Identifying and Managing Eyelid Styes: Causes and Symptoms
This article explores the causes and symptoms of eyelid styes, highlighting common risk factors like bacterial infections and poor eyelid hygiene. It details the differences between internal and external styes and advises when to seek professional care to prevent complications.
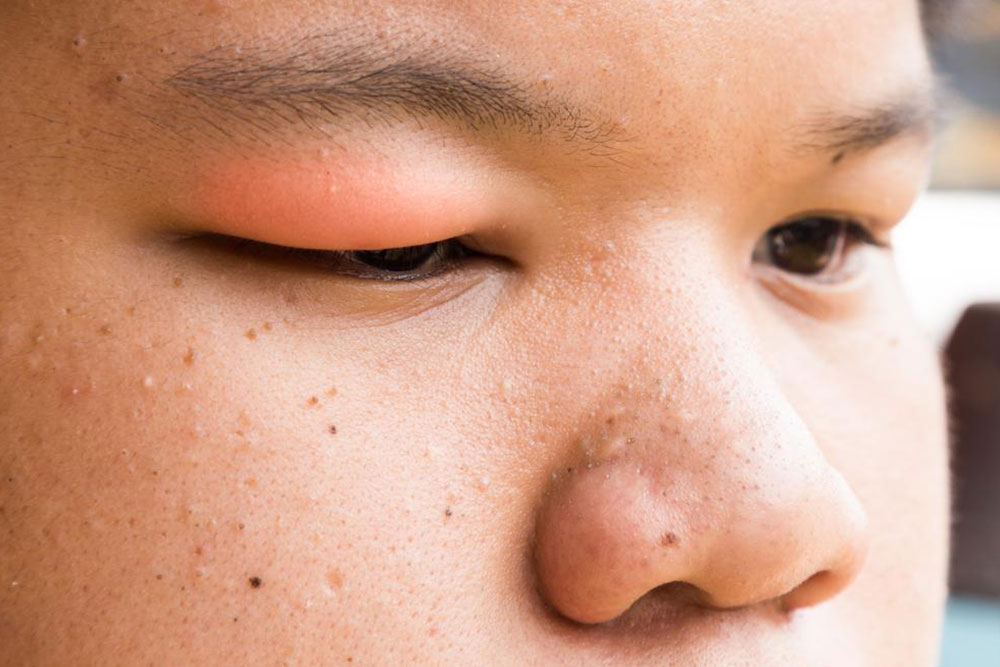
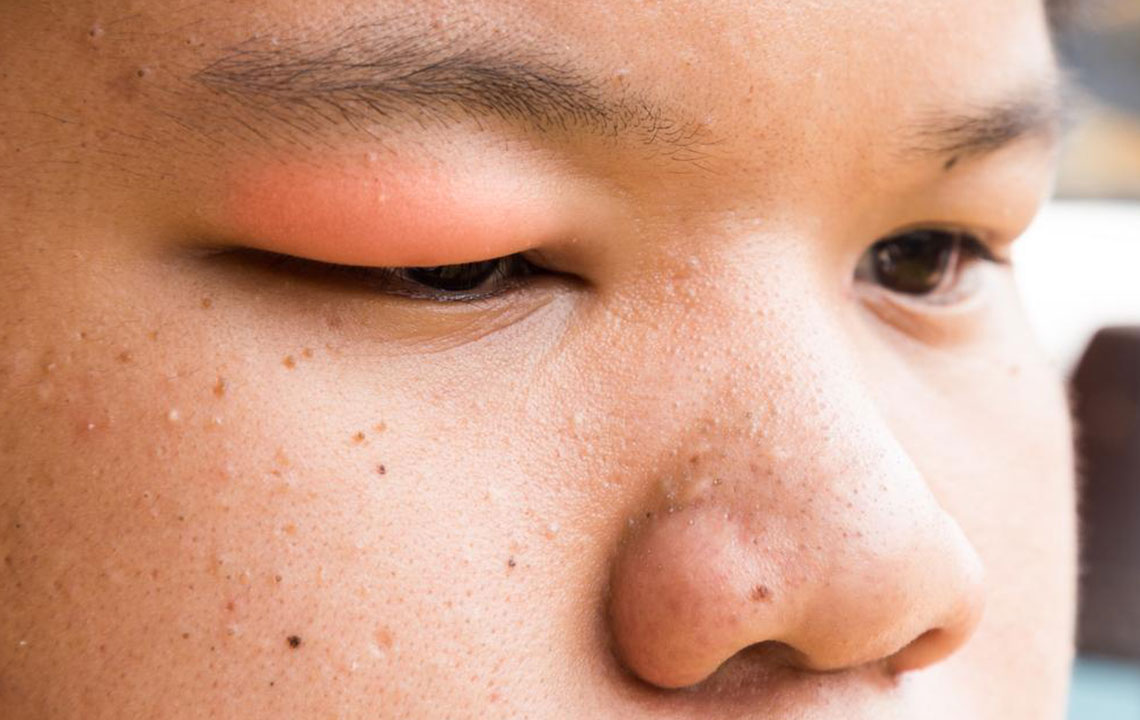
A stye, or hordeolum, is a tender, swollen bump on or inside the eyelid caused primarily by bacterial infection, typically Staphylococcus. These common eye conditions can affect anyone, especially those aged 20 to 50, and are often linked to poor eyelid hygiene or inflammation. Styes can be on the upper or lower eyelid, or both, developing from bacteria that thrive on skin debris, leading to pus-filled lumps. Internal styes result from infected Meibomian glands, while chalazion involves blocked oil glands causing swelling over time.
Recognizing Symptoms and Causes
A stye appears as a small, red, pimple-like bump, often accompanied by eyelid swelling.
Swelling may occur before the bump becomes visible.
Severe cases involve pain, redness, and swelling in surrounding tissues; itching may suggest additional eye issues.
Pus formation and enlarged lymph nodes near the ears can also be signs.
If you notice these signs, consult an eye specialist for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.