Comprehensive Guide to Pneumonia: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
This article offers an in-depth overview of pneumonia, highlighting symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options tailored to different infectious agents. It emphasizes the importance of timely medical intervention and proper care strategies for effective management, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly.
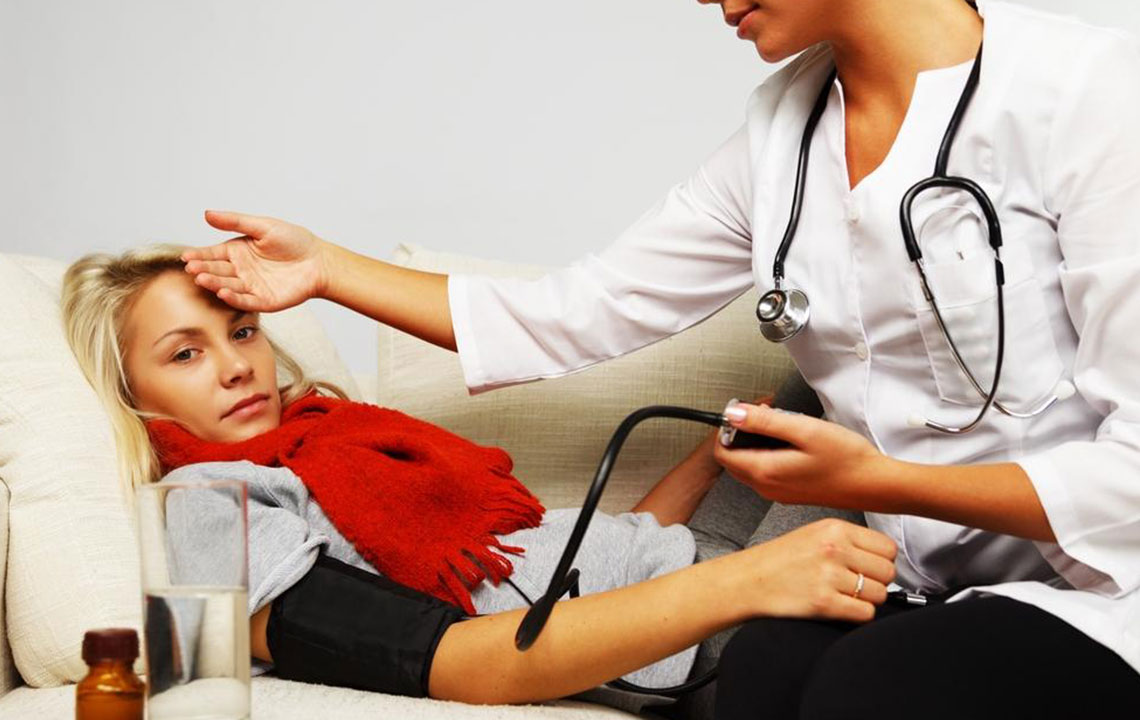
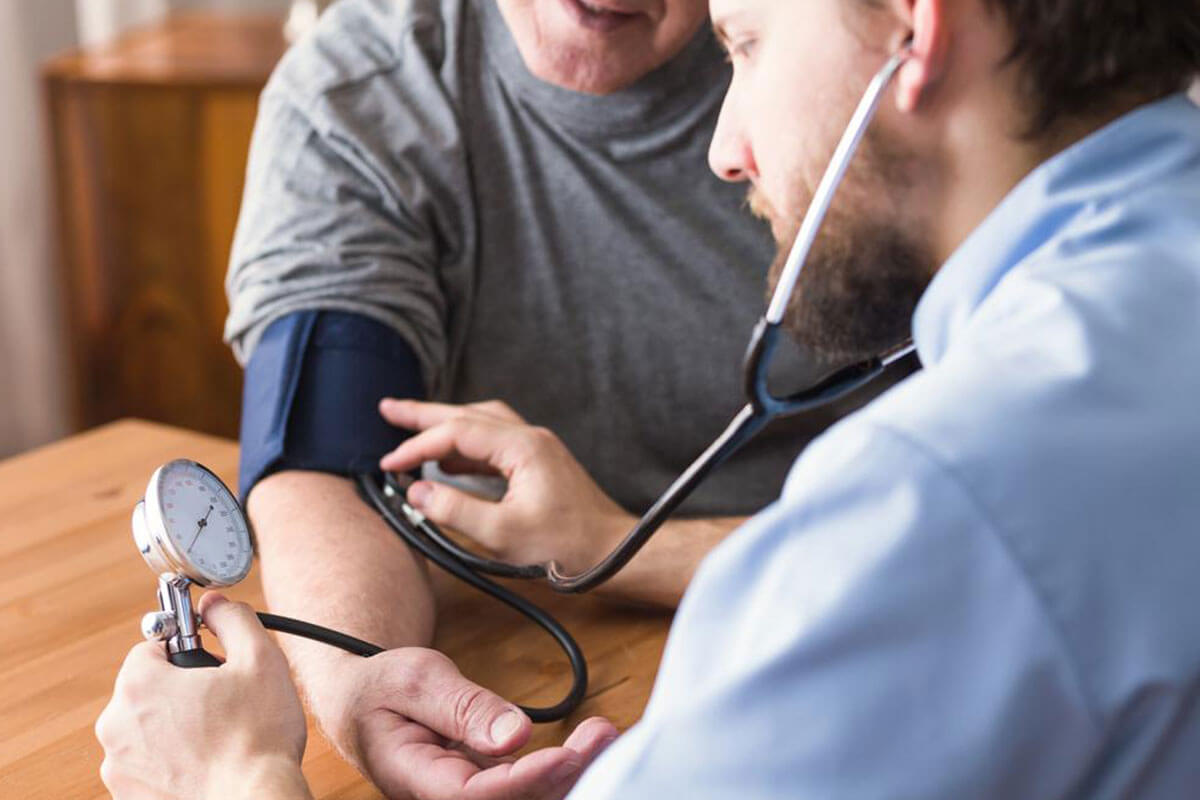
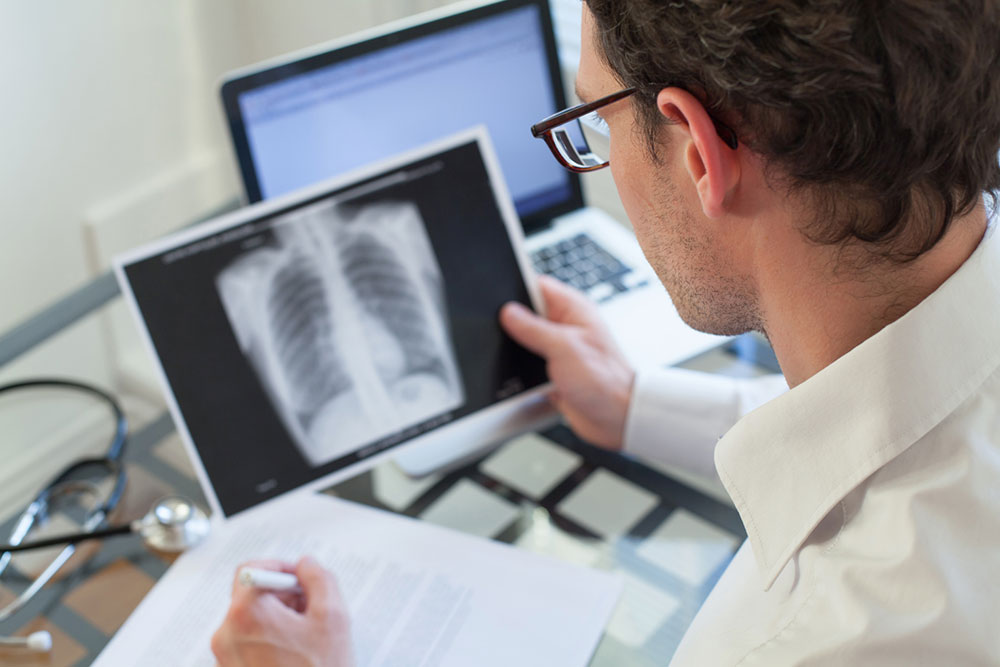
Pneumonia results from various infectious agents, each requiring specific diagnostic approaches. Healthcare facilities, particularly those caring for elderly or chronically ill patients, may encounter resistant bacteria. Common symptoms include chest discomfort when breathing or coughing, a persistent cough potentially with mucus, fever accompanied by sweating or chills, unexplained fatigue, and shortness of breath. Older adults might also show atypical signs such as low-grade fever, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Diagnosis involves physical assessments, lung sounds examination, blood and sputum tests, and imaging procedures like X-rays or CT scans. Blood oxygen saturation is measured using pulse oximetry. Treatment varies based on the pathogen, with antibiotics for bacteria, antifungals for fungi, and supportive therapy for viral cases. Severe cases or high-risk patients may require hospitalization. Always seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and care.