Comprehensive Guide to Lung Infection: Symptoms and Prevention Strategies
Learn essential information about lung infections, including pneumonia symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures. Early detection and proper care are crucial for recovery. Adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of lung-related illnesses and improve overall respiratory health.

Comprehensive Guide to Lung Infection: Symptoms and Prevention Strategies
Lung infections, including pneumonia, are illnesses that cause inflammation of one or both lungs due to viruses, fungi, or bacteria. This leads to fluid or pus accumulation, impairing breathing. Symptoms often include cough with mucus, chills, sweating, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. The severity depends on age, health, and infection type. While contagious, effective treatment usually results in recovery. Early detection and intervention are crucial to avoid complications. Preventive actions like practicing good hygiene, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower infection risks.
Recognizable signs of lung infection
The presentation varies from mild to severe, influenced by age and overall health. Typical symptoms include fever, chills, cough, and breathlessness, especially during activity.
Other signs can include sharp chest pain worsening with deep breaths, headaches, clammy skin, and excessive sweating. Mild cases may lead to fatigue, lack of appetite, and lowered energy.
Older adults may experience confusion. Since lung infections can be bacterial or viral, symptoms differ: bacterial cases often cause high fever, rapid breathing, and bluish lips or nails due to oxygen shortage. Viral infections typically mimic flu symptoms, like weakness, muscle aches, and dry cough.
Identify these symptoms early and seek medical advice. Risk factors involve smoking, existing respiratory issues, recent surgeries, or trauma.
Approaches to treating lung infections
Most treatments involve medications such as antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals, depending on the cause. Antibiotics are used mainly for bacterial infections. Over-the-counter medicines can reduce fever and pain, while cough suppressants help clear lung secretions.
Home care includes following prescribed medication regimens, staying hydrated, resting adequately, and avoiding strenuous activities. Full recovery requires patience and sufficient rest.
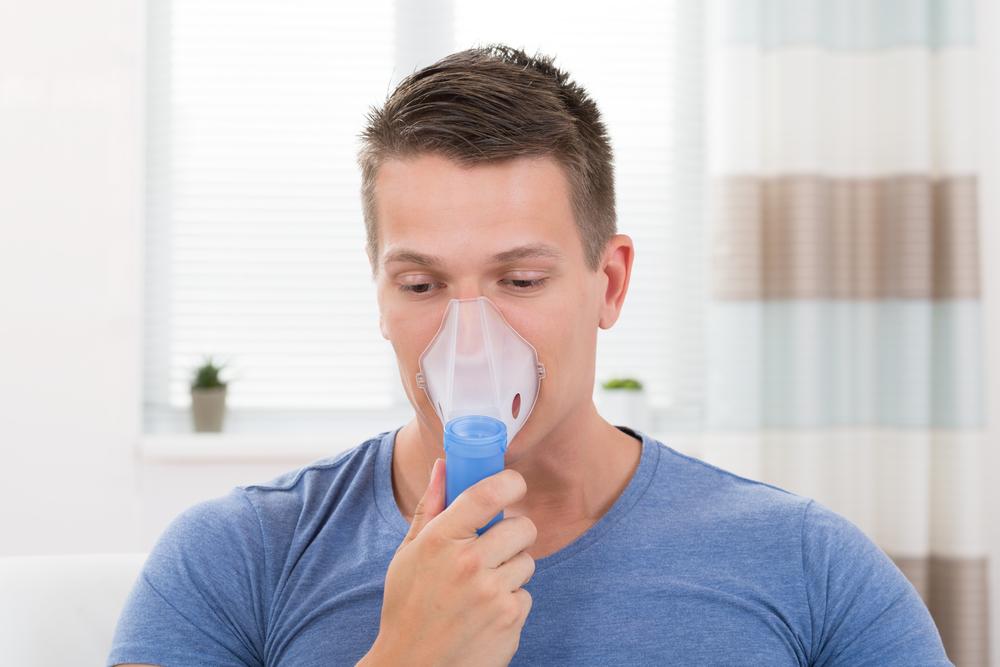
In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary with close monitoring. Treatments can include IV antibiotics, respiratory therapies, and oxygen therapy via masks or tubes. Critical cases may need ventilator support.
Oxygen support ensures proper oxygenation, aiding recovery. Techniques like specific breathing exercises and respiratory assistance can improve oxygen levels.
Untreated lung infections can be serious; thus, prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital. Preventive measures such as quitting smoking, good hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle help strengthen immunity and reduce infection risk.