Essential Medications for Managing Neutropenia
This article covers key medications used to treat neutropenia, emphasizing growth factors like G-CSF and GM-CSF, and the importance of medical supervision. It highlights symptoms, causes, and treatment options for managing low neutrophil levels effectively.

Primary Medications for Neutropenia Treatment
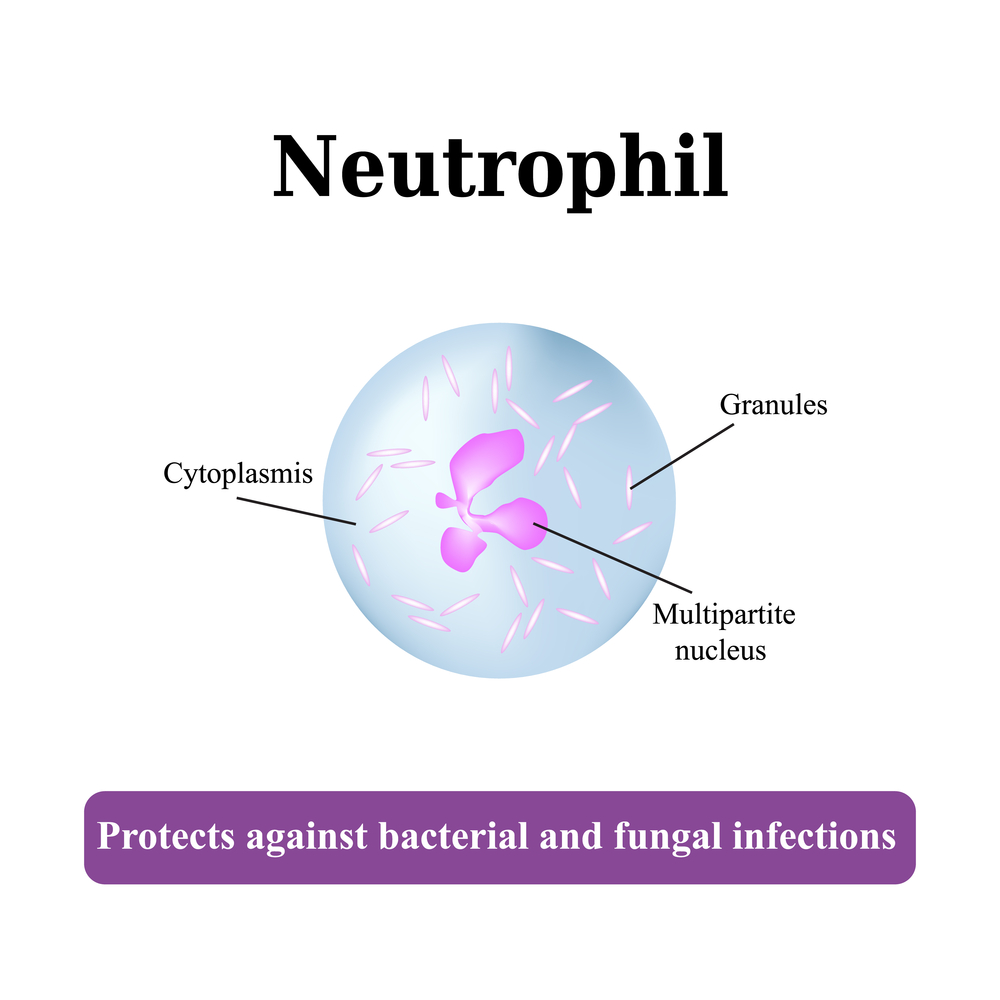
Neutropenia is a condition characterized by a deficiency of neutrophils, a vital white blood cell type responsible for combating infections. Adequate neutrophil levels are crucial to prevent bacterial and fungal infections. Patients with low counts should adhere to strict hygiene practices, including regular handwashing, to minimize infection risk.
Signs and Symptoms
Often silent, neutropenia may cause infections manifesting as sore throat, mouth ulcers, urinary discomfort, abdominal or anal pain, unusual vaginal discharge, redness or swelling around wounds, diarrhea, or respiratory problems.
Causes
Neutrophil production occurs in the bone marrow; any interference—particularly chemotherapy—can lead to neutropenia. Nearly 50% of chemotherapy treatments result in some degree of this condition.
Common Treatments and Medications
Therapies often include growth factors like G-CSF (filgrastim) and GM-CSF, which stimulate the bone marrow to produce more neutrophils. Antibiotics are also used to treat or prevent infections resulting from low white blood cell counts. In critical cases such as febrile neutropenia, prompt medical response is essential.
Popular drugs include Pegfilgrastim (brands: Neulasta, Udenyca, Fulphila), Sargramostim (Leukine), and Filgrastim (Granix, Zarxio). Always seek guidance from a healthcare provider before using any medication, to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
Note:
This article offers informational content about neutropenia treatments but is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and personalized treatment options.