Comprehensive Guide to COPD: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Approaches
This detailed guide on COPD explains its symptoms, causes, and management strategies. Highlighting early detection and treatment options, it emphasizes lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and the importance of medical intervention. It covers symptoms progression, potential complications, and surgical options, offering comprehensive insights into effective COPD control and improving patient quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to COPD: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Approaches
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) includes progressive lung conditions like chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and refractory asthma, all of which disrupt normal breathing. Chronic bronchitis causes airway inflammation and mucus buildup, while emphysema damages alveoli in the lungs. Although there is no complete cure, early intervention can ease symptoms, prevent complications, and improve life quality. Nearly 24 million people are affected nationwide, with many undiagnosed. While smoking is a key risk factor, some sufferers have never smoked. Recognizing initial signs and seeking medical attention early is essential.
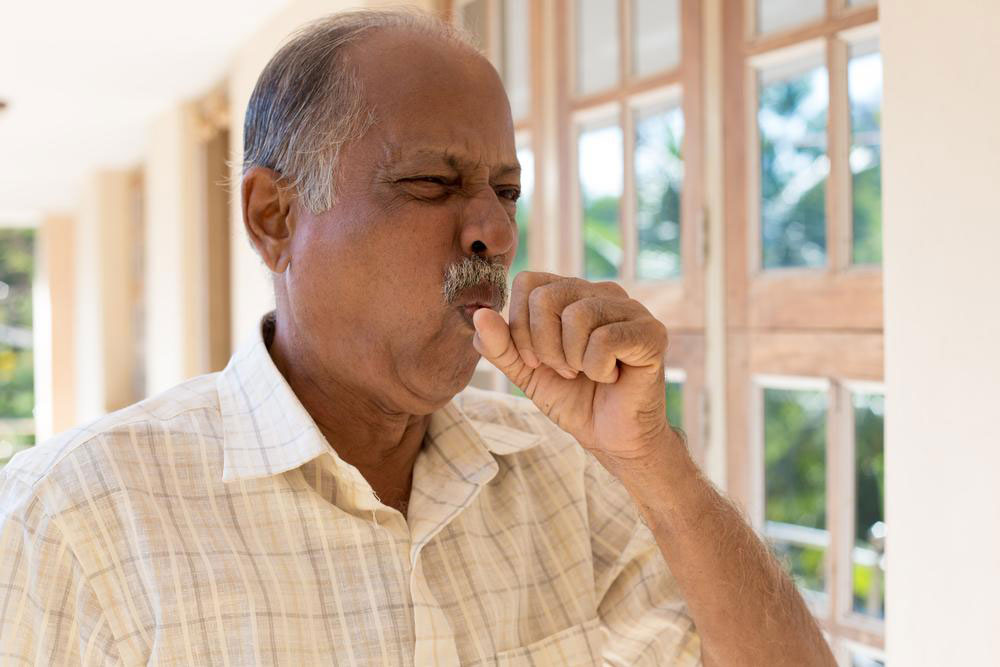
In initial stages, symptoms such as occasional breathlessness after activity, frequent throat clearing, and mild coughs may appear. As the condition advances, symptoms intensify, leading to frequent infections, wheezing, fatigue, and mucus overproduction. Advanced stages may cause difficulty speaking, rapid heartbeat, bluish lips or fingertips, and mental confusion. COPD can lead to complications like lung cancer, cardiovascular issues, pneumonia, malnutrition, weight loss, hypertension, and depression. While incurable, treatments aim at symptom control, quitting smoking, and enhancing daily life.
Stopping Smoking: Support options like nicotine replacement and counseling help in quitting.
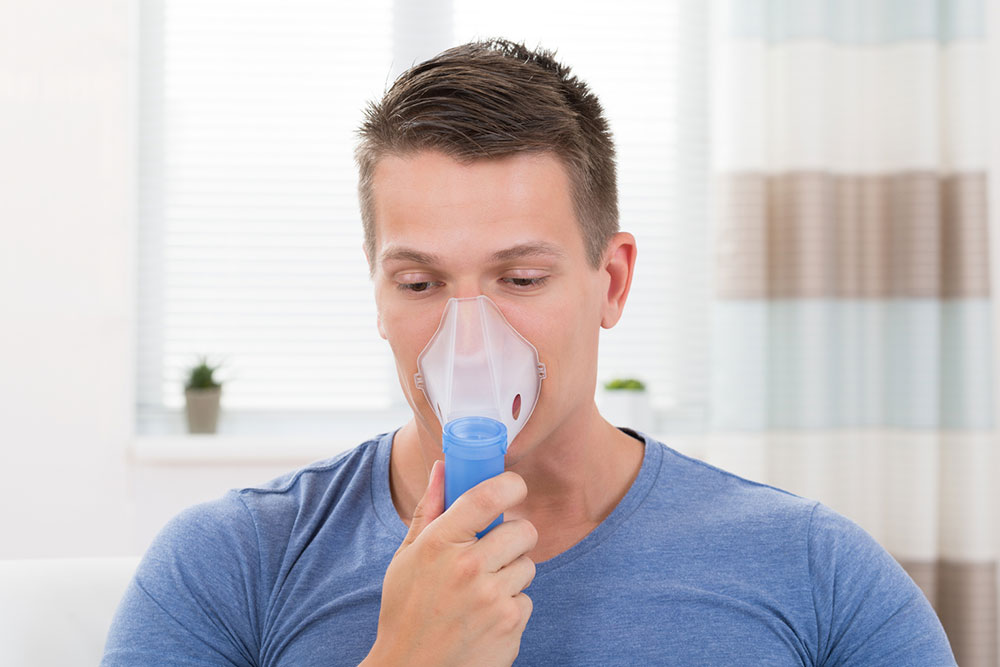
Supplemental Oxygen: For decreased blood oxygen, oxygen therapy via masks or nasal tubes improves sleep, organ function, activity, and lifespan.
Operative Procedures: When necessary, lung transplants, surgery to reduce lung volume, or bullectomy (removal of damaged air sacs) can improve breathing. These methods carry risks such as infections and scarring, complicating treatment.
Medications offer relief from symptoms, but early diagnosis combined with lifestyle changes—like healthy eating and smoking cessation—is vital. Consulting a healthcare provider at early signs ensures timely treatment. Proper management lessens COPD’s impact, helping individuals maintain active and healthier lives.