Innovative Approaches to Managing Advanced Melanoma
This article explores advanced strategies for treating metastatic melanoma, highlighting surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. It emphasizes personalized treatment approaches designed to improve survival and quality of life for patients. Stay informed about the latest developments in melanoma care with this comprehensive overview.
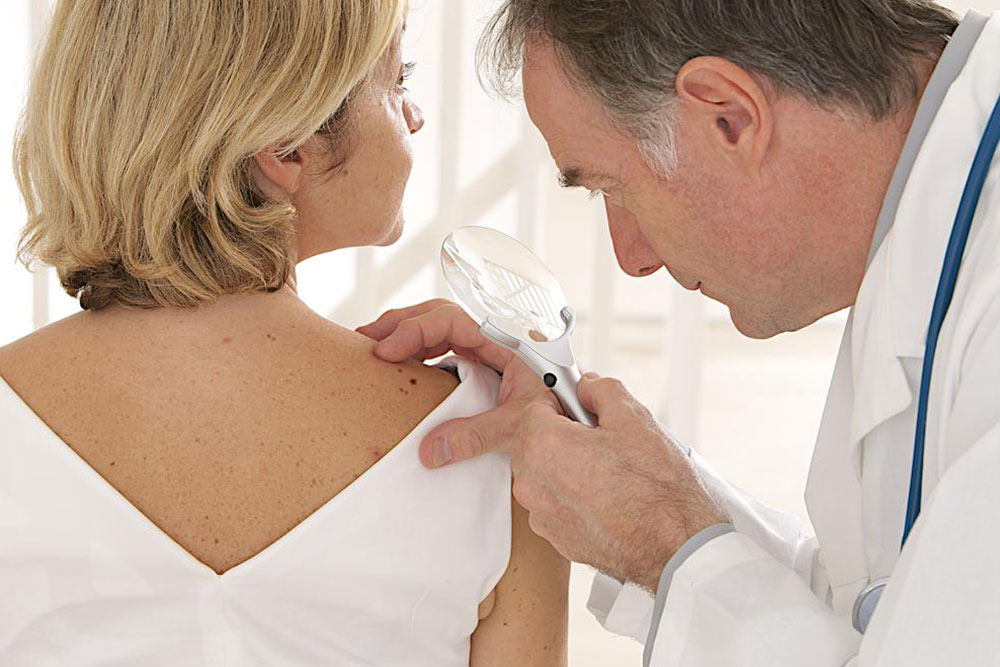
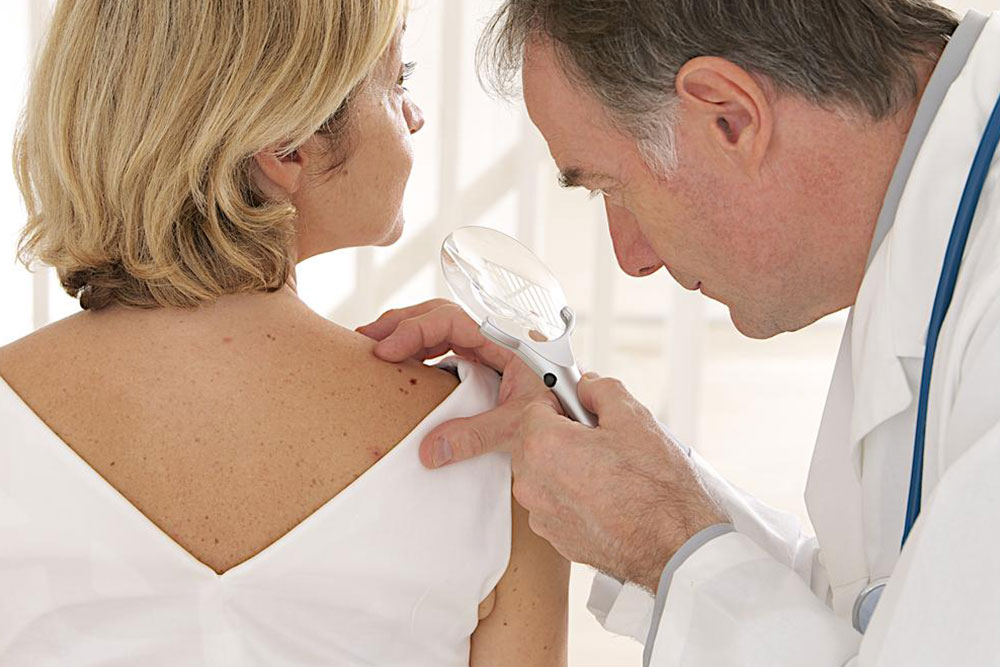
Managing advanced melanoma remains complex, but various treatment strategies exist. The choice depends on tumor spread and patient health status. Main objectives focus on controlling or eliminating cancer growth and preventing further metastasis. Treatment options include surgical removal, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, often used in combination. Recent advancements focus on therapies that reduce side effects and improve patient comfort. Surgery involves excising tumors or affected tissues, while radiation uses targeted high-energy rays to destroy malignant cells. Chemotherapy employs drugs to attack fast-growing cancer cells, and immunotherapy enhances the body's immune defenses. Personalized treatment plans aim to increase survival and enhance quality of life.
Depending on individual cases, surgical procedures can remove tumors or compromised organs, especially in severe cases. Chemotherapy, administered through injections or topical agents, targets rapidly dividing cells but may cause side effects such as hair loss and fatigue. Radiation therapy, including external beam or internal methods like brachytherapy, aims to reduce tumor size. Immunotherapy strengthens immune response mechanisms to combat melanoma more effectively, often resulting in fewer adverse symptoms. Customized therapy plans are designed to improve patient survival and well-being.
Note:
This information is intended for educational purposes. Always seek advice from qualified medical professionals for personalized treatment guidance. Data accuracy may vary across sources, and this content is not a substitute for professional consultation.