Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Shingles
This guide provides essential information on shingles, including symptoms, treatment options like antivirals and pain relief, home remedies, and preventive vaccines. Early diagnosis and vaccination can significantly reduce severity and risk. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care strategies.
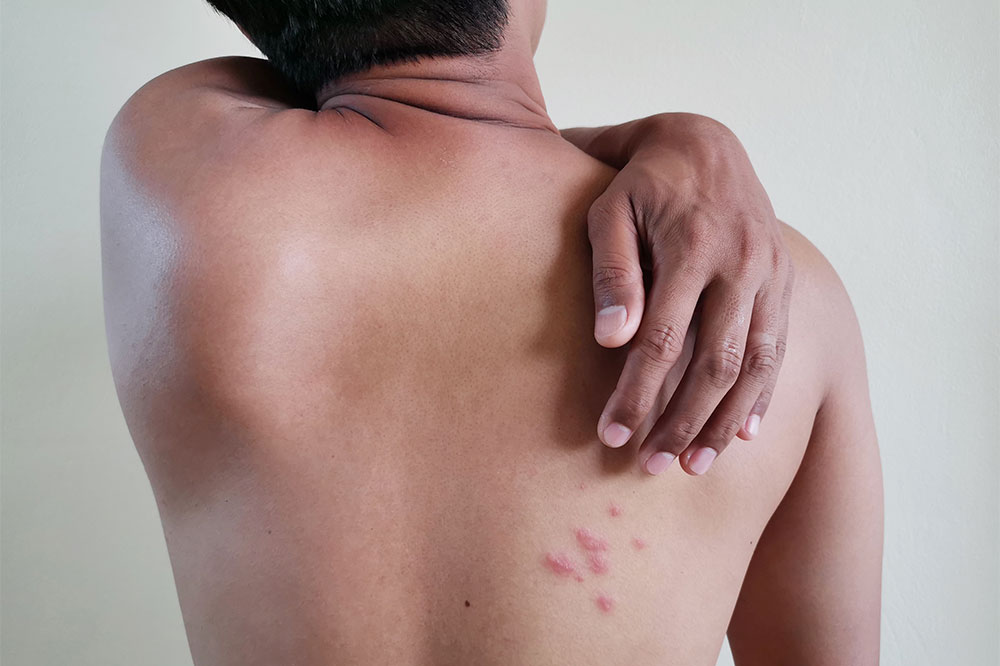
Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Shingles
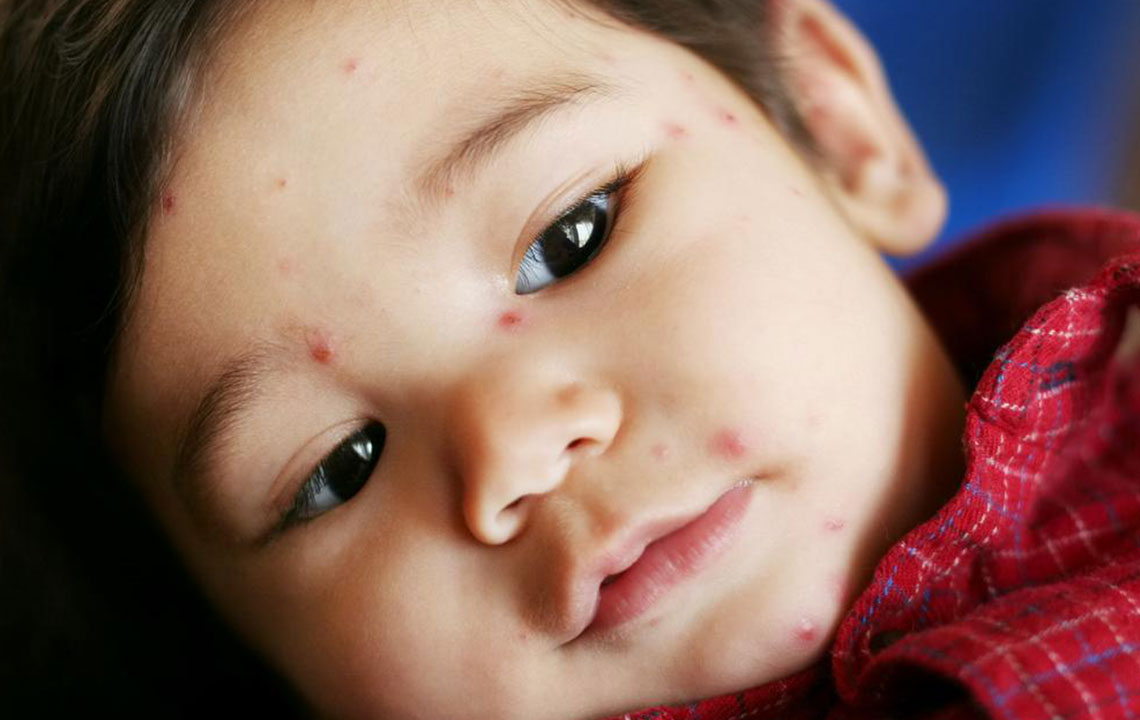
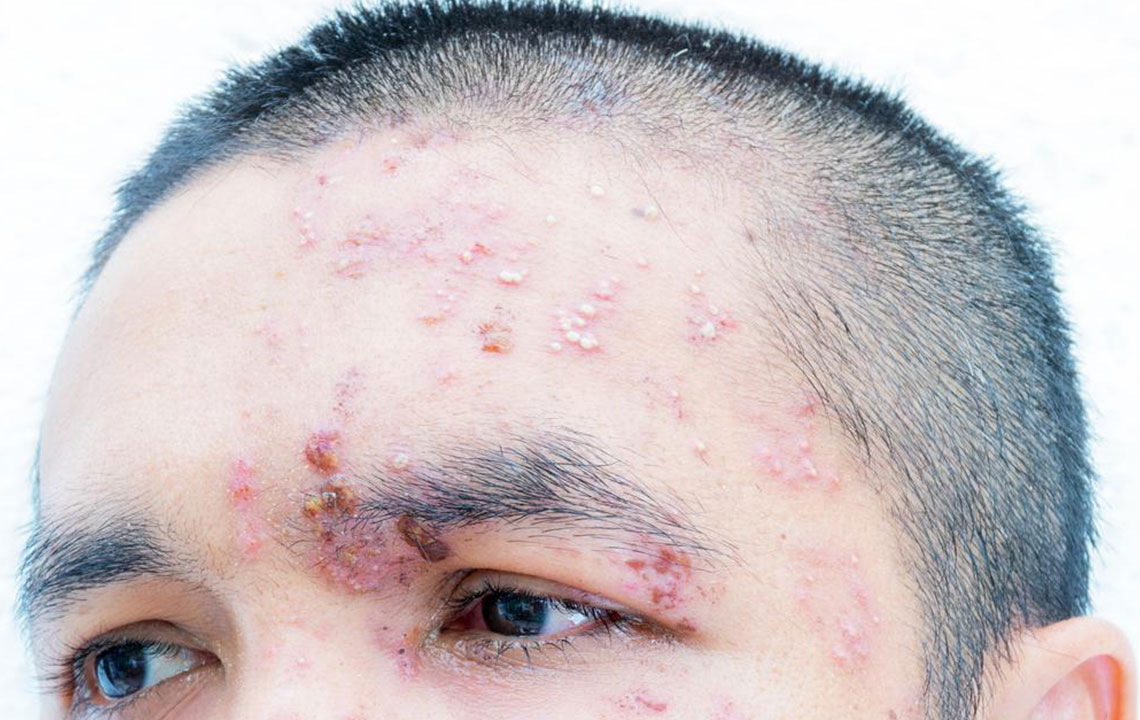
Shingles, medically known as herpes zoster, results from the activation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus causing chickenpox. After recovery from chickenpox, this virus remains inactive in the nervous system and can reactivate years later, causing shingles. Although there's no cure, early detection and treatment significantly reduce symptoms and complications.
Strategies for Shingles Relief
Antiviral Therapy
Medications like Acyclovir are effective when started within 72 hours of symptom onset to decrease viral replication.
Pain Control Measures
Over-the-counter analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications help alleviate discomfort associated with shingles.
Home Remedies and Care Tips
Shingles treatment typically lasts two to six weeks. Keeping affected areas clean and dry helps prevent complications.
Warm baths can soothe itching and pain; avoid hot or ice-cold water.
An oatmeal bath for 15 minutes can deliver soothing relief.
Using a moist bandage or cloth can ease discomfort, provided the area is clean.
Calamine lotion helps dry blisters and reduce rash spread.
Applying manuka honey topically may lessen viral symptoms.
Diluted essential oils like lavender, tea tree, lemongrass, and geranium can help reduce itching and pain.
Preventive Measures against Shingles
Vaccines such as Zostavax and Shingrix effectively lower the risk and severity of shingles. A single dose, combined with good hygiene, can decrease the likelihood of developing shingles by half. The CDC recommends Shingrix as the preferred vaccine, even for those previously vaccinated with Zostavax.
Important Notice:
This article offers useful insights into shingles management and prevention. While based on current research, it does not replace professional medical advice. For personalized treatment options, consult a healthcare provider.