Harnessing Okra: A Natural Strategy for Blood Sugar Management in Diabetes
Explore the natural potential of okra as a supplement for managing blood sugar levels. Known for its fiber and health benefits, okra offers a simple way to support blood glucose regulation, especially for pre-diabetics. Always consult a healthcare provider before trying new remedies to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Natural Blood Sugar Control with Okra — A Healthy Green Solution
High blood sugar levels affect many individuals across the United States. Diabetes arises when the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin, disrupting normal metabolism. The main types are Type 1 and Type 2, with Type 2 being the more common and severe form. Contributing factors include lifestyle choices, diet, obesity, and genetics. Standard treatments involve medications, nutritional adjustments, and physical activity.
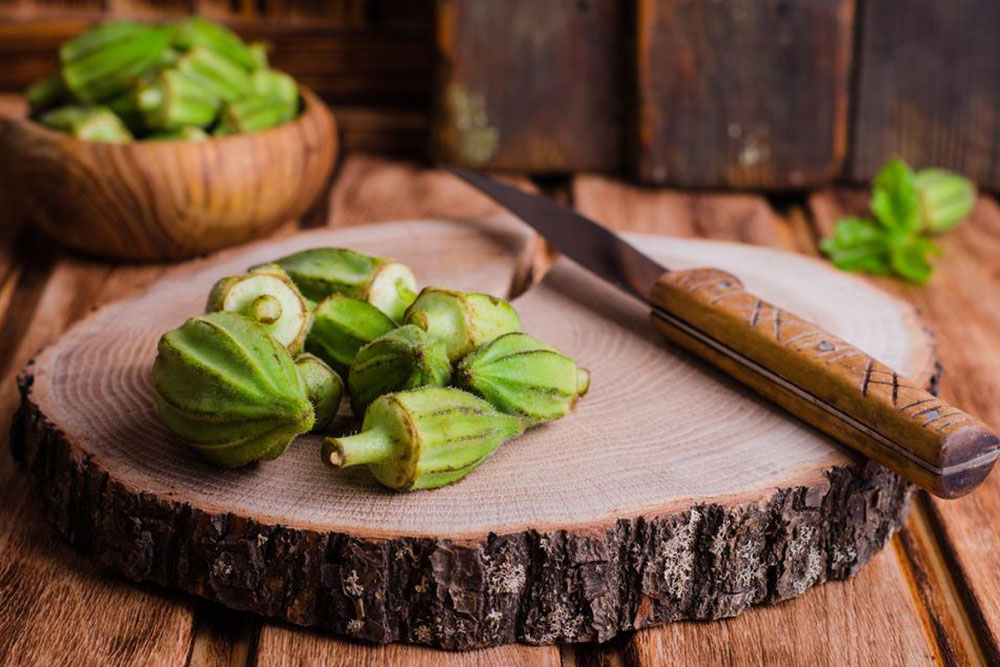
Alongside conventional methods, natural remedies are gaining popularity. One such approach uses okra, a nutritious green vegetable renowned for its health-promoting properties. Known as ladies’ finger in some areas, okra features prominently in various culinary traditions.
To utilize this natural method, soak 4-5 okra pods overnight in water. In the morning, remove the pods and drink the infused water daily. Consistent intake may help lower blood sugar levels, aiding in normalizing glucose levels in pre-diabetic individuals.
Thanks to its high fiber content and low calories, okra is beneficial for managing diabetes. Research indicates that okra can hinder glucose absorption, aiding blood sugar stability. While many studies are animal-based, the medicinal potential of okra is encouraging. The seeds also show promise for blood sugar regulation. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning this natural treatment, especially if you're on medication, to ensure safety. This simple, accessible approach could support natural blood sugar control effectively.
Important Reminder:
Always seek medical advice when exploring natural remedies to confirm they won't interfere with your current treatment plan. This method may be particularly effective for pre-diabetic or newly diagnosed patients. Be cautious with dietary modifications and discuss them with your healthcare professional.