Causes and Effects of Spinal Canal Stenosis on Health
Spinal canal stenosis is a condition characterized by narrowing of spinal spaces, often caused by aging, injuries, and poor posture. It can lead to pain, numbness, and mobility issues, especially in the neck and lower back. Early intervention with chiropractic care, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures can significantly improve quality of life and prevent permanent nerve damage.
Causes and Effects of Spinal Canal Stenosis on Health
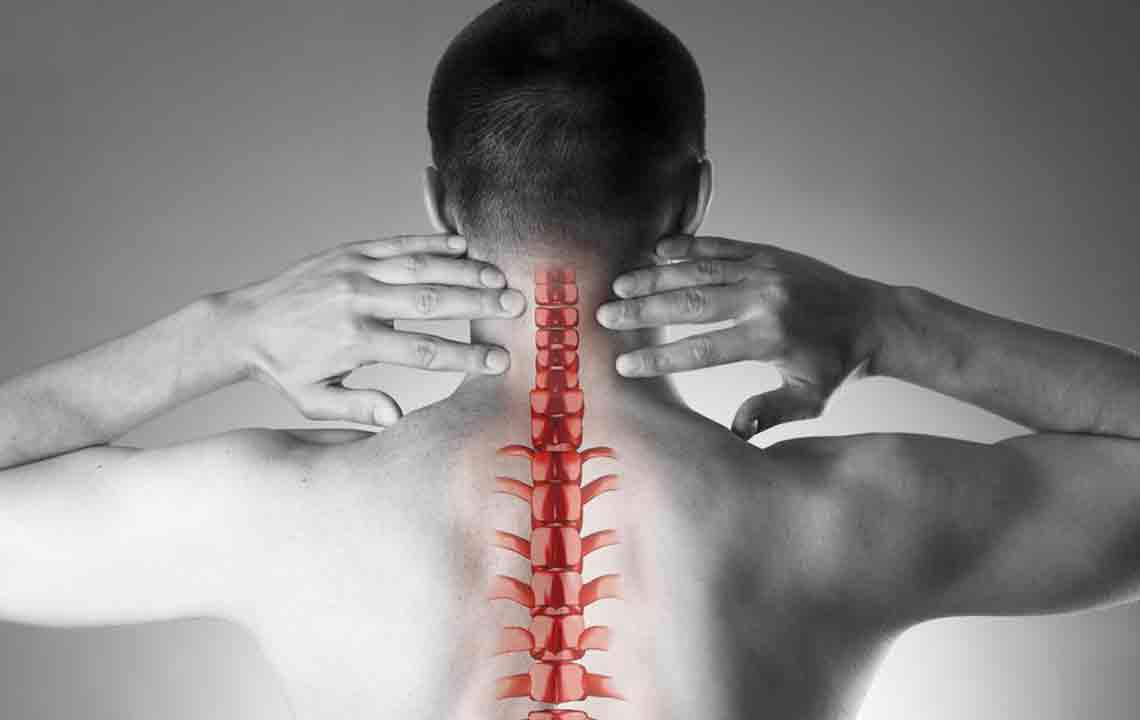
The backbone provides essential support for the body and houses the spinal cord, a vital part of the central nervous system (CNS) responsible for transmitting signals that govern movement, sensation, and reflexes. Any issues affecting the spine can interfere with these signals, leading to health problems.
One common spinal condition is stenosis, characterized by narrowing of spaces within the spinal canal. Contributing factors include aging, injuries, poor posture, or dislocations. This narrowing presses on nerves, causing pain, discomfort, and mobility issues, especially in the neck and lower back, which bear most pressure.
Symptoms may develop gradually, and some individuals remain asymptomatic for years. Once pain, weakness, or numbness appear, seeking a chiropractor’s advice is crucial. Early diagnosis helps prevent nerve damage and worsened symptoms.
Activities such as sitting for long periods, poor ergonomic habits, or nutritional deficiencies can worsen stenosis. Chiropractors specialize in diagnosing and managing neuromuscular disorders through manual adjustments and therapies. Most patients seek interventions early for pain relief, improved mobility, and supportive guidance. Treatment options include dietary adjustments, exercises, ergonomic counseling, and therapeutic procedures.
There are different types of spinal stenosis based on their location and cause:
Cervical stenosis: affects the neck, causing neck pain and neurological symptoms.
Lumbar stenosis: occurs in the lower back, leading to lower back pain and leg weakness, common among adults.
The condition results from gradual degenerative changes and nerve pressure, impacting quality of life over weeks or years. Treatment varies and may involve medications, manual therapy, surgery, or lifestyle modifications. Preventive strategies such as regular exercise, proper posture, massages, balanced diet, and avoiding excessive strain are highly beneficial.