Comprehensive Guide to Managing Type 1 Diabetes
This article offers a detailed overview of Type 1 Diabetes, covering its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of personalized insulin therapy, proper injection techniques, and professional guidance to maintain optimal health in affected individuals.
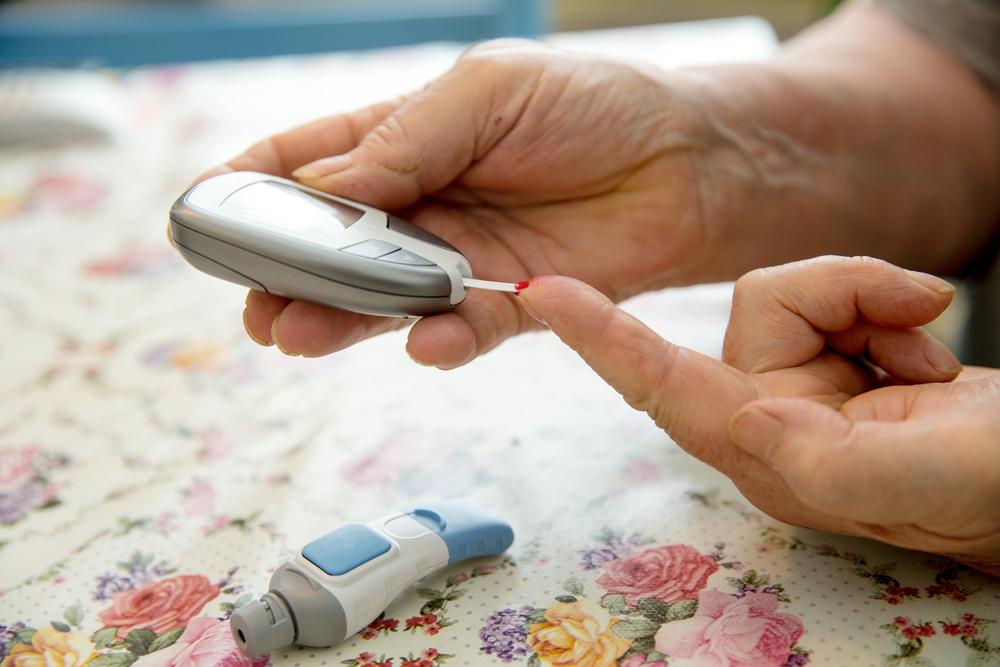
Type 1 Diabetes is an uncommon autoimmune disorder affecting approximately 5-10% of individuals with diabetes, usually identified before the age of 30. It results from the immune system attacking insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, causing a need for lifelong insulin supplementation. Though the exact cause is unknown, genetic predisposition and environmental factors may contribute, leading to the formation of antibodies that target the pancreas. Early signs include pre-diabetes symptoms such as abnormal antibody levels and decreasing insulin output. Symptoms encompass frequent urination, unintended weight loss, intense thirst, excessive hunger, blurred vision, and infections. Managing the condition requires continuous insulin therapy, customized to each patient's needs, delivered via injections. Proper technique, site selection, and storage are vital, often utilizing the abdomen and thigh. Potential side effects include low blood sugar, weight gain, and skin irritation. Regular consultation with healthcare providers ensures optimal control and personalized care.


