Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Shingles: Medical and Natural Treatments
Explore effective strategies for managing shingles, combining antiviral medications with natural remedies. Learn about symptoms, supportive care options, and when to seek medical advice to minimize complications and promote healing.

Overview of Shingles and Its Treatment Methods
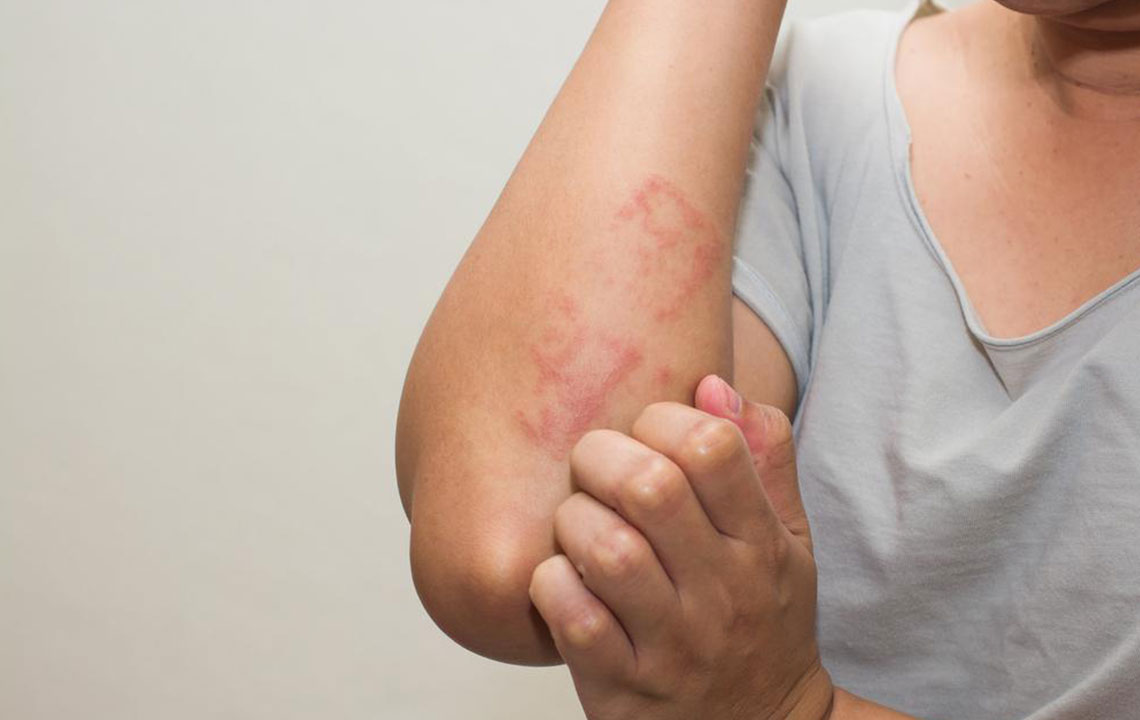
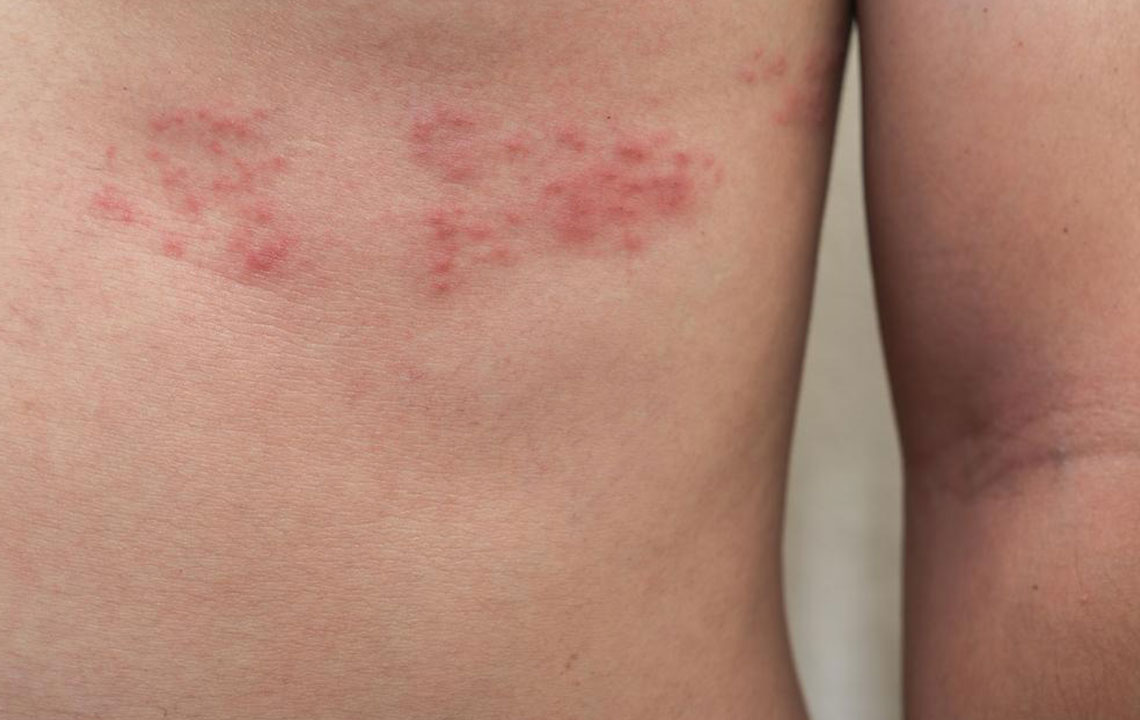
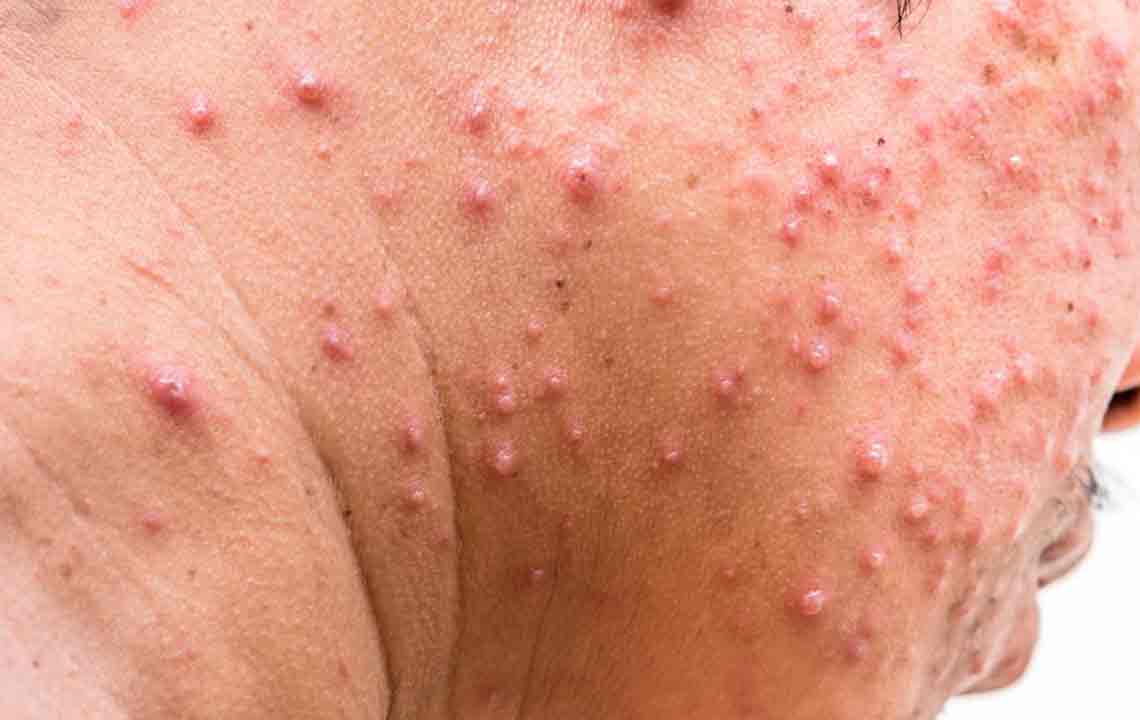
Approximately one in three people will experience shingles at some point in their lives. Also known as Herpes Zoster, it emerges from the reactivation of the Varicella Zoster virus, the same pathogen responsible for chickenpox. The primary symptom is a painful skin rash that may appear in small, localized sections of the body. Initial signs often include localized pain, followed by blister formation. Additional symptoms can include fever, fatigue, and light sensitivity.
Post chickenpox, the virus remains inactive in nerve cells. When reactivated, shingles occur. While no definitive cure exists, antiviral medications help lessen symptoms and shorten illness duration. If not treated, complications such as nerve pain, skin scarring, or internal issues can develop. Seeking prompt medical care is vital to reduce risks.
Natural and Supportive Care Tips
Alongside antiviral treatments, natural approaches can alleviate discomfort. Applying cold compresses can soothe affected skin and decrease inflammation—avoid icy packs to prevent skin sensitivity. Warm baths with colloidal oatmeal or cornstarch can relieve itching and promote healing. Remedies like homeopathy, baking soda, or cornstarch pastes may provide additional comfort. Moisturizers such as calamine lotion or capsaicin-based ointments can help reduce itching and soreness.
Strengthening your immune system is key—consume foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, B12, and amino acids like lysine, found in leafy greens, fruits, eggs, and lean meats. Limit items that might prolong infection, including sugary, processed foods, and arginine-rich foods like nuts and chocolates. Herbal supplements such as lemon balm, echinacea, and green tea can support stress management and immunity, but consult healthcare professionals before use.
Shingles typically lasts 2 to 4 weeks, with management combining medications and supportive care. Using antiviral drugs along with natural remedies can speed up recovery, reduce pain, and prevent long-term issues.
Important Reminder:
This article presents general guidance on shingles management and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. The information aims to support understanding but does not guarantee specific results. Seek medical guidance as the primary resource for health concerns.