Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Melanoma: Symptoms and Treatment Strategies
This article provides an in-depth overview of advanced melanoma, highlighting key symptoms, diagnosis procedures, and available treatments. Emphasizing the importance of early detection through self-examinations, it discusses various therapeutic strategies, including surgery, immunotherapy, and targeted drugs, to improve patient outcomes. Staying informed about melanoma signs and treatment options is crucial for timely intervention and effective management of the disease.

Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Melanoma: Symptoms and Treatment Strategies
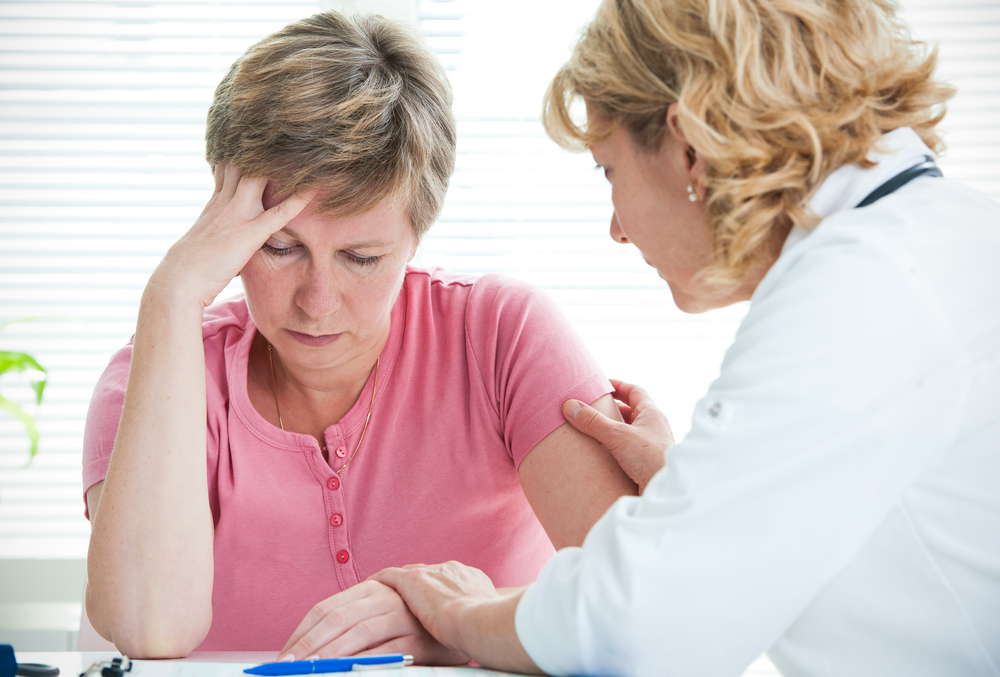
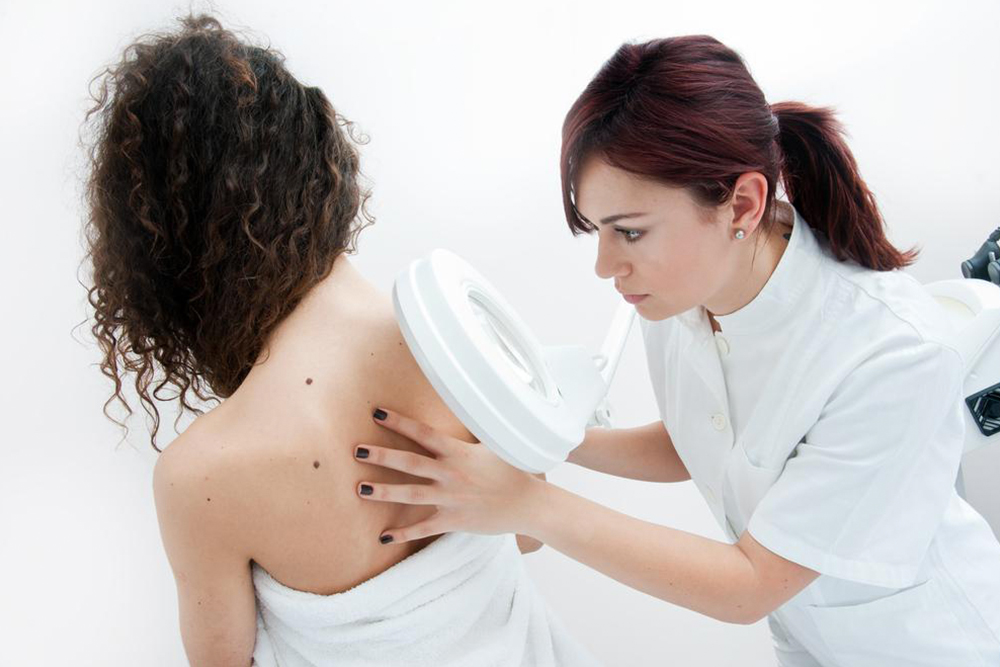
Melanoma represents the most dangerous type of skin cancer, resulting from genetic mutations often triggered by sun exposure. It typically manifests as dark or brown moles. Early detection significantly improves treatment success. When melanoma reaches stage four, it extends beyond nearby lymph nodes and may metastasize to organs such as the lungs, liver, bones, brain, or stomach. Warning signs include changes in mole appearance, like thickening or skin ulcers. Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasounds, and biopsies.
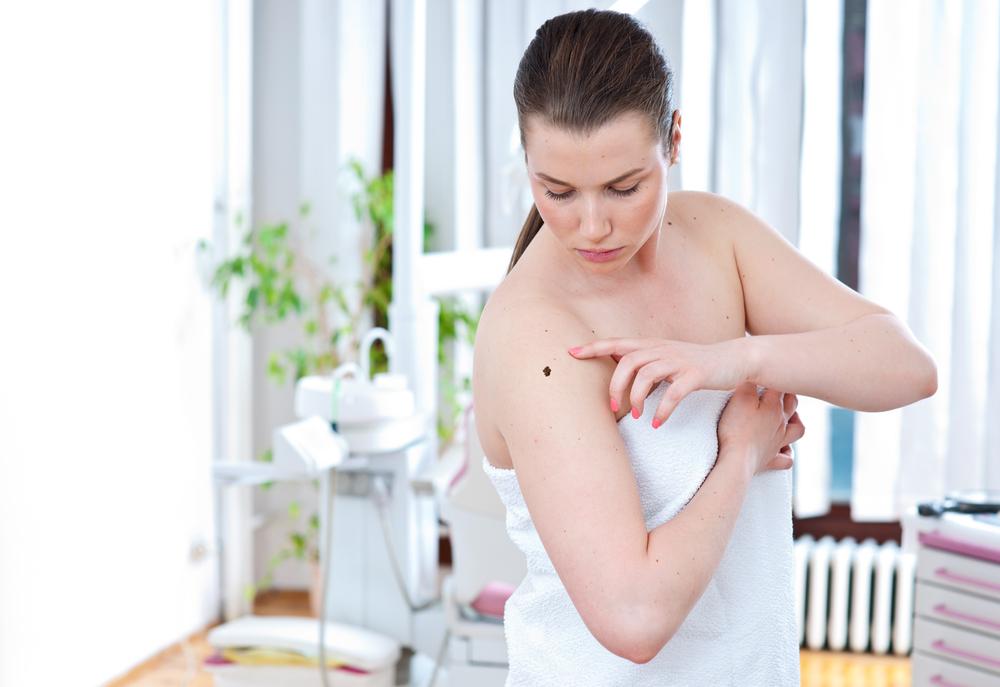
Performing regular self-examinations is crucial. Follow the ABCDE criteria: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter exceeding a pencil eraser, and Evolution of shape or size. Treatment depends on tumor size, spread, overall health, and previous responses. Options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted medications based on genetic profiles. Clinical trials may offer options for cases unsuitable for surgery.
Skin tumor
Melanoma warning indicators
Advanced melanoma therapies
Recognizing the signs of stage four melanoma and seeking prompt medical attention is vital. Regular self-examinations using the ABCDE method aid early detection, while diagnostic tests verify diagnosis. Treatment modalities include surgical removal, medications, and cutting-edge options like immunotherapy and targeted treatments, offering hope to those with advanced disease.