Effective Approaches for Managing Severe Psoriasis
This article explores comprehensive treatment strategies for severe psoriasis, including topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications. It offers insights into management options for patients with persistent or extensive symptoms, helping to control inflammation and improve skin condition effectively.

Effective Approaches for Managing Severe Psoriasis
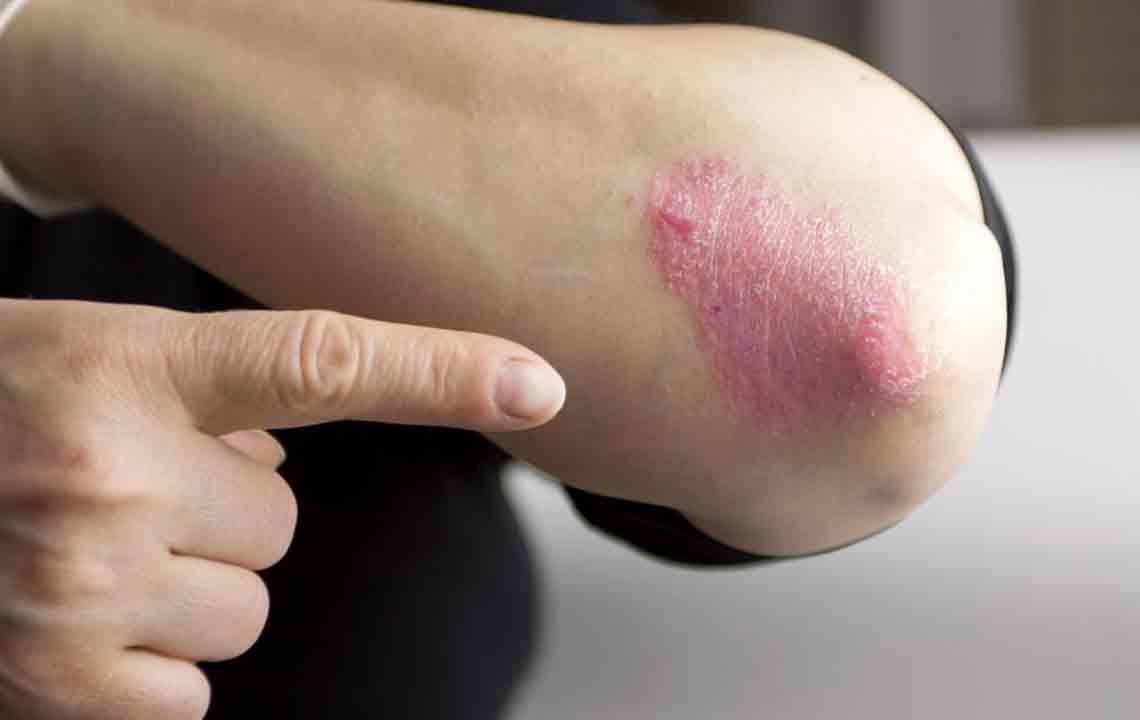
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition marked by red, itchy, and scaly skin lesions. It results from accelerated skin cell production, causing inflammation and buildup of dead skin cells.
Treatment options for psoriasis
Although a complete cure has not been found, various therapies can control symptoms effectively. These are mainly divided into three categories.
Topical Treatments
Steroid creams – Mild corticosteroids help reduce redness, swelling, and itching, particularly on sensitive areas like the face or skin folds.
Vitamin D analogs – Synthetic vitamin D derivatives, like Calcipotriene, slow down excessive cell growth in mild to moderate psoriasis.
Moisturizers – Using emollients such as petroleum jelly helps soften the skin and reduce plaque formation.
Anthralin – This medication helps slow skin cell turnover and decreases scales, but should be washed off carefully to minimize irritation.
Salicylic acid – Promotes removal of dead skin cells; effective in medicated shampoos and scalp solutions, especially with other treatments.
Coal tar – Derived from coal tar, it diminishes inflammation and scaling; available as creams, shampoos, or oils, though it has a strong odor.
Topical retinoids – Vitamin A derivatives that reduce inflammation; caution needed regarding sun exposure.
Phototherapy Methods
Sunlight – Controlled exposure can slow skin growth but overexposure increases risks.
UVB therapy – Specific UVB light treatments target localized psoriasis patches; offered as broadband or narrow-band options.
Goeckerman therapy – Combines UVB with coal tar for enhanced effectiveness in some cases.
PUVA therapy – Uses psoralen to sensitize skin before UVA exposure, penetrating deeper than UVB.
Systemic Therapies
When other options prove ineffective, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed:
Methotrexate – Reduces inflammation and controls skin cell proliferation.
Cyclosporine – Modulates immune function but is generally for short-term use.
Additional Medications – Including Etanercept, Infliximab, Adalimumab, Ustekinumab, Golimumab, Apremilast, Secukinumab, and Ixekizumab for resistant cases.