Key Factors to Consider Before Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
This article discusses important factors to consider before starting head and neck cancer treatment, including potential side effects, preventive strategies, and prognosis. It emphasizes early detection, managing oral complications, and maintaining regular follow-ups to improve treatment success and quality of life for patients.

Essential Preparations Prior to Head and Neck Cancer Therapy
The head and neck areas are vital yet sensitive parts of the body. Receiving a diagnosis of cancer in these regions calls for thorough planning before treatment begins. Knowing the treatment timeline and success potential is important. Since such conditions can deeply affect patients and their families, choosing the most suitable treatment approach is crucial. Being well-informed enables better decision-making and helps patients prepare emotionally and physically for the treatment journey.
Common Oral Side Effects
During therapy, patients often face oral issues that may slow recovery and cause discomfort. These side effects include mouth sores, gum infections, damage to salivary glands, and taste changes, which can interfere with healing.
Prevention of Oral Complications
If oral problems arise, prompt medical intervention is essential. Strategies involve adjusting treatment plans, scheduling treatments appropriately, and starting early preventive measures. Proactive steps help identify issues early and support better recovery outcomes.
Possibility of Cure
Success of treatment depends heavily on early diagnosis and the patient’s overall health. The cancer type and stage significantly influence treatment results. Younger and healthier individuals tend to respond better to options like surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, increasing chances of remission.
Typical Side Effects
Therapies can cause immune suppression, hair loss, appetite loss, brittle nails, and emotional stress. These effects may extend the recovery process and benefit from professional healthcare and counseling support.
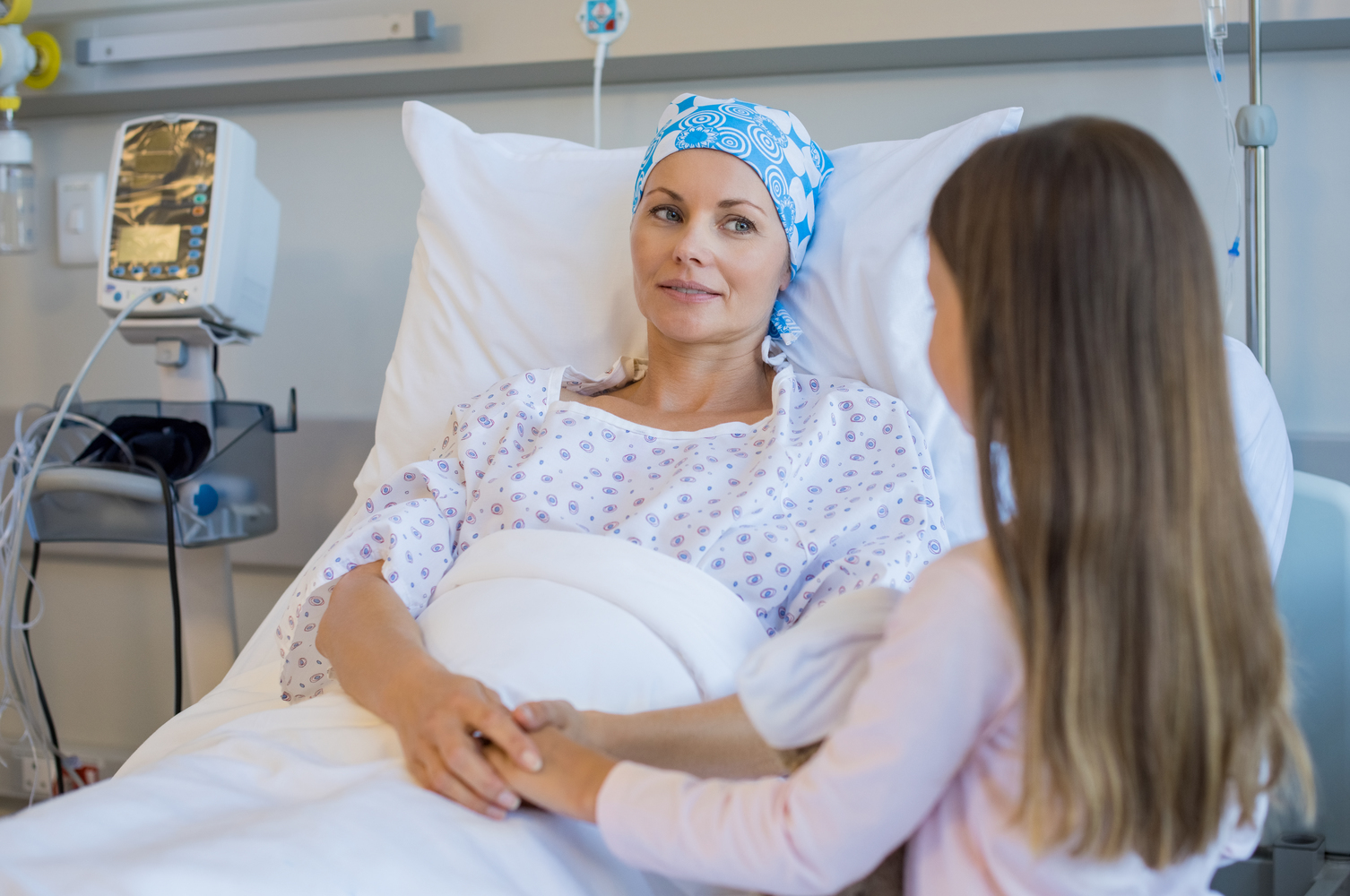
Recurrence and Remission Potential
Cancer can recur in the original or new locations. Managing fears of recurrence involves regular check-ups and clear communication with healthcare providers. Ongoing monitoring is key to maintaining remission and detecting any signs of return.