Proven Methods to Alleviate Peripheral Nerve Injury
This article offers practical strategies for managing peripheral nerve injuries, emphasizing lifestyle changes, diet, and proper foot care. Recognizing risk factors like diabetes and high blood pressure is essential for prevention and early intervention. Implementing these tips can alleviate symptoms, promote nerve health, and improve quality of life.
Effective Approaches for Managing Nerve Damage
Peripheral nerve injury can cause pain, numbness, and discomfort, impacting daily activities. While medical interventions like medications and surgeries are common, adopting proper self-care routines is essential for symptom relief. These practical strategies can help reduce pain and enhance overall well-being. Whether you are at risk or currently experiencing symptoms, implementing these tips can offer meaningful relief.
Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption can harm nerves, exacerbating nerve issues. Reducing intake or seeking support for alcohol dependence can lessen symptoms. If nutritional deficiencies are detected, your doctor might recommend dietary supplements.
Maintain a strict medication regimen.
Follow a Nutritious Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports nerve health and can reduce symptoms. Your healthcare provider may suggest personalized diet plans to suit your needs.
Incorporate Physical Activity
Regular exercise strengthens muscles and joints, helping to lessen nerve pain. If vigorous workouts are not suitable, consider gentle activities like yoga or walking. Aim for at least three 30-minute walks weekly to promote low-impact benefits.
Stop Smoking
Smoking impairs blood circulation and worsens nerve damage by limiting nutrient flow. Quitting may be challenging, but healthcare professionals can offer strategies, including nicotine replacement therapy and medications.
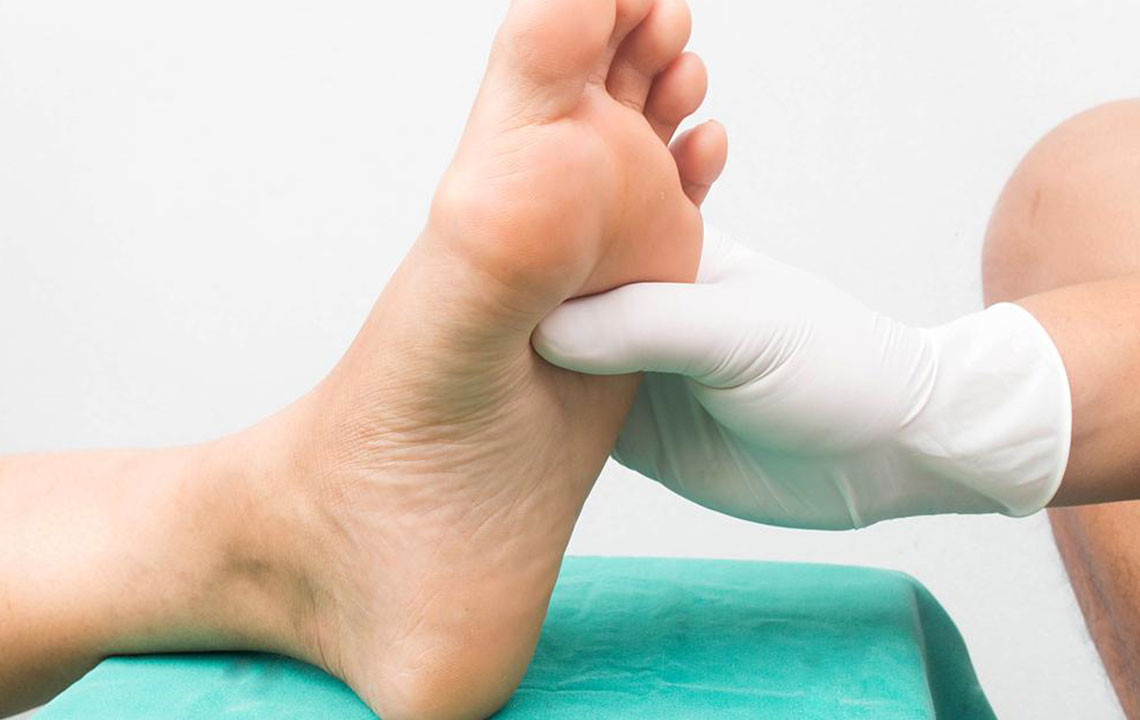
Care for Your Feet
Individuals with peripheral nerve problems, especially diabetics, should regularly examine their feet for cuts, blisters, or sores. Using proper footwear such as padded shoes and cotton socks can prevent complications. Daily foot assessments are crucial for early detection and management.
Factors Increasing the Risk of Nerve Damage
Various factors can contribute to peripheral nerve injury, with certain groups being more vulnerable. Managing these risks is important, particularly if you belong to high-risk categories:
Overweight individuals
Patients with high blood pressure
Adults above 40 years old
People with diabetes
Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy
Individuals living with HIV
Peripheral nerve damage may be temporary or persistent, affecting single or multiple nerves. Early detection and treatment are key to reducing symptoms and potentially reversing damage. If you notice numbness or pain, especially in your feet, consult a healthcare professional promptly.