Comprehensive Approach to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Learn effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis, including medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and alternative treatments. This comprehensive guide helps patients reduce symptoms and improve quality of life through proven methods and professional support.
Comprehensive Approach to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
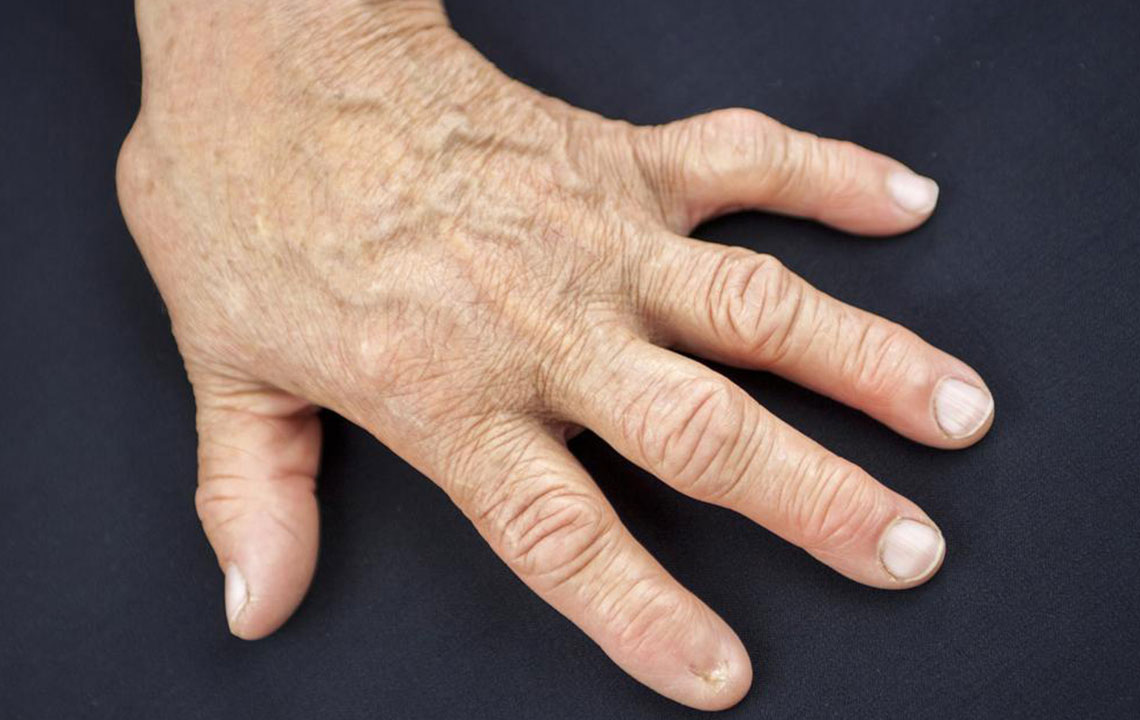
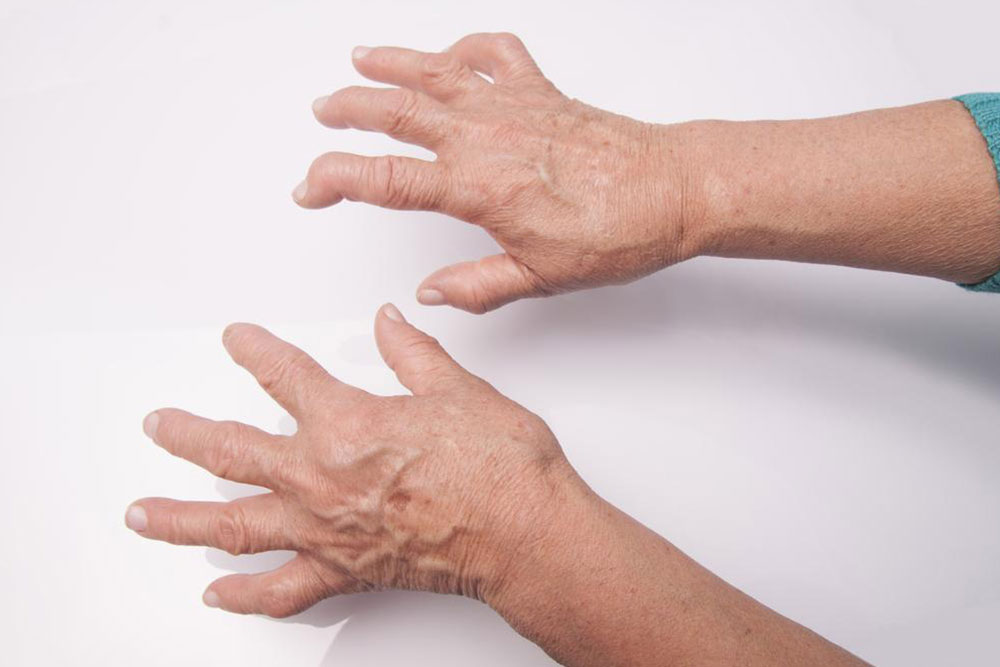
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by joint pain and inflammation.
Common RA Indicators
Stiffness in affected joints
Ongoing joint discomfort
Swelling around joints
Limited joint movement
Diagnosis often involves blood tests and imaging scans. Family history can elevate risk.
Underlying Causes of RA
Smoking
Being overweight
Injuries, such as fractures or trauma
Standard Treatments for RA
Managing rheumatoid arthritis involves various strategies, including:
Medications
Drugs like corticosteroids, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen help decrease pain and prevent joint deterioration.
Physical Exercise
Gentle activities such as yoga can reduce joint pain and boost flexibility. Consistent movement supports joint health.
Assistive Devices
Using supports like braces, crutches, or grab bars enhances mobility and alleviates joint strain.
Diet and Nutrition
Incorporate foods rich in vitamins A, C, and selenium—like dark chocolate, berries, spinach, and beans—to promote joint wellness. Flavonoid-rich foods, including green tea, broccoli, and soy, are beneficial. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish, walnuts, and seeds help reduce inflammation. Avoid trans fats and simple carbohydrates to better manage symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
Procedures such as joint fusion, replacements, or tendon repairs are options when conservative treatments are inadequate.
Lifestyle Changes
Quitting smoking, maintaining activity levels, managing weight, and reducing stress can greatly improve quality of life.
Complementary Methods
Techniques like acupuncture and aromatherapy can assist in pain relief and relaxation.
Topical Remedies
NSAID creams, gels, and injections directly target inflamed joints for localized relief.
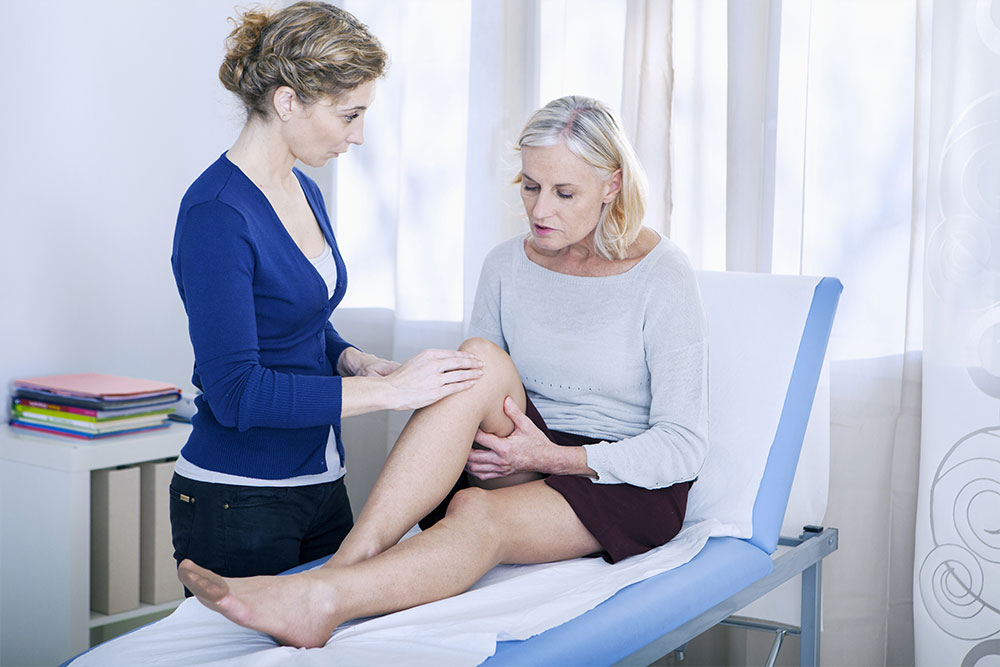
Professional Assistance
Engaging occupational and physical therapists supports daily activities and joint preservation. Physiotherapy helps strengthen muscles and improve movement.
Thermal Therapy
Hot or cold compresses can soothe stiffness and reduce discomfort.
Alternative Therapies
Chiropractic, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, massage, and osteopathy are additional options to alleviate symptoms and enhance joint function.
While no cure exists for RA, these treatments manage symptoms effectively, enabling patients to enjoy greater comfort. Support systems and mindfulness practices further contribute to overall health. Always seek professional guidance before starting new treatment plans.