Comprehensive Strategies for Effective Eczema Management
This comprehensive guide offers practical tips and treatment options for managing eczema effectively. It covers symptoms, triggers, home remedies, and medical treatments to help individuals reduce flare-ups and improve skin health through personalized care and lifestyle adjustments.
Comprehensive Strategies for Effective Eczema Management
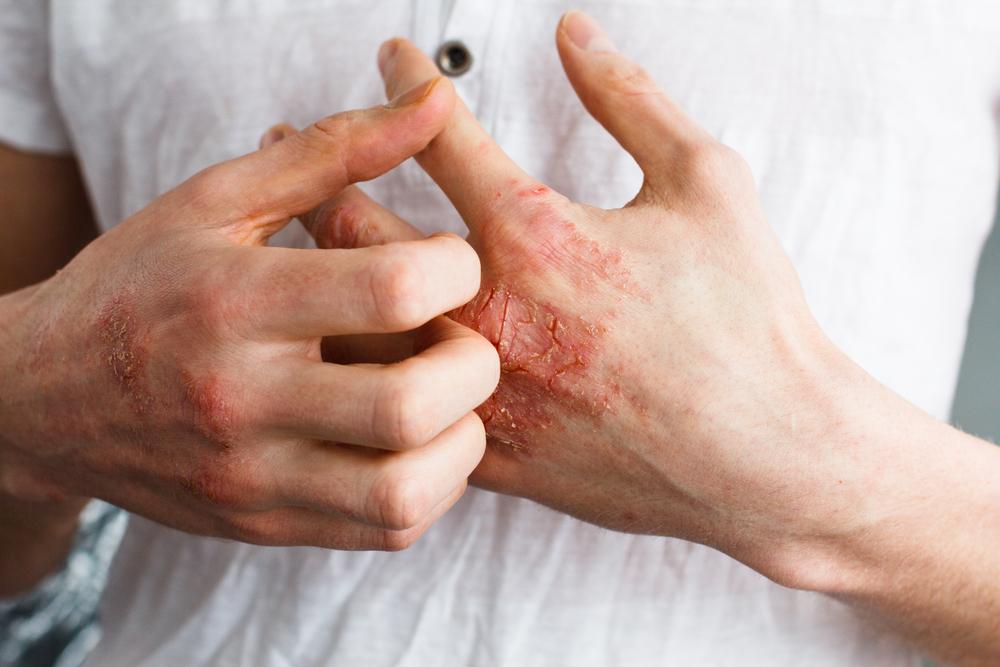
Eczema is a prevalent skin condition marked by inflamed, itchy, and cracked skin patches. In some cases, blood-filled blisters may develop. It includes various types such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, hand eczema, neurodermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and nummular eczema. Some individuals experience occasional symptoms, while others face constant flare-ups. Employing natural remedies and proper skincare routines can greatly enhance quality of life for those managing this condition.
Important Facts About Eczema
Dietary triggers like dairy and nuts may provoke flare-ups.
Symptoms differ across age groups but typically involve red, itchy patches.
Environmental factors such as pollen, dust, and smoke often trigger symptoms.
No cure exists; treatment aims to reduce discomfort and soothe the skin. Eczema is non-contagious.
Identifying Eczema Symptoms
Small bumps that may leak fluid during outbreaks.
Dry, scaly, and cracked skin that can become coarse.
Red or brown patches on the face, hands, feet, wrists, neck, eyelids, ankles, or scalp.
Swollen and inflamed skin from scratching.
Persistent itching and irritation.
Rashes related to atopic eczema.
Effective Management Approaches
While a full cure isn't currently available, symptom relief and skin healing are possible through targeted treatments. Some individuals see remission over time, though others may experience chronic symptoms.
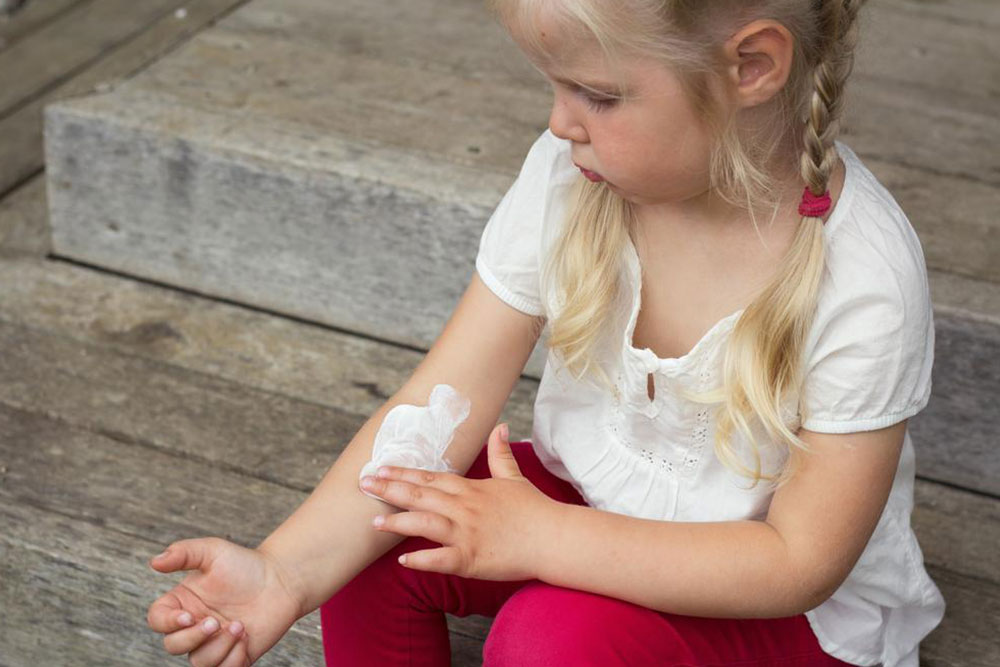
Home Remedies and Care Tips
Vegetable Shortening: A natural moisturizer for dry, flaky skin.
Turmeric: Features curcumin, an antioxidant that accelerates healing.
Tea Tree Oil: Offers antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects to reduce itching.
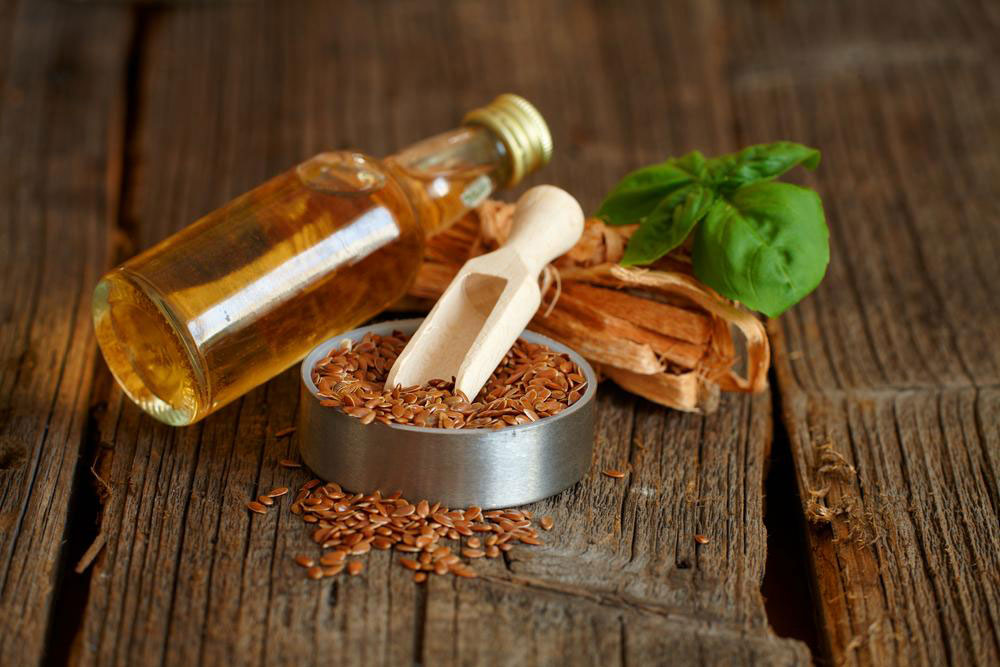
Consume Flaxseeds: Rich in omega-3s that help lower inflammation.
Fermented Cod Liver Oil: Supplies healthy fats to decrease inflammation.
Magnesium Baths: Use magnesium flakes with sea salt and essential oils for skin repair.
Probiotic-Rich Foods: Items like kefir, miso, and dark chocolate may help lower flare-ups.
Medical Treatment Options
Topical Steroids: Reduce inflammation and alleviate itching directly on the skin.
Systemic Steroids: Oral or injectable forms for severe cases, under medical supervision.
Antiviral, Antifungal, and Antibiotics: Treat infections related to eczema outbreaks.
Antihistamines: Help diminish nighttime itching.
Moisturizers and Barrier Creams: Keep skin hydrated and shielded.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Suppress immune responses and reduce inflammation.
Phototherapy: Controlled UV light exposure to modulate immune activity and improve skin health.
Though complete eradication isn't feasible currently, following personalized treatment plans and skin protection routines can effectively manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Consistent skincare is critical to maintaining healthy skin long-term.