Understanding Shoulder Rotator Cuff Injuries and Their Symptoms
This article explains the key signs and causes of rotator cuff injuries in the shoulder. It highlights common symptoms such as limited mobility, pain, and difficulty sleeping, and emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis through physical exams and imaging. Suitable for athletes and workers with repetitive arm activities, it provides insights into injury prevention and management strategies.

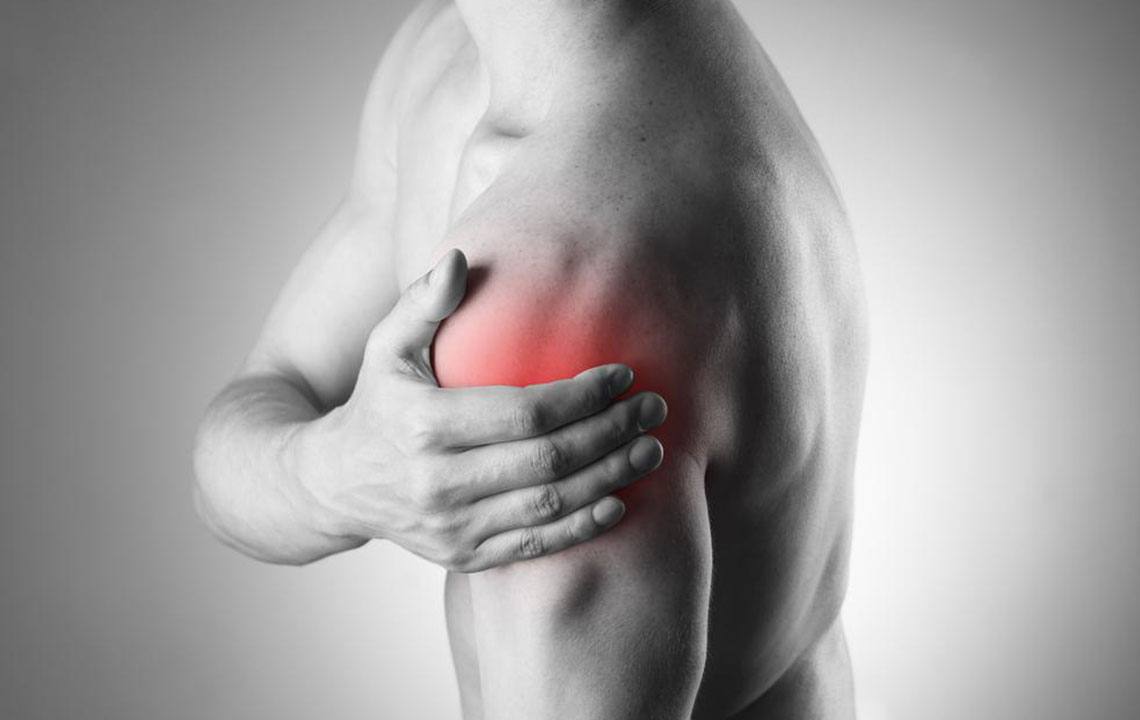
The shoulder rotator cuff plays a vital role in maintaining shoulder stability and facilitating smooth movement. Injuries to these muscles and tendons are prevalent in athletes engaged in overhead sports such as baseball, tennis, and volleyball, as well as workers performing repetitive arm tasks like painting, cleaning, or lifting. Repeated shoulder motions over time can cause wear and tear, leading to conditions like tendinitis, bursitis, strains, or tears. These injuries often result in pain, weakness, and restricted shoulder mobility, impacting daily life.
Causes
Excessive use of shoulder muscles causes tendinitis, especially with repetitive activities. Bursitis develops when bursae, fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints, inflame. Sudden trauma or accidents causing overstretching or tearing tendons can lead to immediate severe pain. Over time, degenerative changes may worsen symptoms, making early diagnosis important.
Signs and symptoms may not always be immediately noticeable, often developing gradually. Typical indicators include limited shoulder range of motion, difficulty sleeping on the affected side, and trouble reaching overhead or behind the back. If symptoms persist, seeking medical assessment is crucial. Diagnosis involves physical examinations, imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans, and evaluating activity history. Imaging can identify bone spurs, structural damage, or nerve impingement, aiding accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.