Recognizing Allergy Symptoms and Identifying Risk Factors
This article explores common allergy symptoms, triggers, and risk factors. It highlights how the immune system overreacts to substances like pollen, foods, and insect stings, leading to mild or severe reactions. Recognizing signs such as sneezing, swelling, and breathing difficulties is crucial. The article emphasizes the importance of understanding genetic and environmental risk factors, especially for those with respiratory issues. Immediate medical attention for severe reactions like anaphylaxis is vital. Stay informed to identify and manage allergies effectively.

Recognizing Allergy Symptoms and Identifying Risk Factors
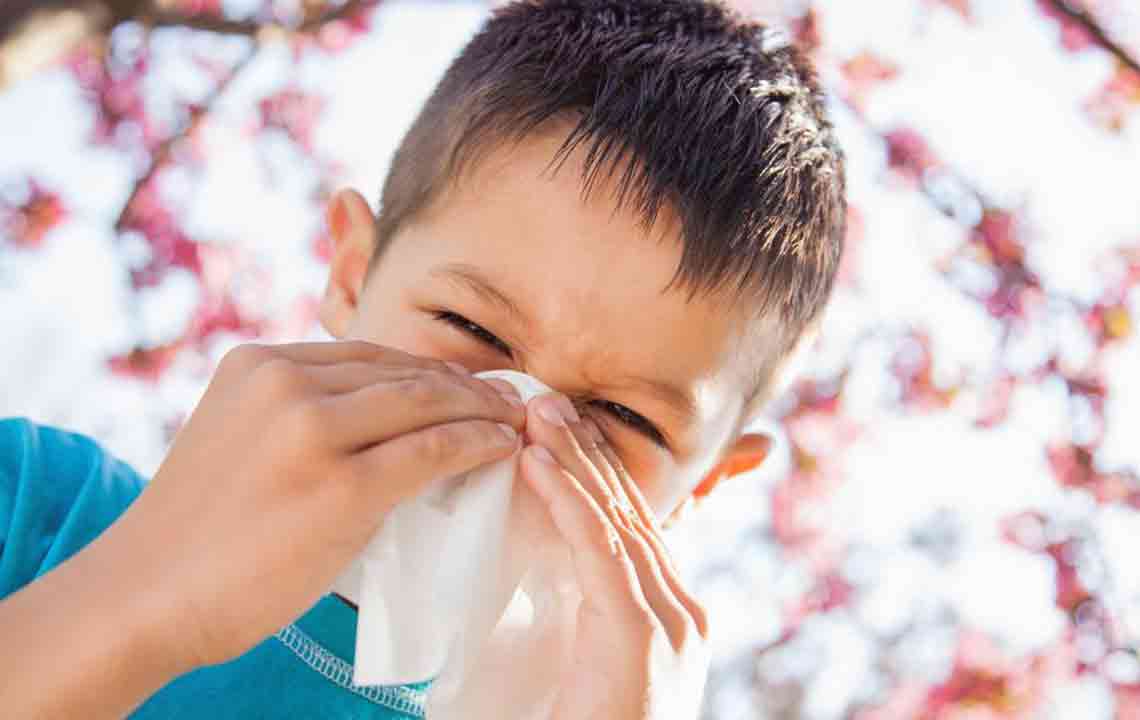
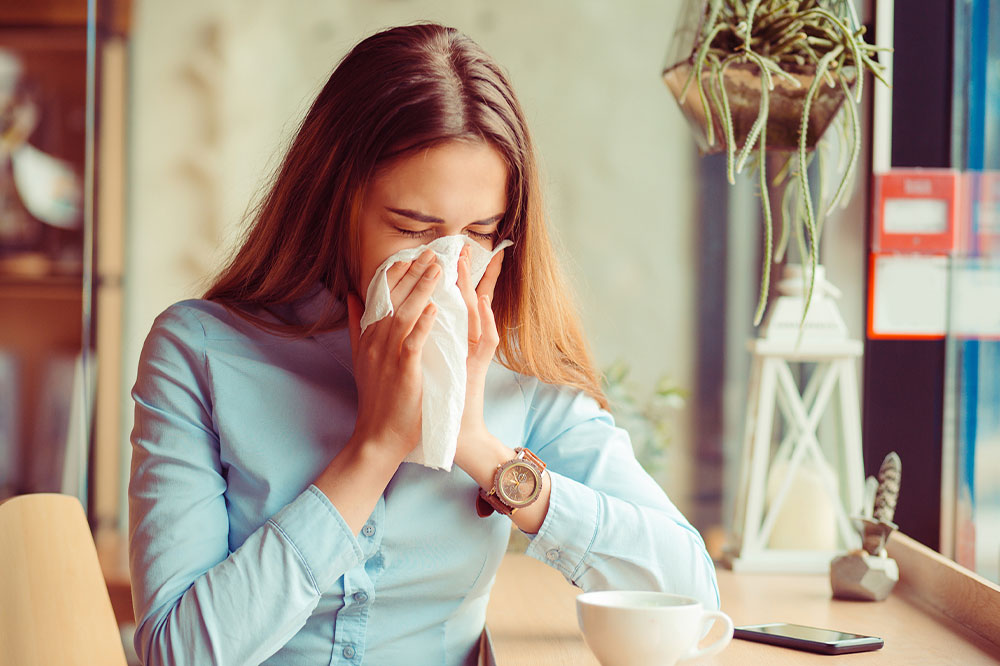
Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to certain foreign substances, producing specific antibodies to combat perceived threats. Symptoms can vary widely, from minor discomforts to life-threatening conditions.
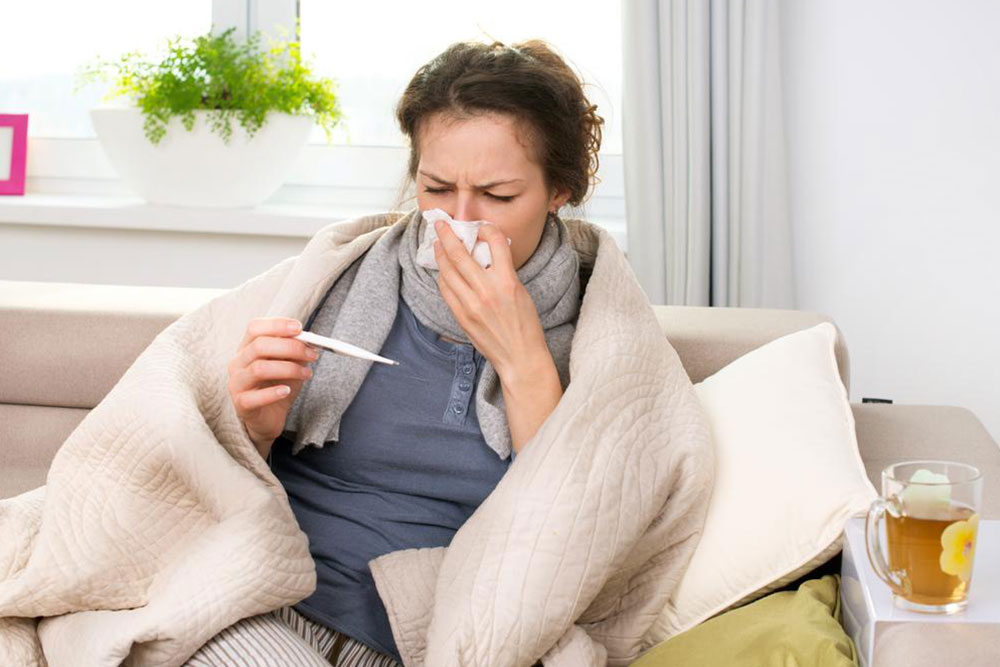
Common signs include sneezing, nasal blockage, itchy eyes, swelling, and breathing difficulties. Types of allergies include hay fever (allergic rhinitis), food allergies, reactions to insect stings, medication responses, and skin conditions such as eczema. Anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction, demands immediate care.
Allergic triggers vary and include airborne allergens like pollen and dust mites, foods such as nuts, seafood, and wheat, insect bites, certain medicines, and contact with latex or other irritants.
Risk factors involve genetic makeup, age, and respiratory health conditions. A family history of allergies increases susceptibility, especially in children. Individuals with asthma or similar sensitivities may experience additional allergic responses over time.
Signs of severe reactions include fainting, low blood pressure, rashes, difficulty breathing, and dizziness. Immediate medical attention is essential in such situations.
Important: This content is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare providers for proper diagnosis and treatment of allergies.