Proven Methods to Prevent and Manage Shingles Effectively
Discover effective strategies to prevent and manage shingles, including vaccination, natural remedies, and lifestyle tips. Learn about risk factors, symptom relief, and safe vaccination practices to reduce complications and improve quality of life.

Understanding and Preventing Shingles
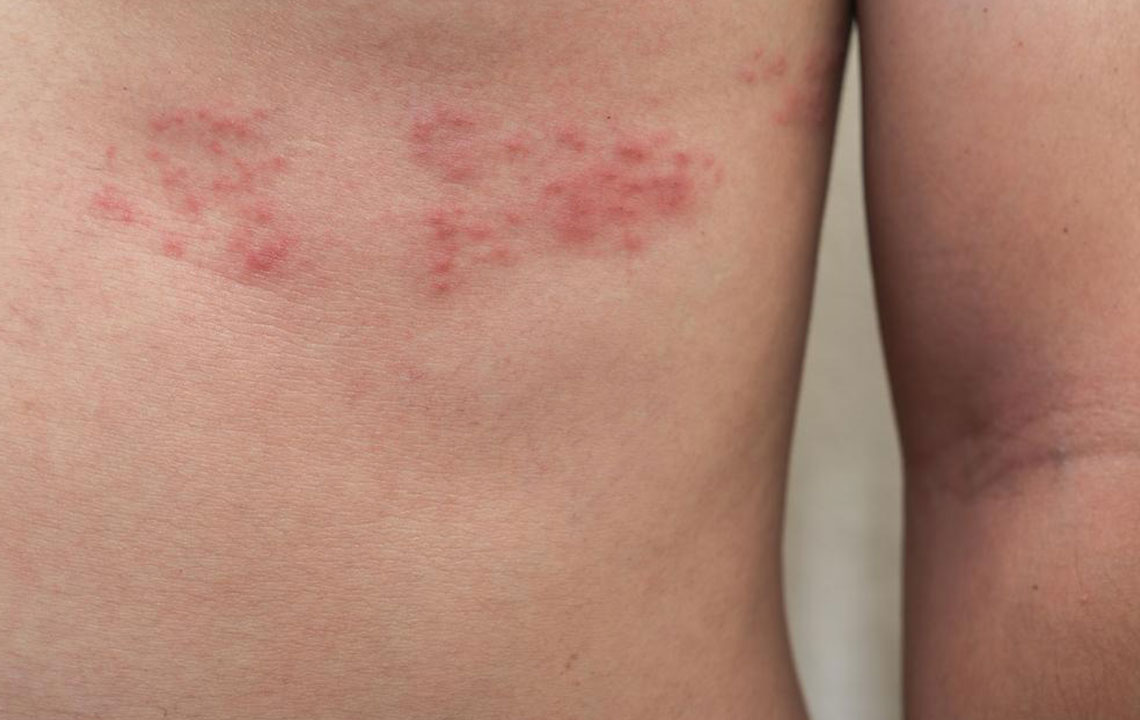
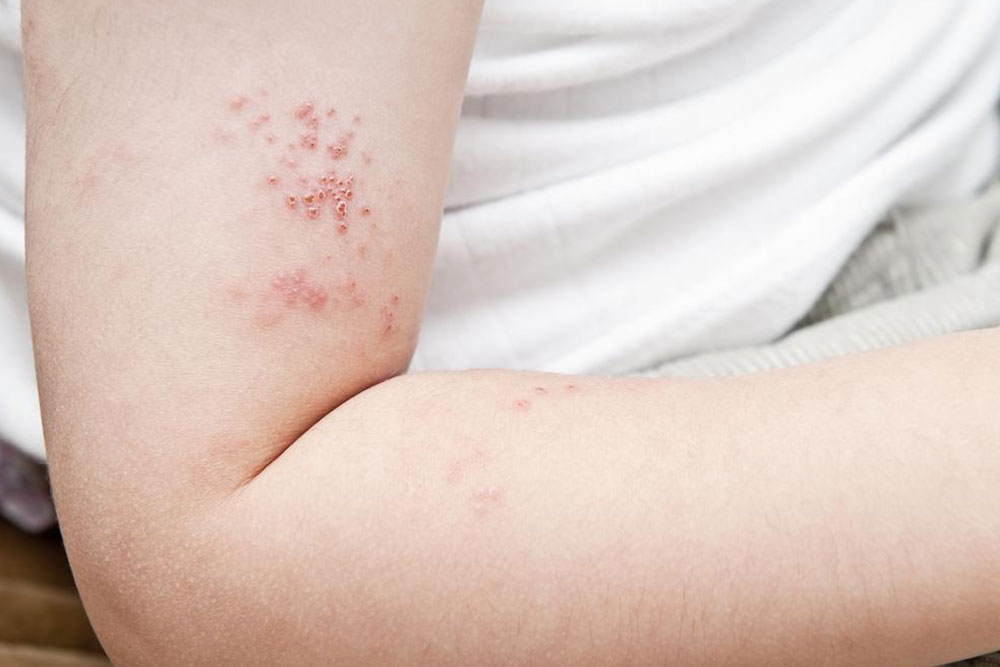
Shingles diagnosis often involves examining the classic rash and blisters that appear as painful red streaks. In some cases, doctors may review your medical history or analyze skin samples or blister fluid to confirm the infection. Vaccination remains the most effective prevention, but maintaining a healthy immune system and following appropriate treatment plans are essential in controlling the condition.
Administering vaccines can significantly lessen symptoms and prevent complications. Since shingles arises from the same virus as chickenpox, children should be vaccinated accordingly. Mild symptoms can sometimes be managed with home remedies.
Preventative Strategies for Shingles
Enhance your immunity through a nutritious lifestyle.
Get vaccinated to reduce the risk of severe symptoms.
Ensure children receive two doses of the chickenpox vaccine.
Adults who haven't had chickenpox should consider the shingles vaccine.
Groups at Higher Risk for Shingles
Pregnant women without prior chickenpox or vaccination
Premature or low birth weight infants
Individuals with weakened immune systems or on long-term antibiotics
Patients undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplants
People living with HIV
Tips to Prevent Shingles from Worsening
Cover skin lesions with a clean cloth to prevent infection.
Avoid contact with vulnerable populations until the rash heals.
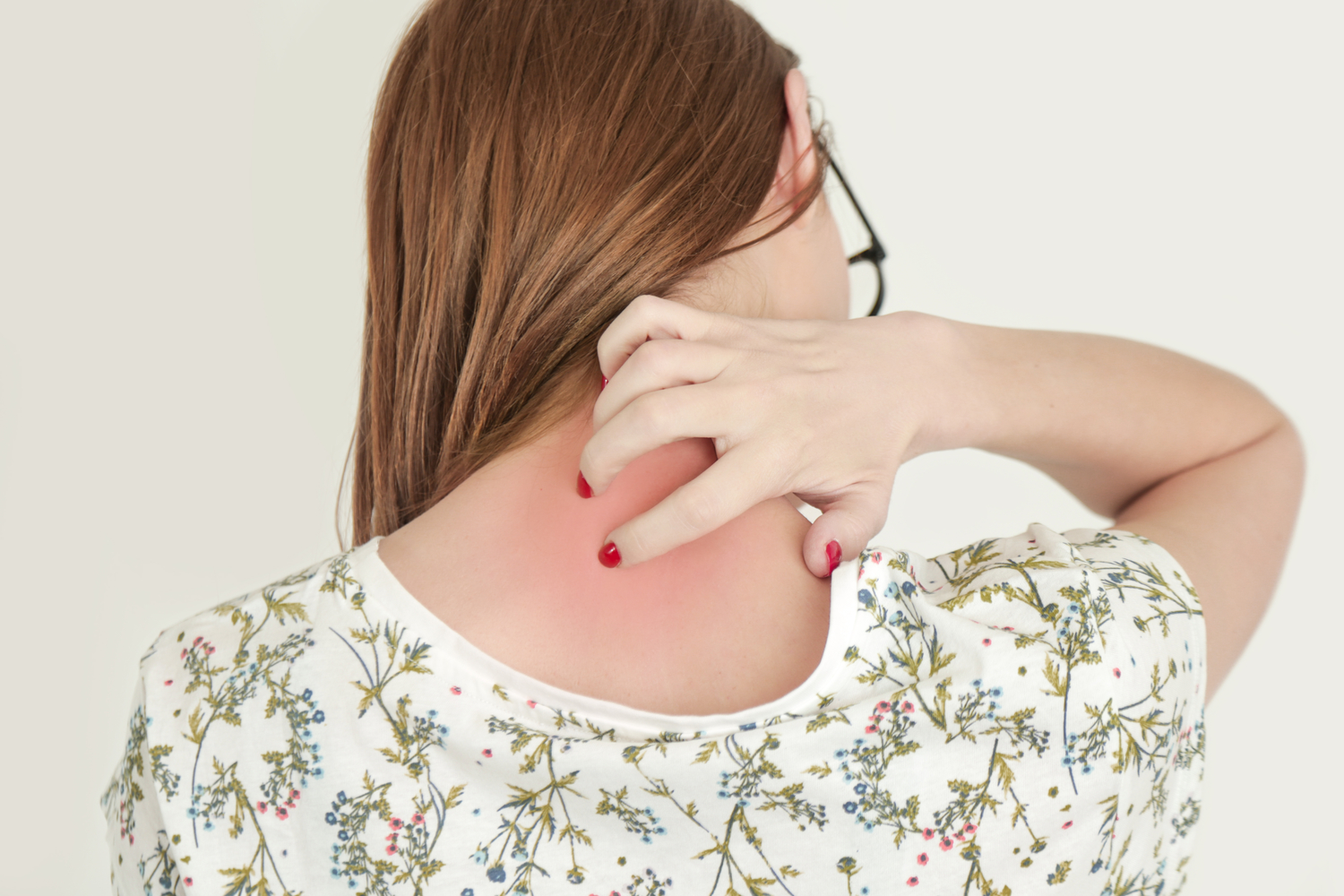
Refrain from scratching or touching the affected skin.
Practice frequent handwashing to limit virus spread.
Natural Relief Methods for Shingles
Cleanse blisters gently daily to prevent infection spread; cool baths can soothe discomfort.
Apply cool, moist compresses to ease pain and itching.
Use paste of cornstarch or baking soda for natural itch relief.
Lotions and soothing creams provide comfort but don’t speed healing.
Diet Strategies to Alleviate Shingles Discomfort
Consume nutrient-rich foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, eggs, chicken, fish, dairy, whole grains, legumes, tomatoes, and spinach to support immunity.
Avoid foods high in sugar, gelatin, nuts (arginine-rich), refined carbs, and saturated fats.
Medications to Ease Shingles Symptoms
Antivirals: Medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are most effective if taken within three days of symptoms appearing, reducing severity and pain.
Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen, naproxen, and ibuprofen can help manage pain. For severe cases, doctors might prescribe topical steroids, lidocaine patches, antibiotics, or antidepressants like amitriptyline.
Complementary Approaches: Natural remedies such as melatonin, oregano oil, echinacea, lemon balm, green tea, and omega-3s may support symptom relief alongside conventional treatments.
Shingles Vaccination Safety Tips
Individuals allergic to vaccine components should avoid vaccination.
Those with weakened immune systems, pregnant, or breastfeeding women should seek medical advice before vaccination.
People without chickenpox immunity should undergo testing or consultation prior to vaccination.