Early Identification Techniques for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder is vital for effective intervention. Through behavioral assessments, genetic testing, and developmental monitoring, professionals can diagnose ASD often by age two. Prompt identification enables tailored support, improving long-term outcomes. This article highlights screening tools, diagnostic procedures, and the importance of early diagnosis for better development and family planning.

Early Identification Techniques for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition influenced partly by genetics, affecting communication, behavior, and social skills. Signs often appear within the first two years, but due to the diverse range of symptoms, early detection is crucial. Since ASD varies widely among individuals, thorough screening helps ensure timely diagnosis and early intervention.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Infants with ASD usually lack distinct physical indicators early on. As they develop, difficulties in social interaction, communication, and learning become more apparent. Recognizing these signs early allows for appropriate support and resource planning.
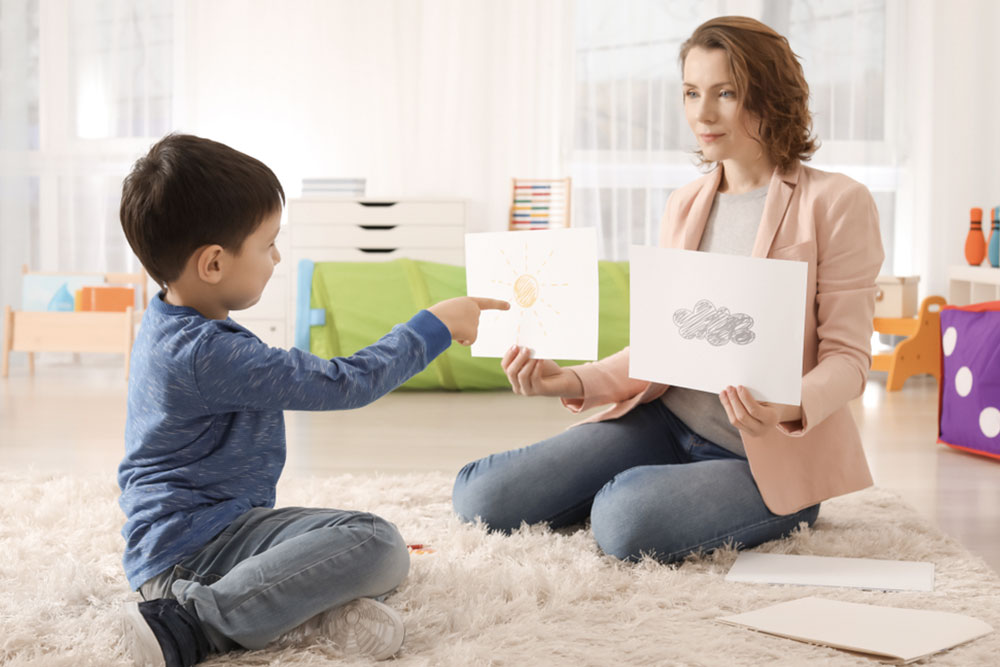
Preliminary screening tools, like online autism assessments, can offer initial insights. These typically involve up to 50 questions and can be completed in minutes. Still, a professional evaluation remains essential for a confirmed diagnosis of ASD.
Evaluation Techniques for Autism
There are two primary assessment methods used by specialists:
Repetitive Behavior Questionnaire (RBQ-2)
Consisting of 20 items, this self-report tool evaluates repetitive actions, routines, and motor behaviors in adults, helping experts assess the nature and severity of ASD-related behaviors.
Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ)
This questionnaire features 50 statements with four response options, designed to determine where an individual may fall on the autism spectrum. Its moderate accuracy makes it suitable for initial screening.
In addition to these assessments, visiting local autism testing centers ensures a comprehensive evaluation. Early identification leads to better treatment options and improved life trajectories for individuals with ASD.
Screening Procedures for Autism
Healthcare professionals analyze developmental history and behavioral patterns to diagnose ASD. Detecting signs by age two is common and particularly beneficial, enabling timely support.
Developmental Monitoring
Physicians observe behaviors such as eye contact and gestures over time, considering familial health histories to spot early ASD indicators.
Comprehensive Behavioral Evaluations
A team of specialists—including psychologists, therapists, neurologists, and physical therapists—reviews behavioral data to determine if further testing is warranted.
Genetic and Medical Tests
Genetic tests like chromosomal microarray analysis and whole exome sequencing can detect chromosomal anomalies linked to ASD. These tests, utilizing blood, saliva, or cheek swabs, provide detailed genetic insights to support diagnosis.
Early and accurate diagnosis improves understanding, planning, and support for individuals with ASD, positively impacting their development and quality of life.