Early Indicators and Signs of Diabetes You Should Know
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for effective management. This article highlights key symptoms such as persistent hunger, fatigue, frequent urination, dry skin, vision issues, and signs specific to type 1 diabetes like rapid weight loss. Recognizing these early indicators allows for timely medical intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring to prevent serious complications. Regular checkups and healthy habits are vital to maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and overall health.

Early Indicators and Signs of Diabetes You Should Know
Recognizing the early symptoms of diabetes is vital for timely intervention, as it affects how your body manages sugar. When insulin production or response is impaired, blood sugar rises, signaling potential diabetes.
What are the initial signs?
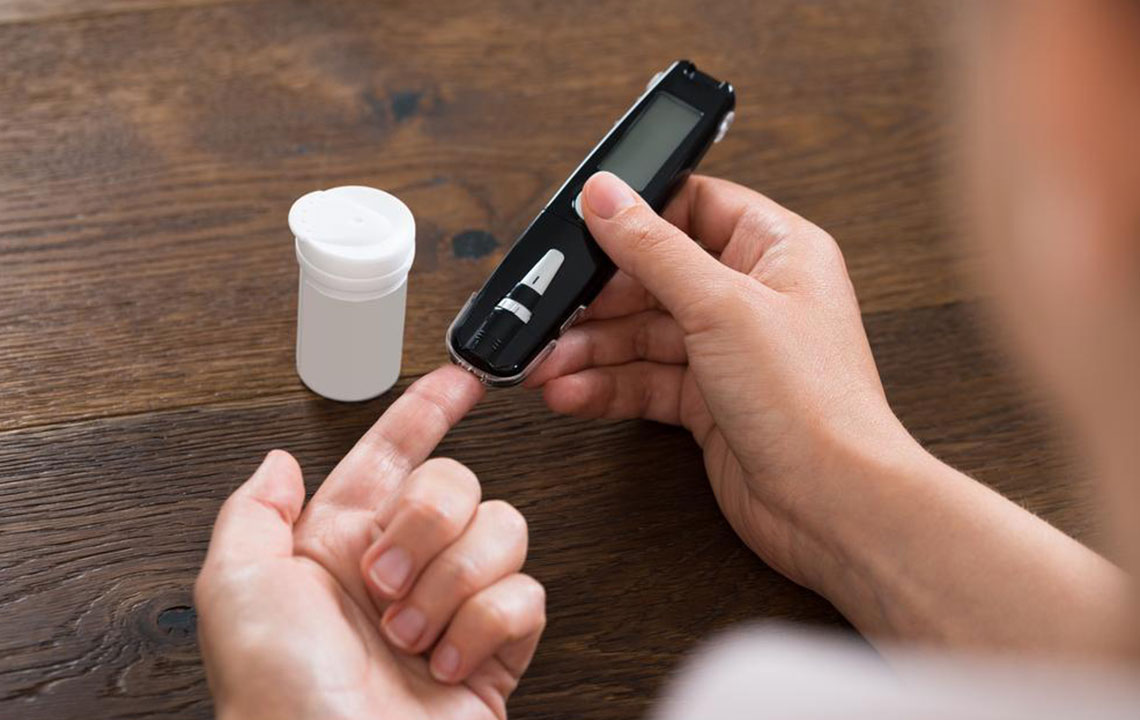
Early symptoms can be subtle and easily missed. Elevated blood glucose levels are typical, especially in type 2 diabetes, which might remain unnoticed until damage occurs. Type 1 diabetes often causes noticeable symptoms within days to weeks.
Common signs across both types include:
Persistent Hunger and Fatigue
When insulin is insufficient or cells resist it, glucose isn't effectively used for energy, leading to increased hunger and tiredness.
Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination
High blood sugar causes kidneys to work harder, leading to more frequent urination. Dehydration amplifies thirst, creating a cycle.
Dry Mouth and Skin Symptoms
Loss of fluids results in dry, itchy skin, especially in warm, humid areas like underarms or genitals.
Blurred Vision
Fluid shifts in the eye can cause swelling of the lens, leading to vision problems.
Yeast Infections
Elevated glucose provides a breeding ground for yeast, causing infections in skin folds and moist areas such as between toes or around genitals.
Healing Difficulties and Numbness
Excess blood sugar can damage nerves, resulting in slow wound recovery and tingling or numbness in extremities.
Distinctive Signs of Type 1 Diabetes
Sudden weight loss occurs as the body burns fat due to lack of energy from food. Nausea and vomiting can develop from ketone buildup, risking ketoacidosis.
When to Consult a Doctor
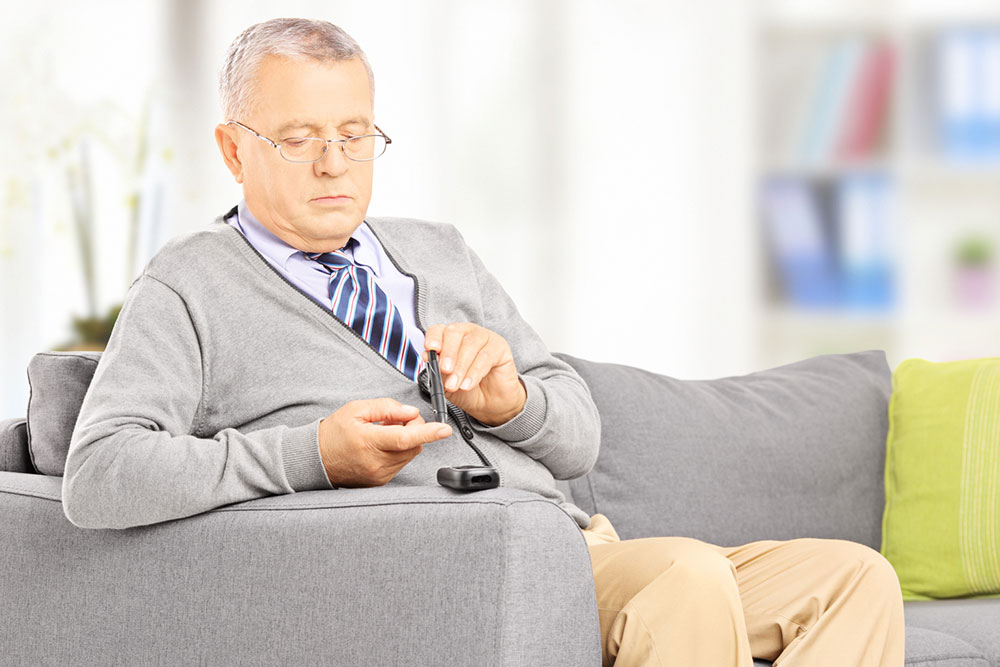
Regular testing is recommended over age 45. Seek immediate medical advice if you experience weakness, excessive thirst, stomach discomfort, frequent urination, rapid breathing, or fruity-smelling breath indicating ketones.
Managing diabetes requires lifestyle changes. Monitoring blood sugar, following medical advice, eating healthily, exercising, sleeping well, and reducing stress are essential.
Consistent medical checkups help control blood glucose and prevent complications.