A Comprehensive Overview of Asthma: Causes, Pathways, and Impact
This article provides an in-depth look at asthma, exploring its causes, immune mechanisms, and effects. It covers triggers, symptoms, and how inflammation impacts lung health, emphasizing the importance of proper management to prevent long-term damage.
Understanding Asthma: Causes, Pathways, and Effects
Asthma presents primarily as intermittent episodes or a persistent condition. Sudden attacks, called exacerbations, are triggered by specific factors, while chronic asthma involves ongoing lung inflammation that alters airway function over time.
Rapid-Onset Asthma Attacks
Exposure to triggers causes airway muscles to tighten, reducing airflow. This is accompanied by increased inflammation and mucus production, resulting in symptoms such as difficulty breathing, coughing, chest tightness, and wheezing.
Persistent asthma results from ongoing lung inflammation, making the airways overly sensitive. Over time, structural changes in lung tissues and increased mucus secretion can develop. Proper treatment can help prevent these long-term effects.
Triggers include physical activity, infections, environmental factors like cold air and pollution, irritants such as tobacco smoke and strong scents, emotional stress, allergies (dust, pollen, pet dander), and certain medications like NSAIDs. These factors can cause airway constriction or inflammation.
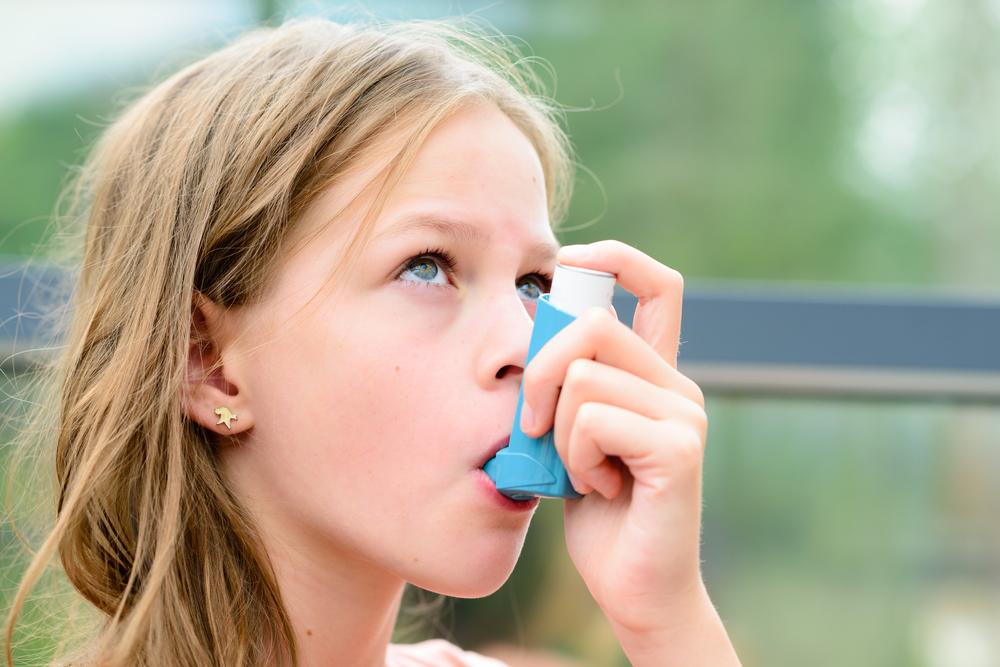
Asthma related to environmental and allergic reactions involves complex immune mechanisms, including pathways like Th1, Th2, and IgE antibody production. Even healthy individuals may experience exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), which can be managed with preventive medications.
Role of the Immune System in Asthma
Immune responses, especially Th2 activity and IgE antibodies, play key roles in asthma development. IgE binds to allergens, prompting mast cells to release histamine, leading to airway inflammation and mucus overproduction.
Important Reminder:
This information is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment of asthma or other health conditions.


