Mycosis Fungoides: Recognizing Symptoms and Early Detection
This article offers insights into mycosis fungoides, a rare skin cancer marked by persistent rashes. It emphasizes symptoms, stages, and the importance of early diagnosis for effective treatment. Being vigilant about skin changes and seeking prompt medical advice can greatly improve outcomes and prevent disease progression.
Mycosis Fungoides: Recognizing Symptoms and Early Detection
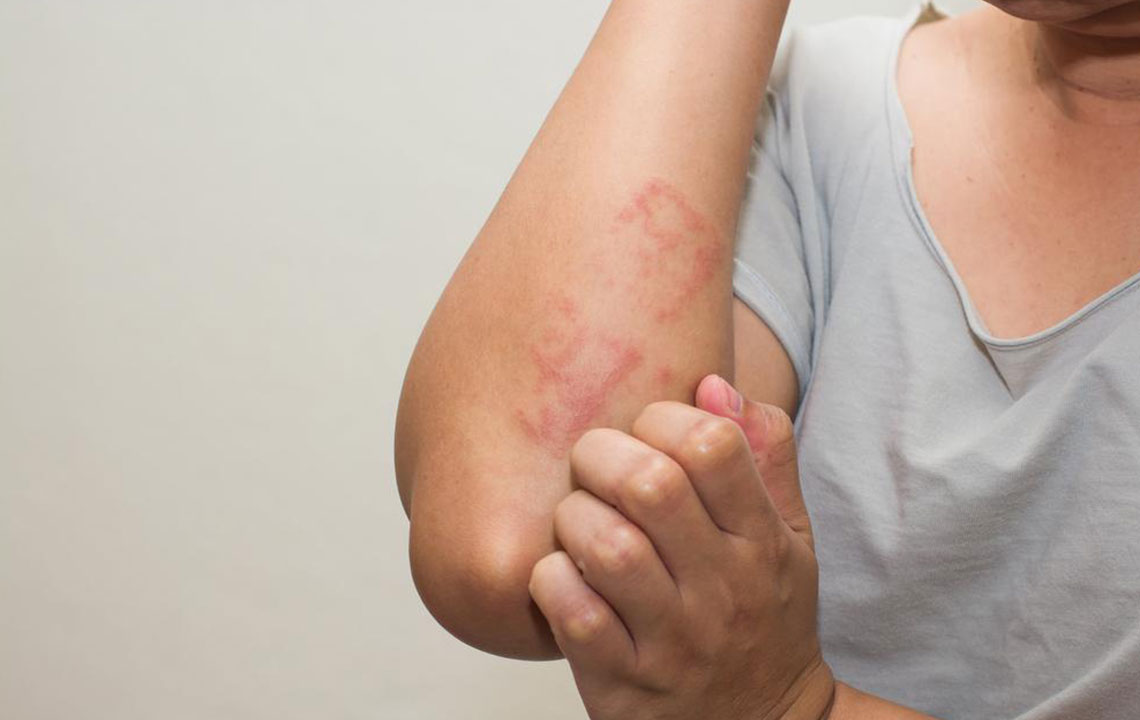
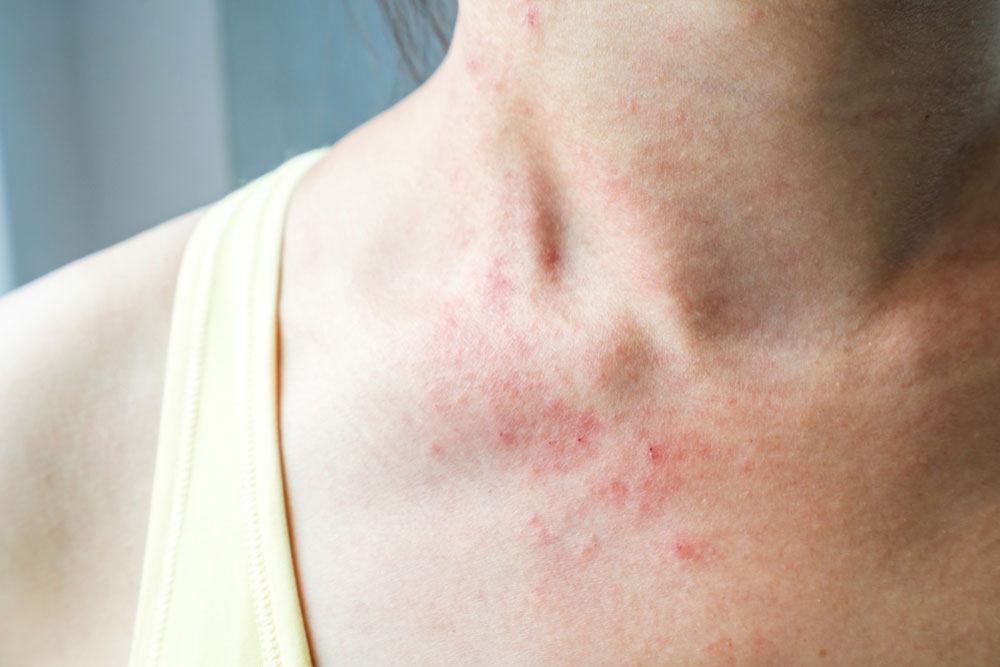
Some skin rashes signal serious health conditions like mycosis fungoides, a rare form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. This blood cancer involves abnormal white blood cells migrating into the skin, causing persistent itchy patches. Often seen in individuals in their 50s and 60s, especially men, its exact cause remains unclear—potentially linked to viruses or chemical exposure. The disease progresses through four stages, from red patches to tumors, and early diagnosis is crucial. Persistent skin changes should always warrant medical evaluation to improve treatment success.
Symptoms to Watch For
The condition typically evolves through red, scaly patches, thickened areas, raised bumps, and finally tumors that may ulcerate. Recognizing these signs early can lead to timely treatment and prevent spread beyond the skin. While primarily skin-related, advanced cases may involve other organs. Consulting a healthcare professional for ongoing skin issues is vital for early intervention.
Medical experts suggest that viral agents or chemical exposures may trigger abnormal T-cell growth in mycosis fungoides. Although rare, early detection significantly improves treatment options. Monitoring persistent skin changes and seeking prompt medical care can lead to better management of this condition. Advances in therapy allow many patients to achieve effective control if diagnosed early enough.