Strategies to Protect Your Lungs from Pulmonary Embolism
This article provides essential strategies to prevent pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition caused by blood clots blocking lung arteries. Recognize symptoms early, understand causes, and adopt preventive measures to protect your lung health effectively. Early intervention reduces serious complications and improves outcomes.
How to Protect Your Lungs from Pulmonary Embolism
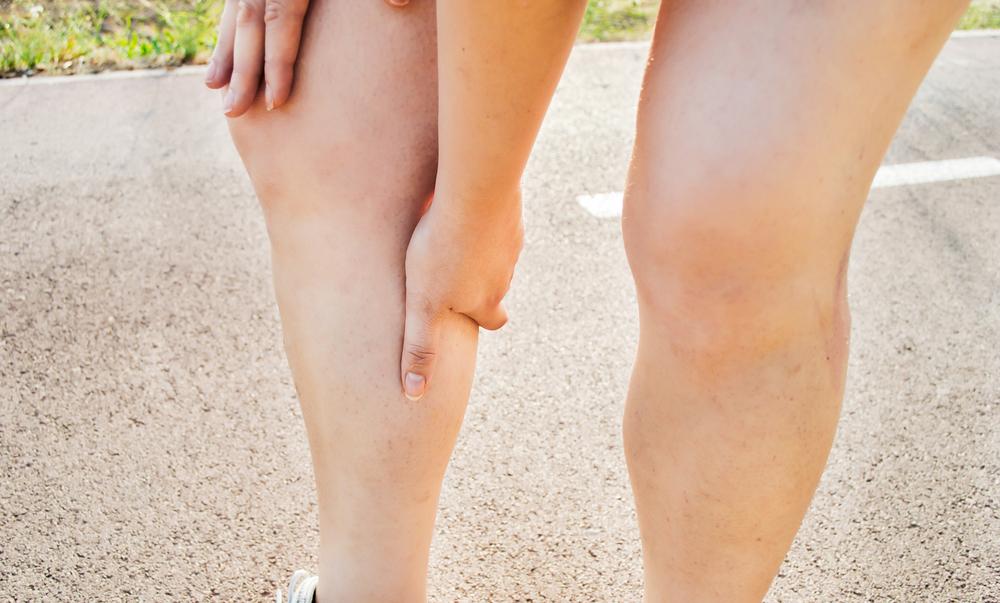
Pulmonary embolism happens when a clot obstructs a pulmonary artery in the lungs, often originating from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the legs. As these clots travel through the bloodstream, they can cause significant blockages, impairing lung function and potentially leading to severe complications if not addressed quickly. Symptoms vary based on clot size and location and may include sudden difficulty breathing, chest discomfort similar to a heart attack, and coughing blood. Other signs may involve swollen legs, skin discoloration, fever, sweating, irregular heartbeat, dizziness, or fainting.
Most pulmonary embolisms result from blood clots forming in deep veins, especially in the legs, which then migrate to the lungs, causing tissue damage or infarction. Rarely, fat particles, tumors, or air bubbles can also cause blockages. Prevention, early detection, and prompt treatment are essential to minimize risks associated with this dangerous condition.