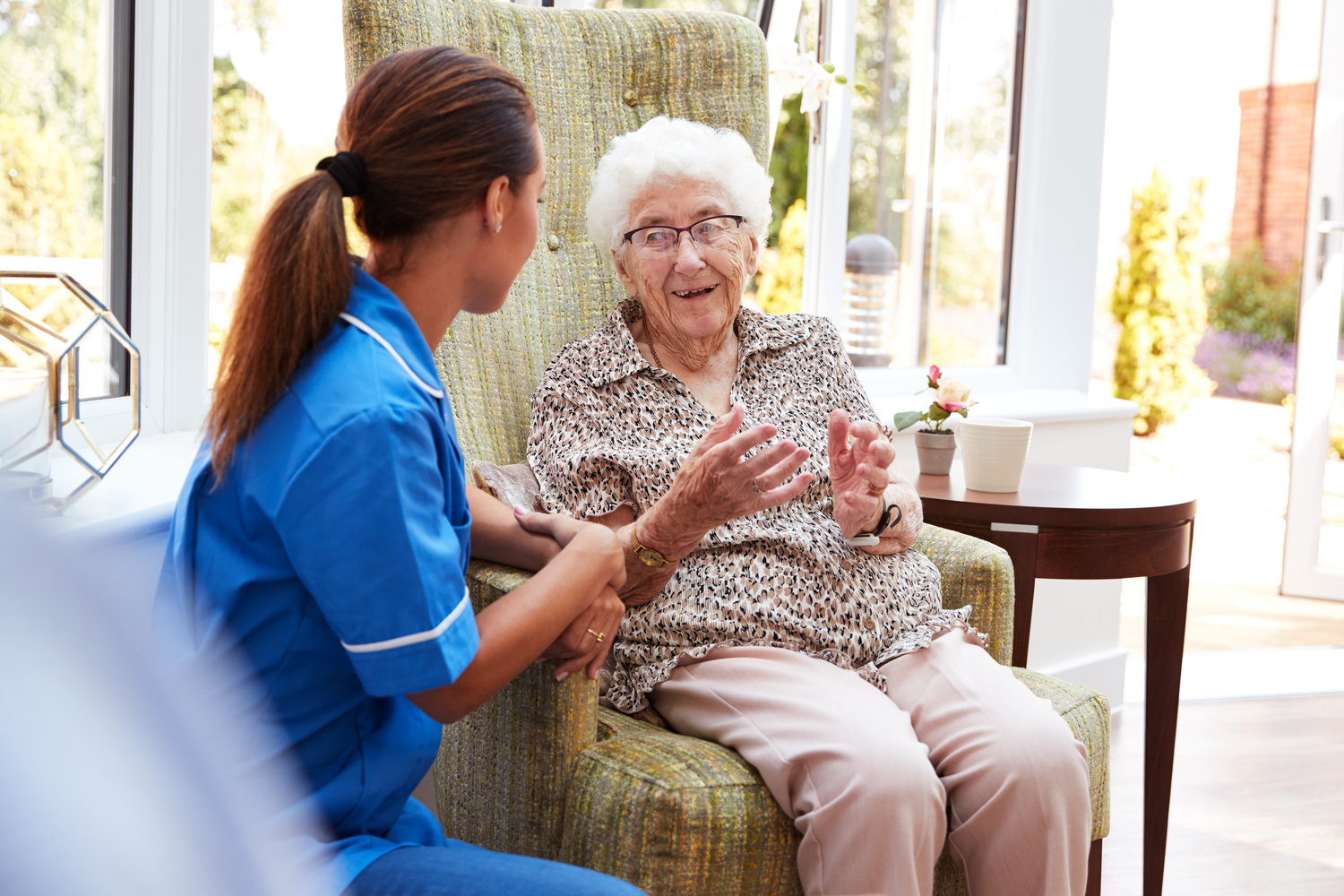
Live-in caregivers play a crucial role in assisting individuals with health challenges, aging, or disabilities. Success in this profession requires a mix of essential skills and personal qualities. Understanding these key traits helps aspiring caregivers provide compassionate and effective support.
Compassion and Understanding
Exceptional caregivers demonstrate deep compassion and sensitivity. Recognizing and empathetically responding to clients' emotions fosters trust and strengthens care relationships. Genuine concern is fundamental to this role.

Empathy allows caregivers to offer emotional comfort, making clients feel appreciated.
Patience
Patience is vital, enabling caregivers to handle daily routines calmly and respectfully. It helps create a peaceful environment suitable for clients’ dignity and comfort.
Reliability
Dependability ensures families trust caregivers with crucial tasks like medication management, hygiene, and daily activities. Consistency builds confidence and ensures safe, quality care.
Effective Communication
Open, clear dialogue with clients, families, and medical professionals is essential. Being attentive to non-verbal cues is also important, especially when clients have speech or cognitive limitations.
Problem-Solving Skills
Unexpected situations require quick thinking. Strong problem-solving abilities help caregivers respond effectively, maintaining client safety and comfort.
Adaptability
Caregivers must modify their approaches to suit each client's changing needs and preferences, delivering personalized care.
Professional Conduct
Respect, confidentiality, and ethical standards are critical. Ongoing training ensures caregivers keep up with best practices and industry standards.
Physical Fitness
The caregiving role can be physically demanding, requiring strength for transfers, household chores, and assisting mobility. Good stamina supports safe and efficient caregiving.
Attention to Detail
Noticing subtle health or behavioral changes helps in early intervention, enhancing overall well-being and preventing issues.
Culinary Skills
Preparing nutritious, tailored meals is often part of caregiving, supporting clients’ health and dietary needs.
Organizational Skills
Managing medications, appointments, and routines ensures seamless and comprehensive care.
Emotional Resilience
Caregiving can be emotionally taxing. Resilience helps caregivers cope with stress and maintain a high standard of care despite challenges.
Cultural Sensitivity
Respecting clients' cultural and religious backgrounds promotes respectful, appropriate care, strengthening relationships.
Learning Commitment
Continuous education keeps caregivers updated on new techniques and best practices, ensuring quality support.
Positive Attitude
A cheerful outlook and sense of humor foster a positive atmosphere, benefiting both caregivers and clients, and making the work more rewarding.
In conclusion, excelling as a live-in caregiver involves combining personal qualities, specialized skills, and a genuine desire to help others. These attributes enable caregivers to significantly improve their clients' quality of life with kindness, dignity, and support.