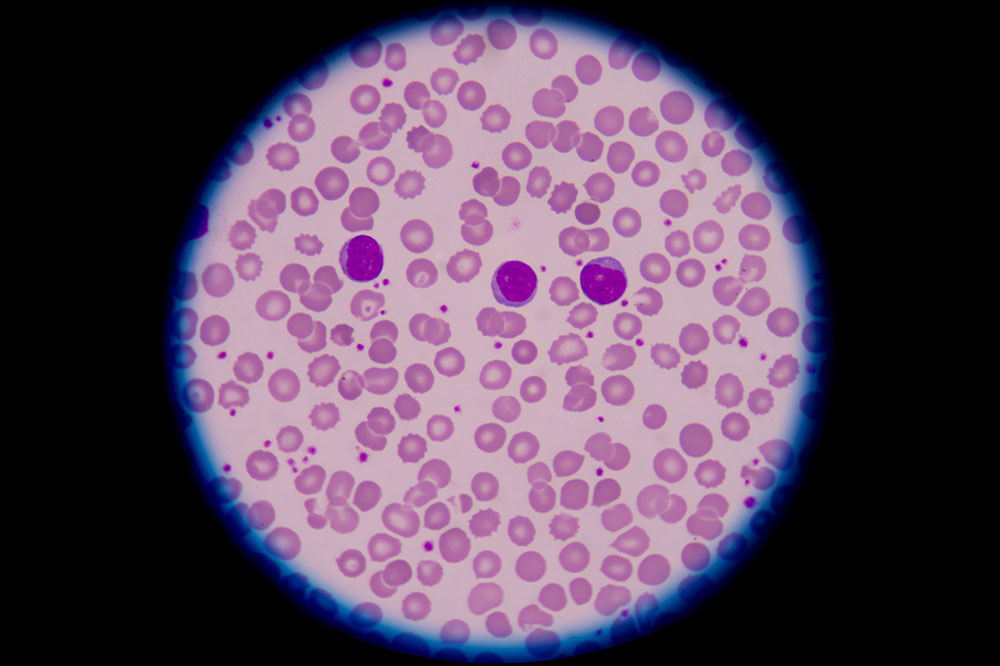
Understanding Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Symptoms and Health Effects
Discover the key signs and health impacts of vitamin B12 deficiency. Learn about sources, symptoms, and effective supplementation strategies to maintain optimal levels and prevent serious conditions like anemia and nerve damage. Suitable for health-conscious individuals seeking to safeguard their well-being.
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is essential for maintaining good health, but it cannot be produced naturally by the body. It is primarily found in animal-based foods like meat, eggs, dairy, and liver. Since our bodies rely on external sources for B12, deficiencies can occur without proper intake or absorption. B12 plays a vital role in DNA production, cell division, and red blood cell formation. Deficiency symptoms include anemia, nerve damage, numbness, and weakness. Supplementation through injections or oral medicines is often necessary to restore levels and prevent serious health problems.
This vitamin also supports protein synthesis and helps maintain a healthy nervous system. Regular monitoring and appropriate supplementation are crucial, especially for vegetarians, seniors, and those with absorption issues. Recognizing deficiency signs early can significantly improve health outcomes and prevent complications.