Comprehensive Overview of Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
Neuropathy involves nerve damage caused by various factors like illnesses, injuries, or vitamin deficiencies. Symptoms range from numbness and pain to muscle weakness. Early diagnosis is vital to prevent serious complications. This article covers causes, symptoms, and nerve types affected, highlighting the importance of prompt medical attention.

Comprehensive Overview of Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
Neuropathy is a condition characterized by damage or dysfunction of the nervous system, caused by factors such as illnesses, infections, medication effects, injuries, alcohol use, or vitamin deficiencies. Sometimes, no specific cause can be identified. About 8% of people over 55 experience neuropathy symptoms, which can differ greatly in severity and presentation. These symptoms may range from mild discomfort to intense pain, posing challenges for accurate diagnosis due to their variability.
Untreated neuropathy can lead to serious health issues, including disability or, rarely, mortality. Affected nerves include sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers. It can target a single nerve, termed mono-neuropathy, like ulnar or radial nerve issues. When multiple nerves are involved, it's called polyneuropathy.
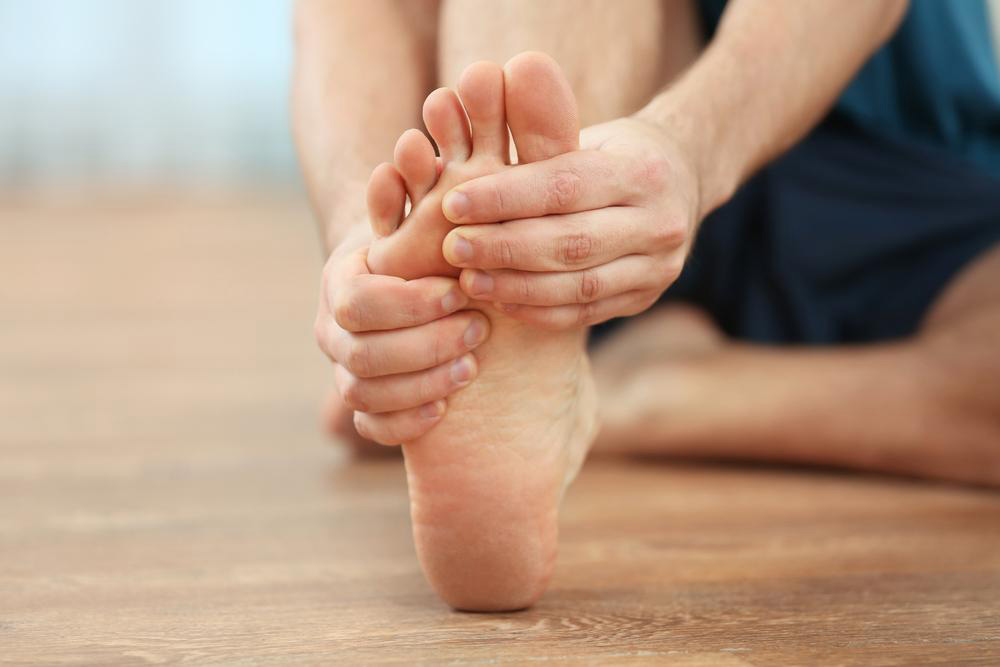
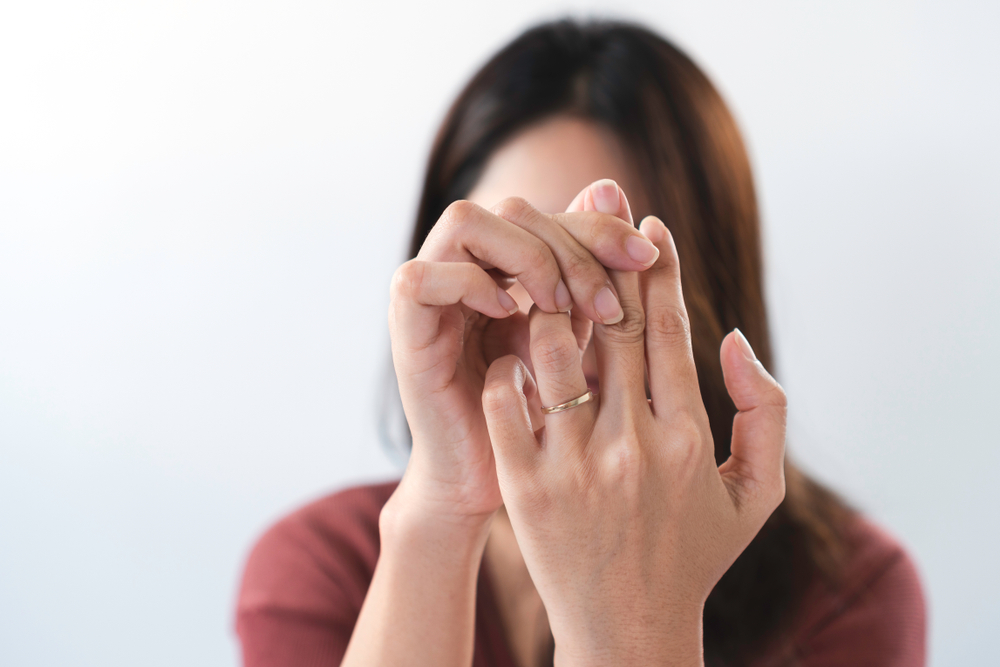
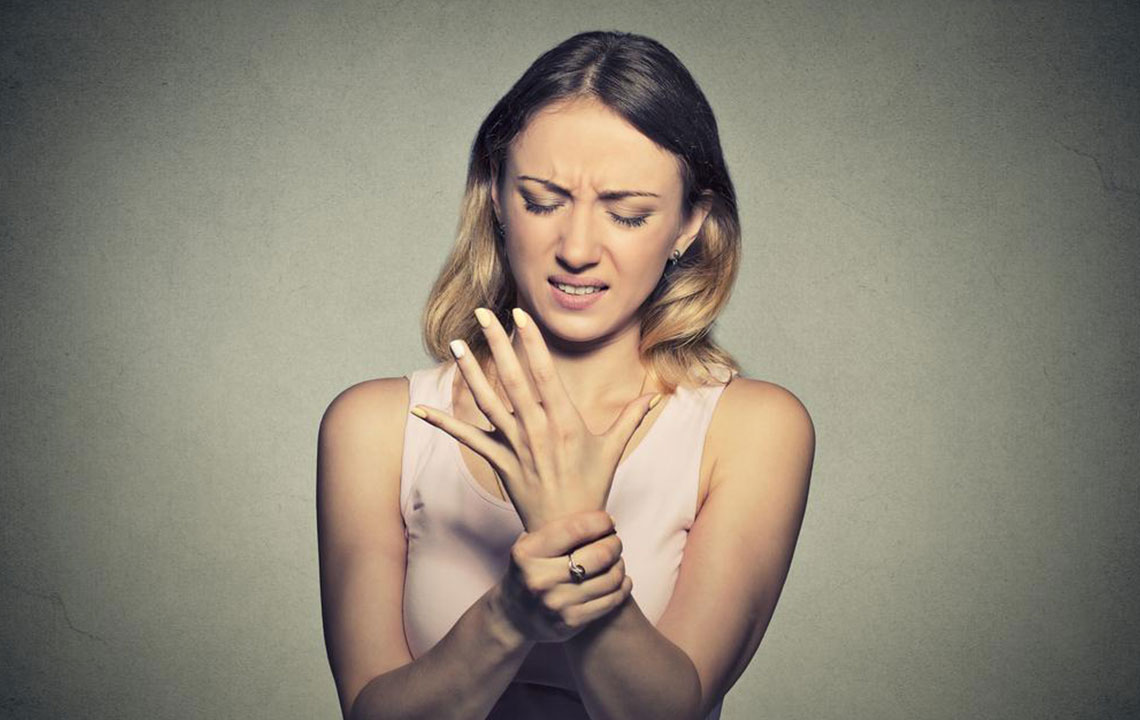
Common signs and symptoms: Motor nerve damage can cause weakness, pain, cramps, twitching, muscle wasting, and changes in skin, hair, or nails. Sensory nerve impairment might result in numbness, balance problems, reflex loss, burning or tingling sensations, hypersensitivity or insensitivity to pain, and neuropathic pain. Autonomic nerve involvement may lead to digestive problems, blood pressure fluctuations, dizziness, erectile issues, abnormal sweating, dry eyes or mouth, and swallowing difficulties.
Early recognition of these signs emphasizes the importance of prompt diagnosis. If symptoms appear, consult a neurologist for accurate assessment and treatment options.