Comprehensive Guide to Oral Cancer: Symptoms, Detection, and Treatment Options
This comprehensive overview details oral cancer's symptoms, detection methods, and treatment options. Early diagnosis improves outcomes, with treatments including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Recognizing early signs can save lives and enhance recovery chances.
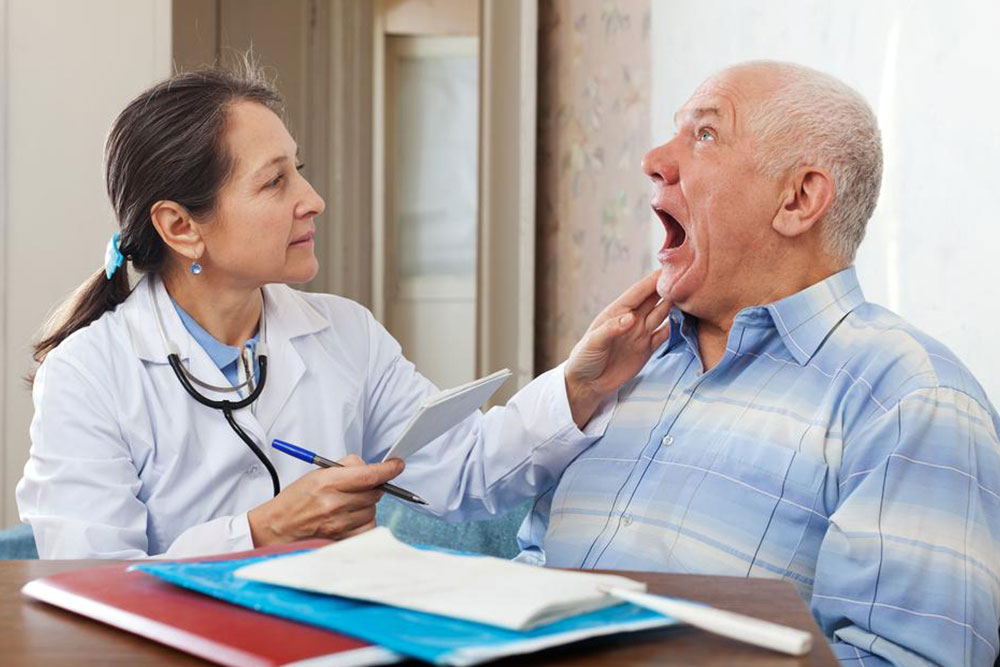

Oral cancer develops from the rapid, uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the mouth. When it spreads to nearby regions like the neck or other facial areas, it is considered metastatic oral cancer.
In later stages, the malignant cells invade surrounding tissues and can travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Early detection is often missed, reducing the chances of successful treatment and decreasing survival rates.
Common signs of oral cancer include:
Persistent sore throat and irritation
Frequent bleeding sores in the mouth
Unusual growths on oral mucosa
Loose teeth due to tissue damage
Jaw pain resulting from tissue destruction
These symptoms typically appear on lips, gums, tongue, palate, or oral floor. Routine dental examinations can help catch the disease early, but symptoms worsen as it reaches lymph nodes, often leading to poorer outcomes due to aggressive tissue damage.
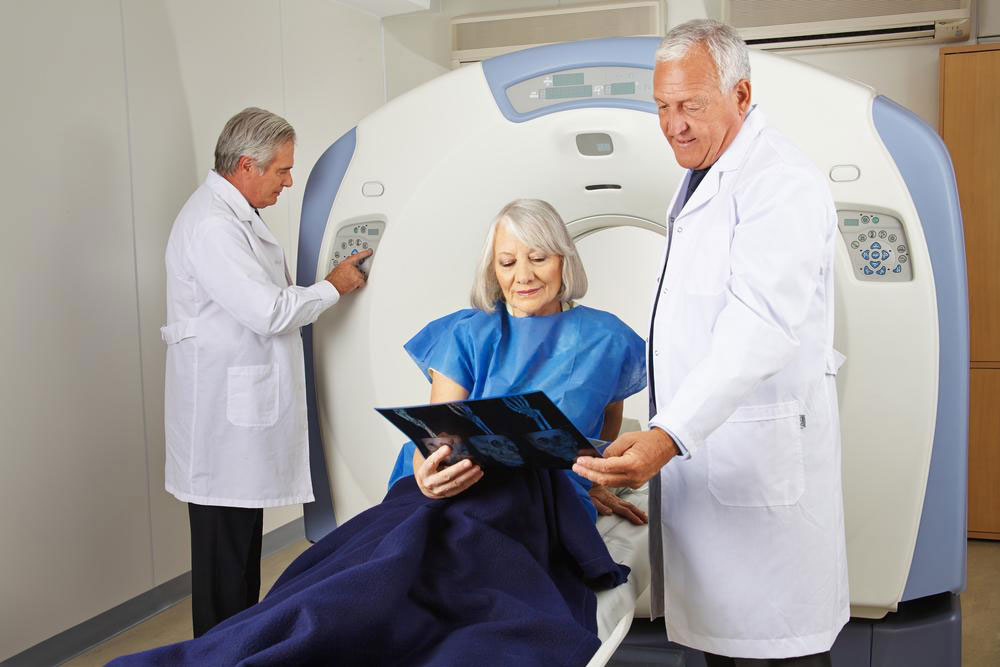
Diagnosis involves physical exams, tissue biopsies, and lab tests to determine the cancer's spread. Sentinel lymph node biopsies help evaluate metastasis, while advanced imaging like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans establish cancer stage and inform treatment choices.
Based on the tumor’s size, location, and stage, treatments vary. Early cases often benefit from surgery and reconstructive procedures, while advanced stages may require radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy uses potent drugs to inhibit growth and prevent spread. Combining targeted therapies with chemo or radiation can enhance effectiveness.
Important Notice: Our blog offers research-based insights on a variety of health topics. While intended to be helpful, these should not replace professional medical advice. We are not responsible for inconsistencies or inaccuracies elsewhere, and offers or schemes discussed may differ locally.