Comprehensive Guide to Ringworm: Causes, Transmission, and Prevention Strategies
Learn about ringworm, a common fungal skin infection, including its causes, transmission routes, symptoms, and effective prevention tactics. Proper hygiene and timely treatment are key to managing and avoiding this contagious condition.
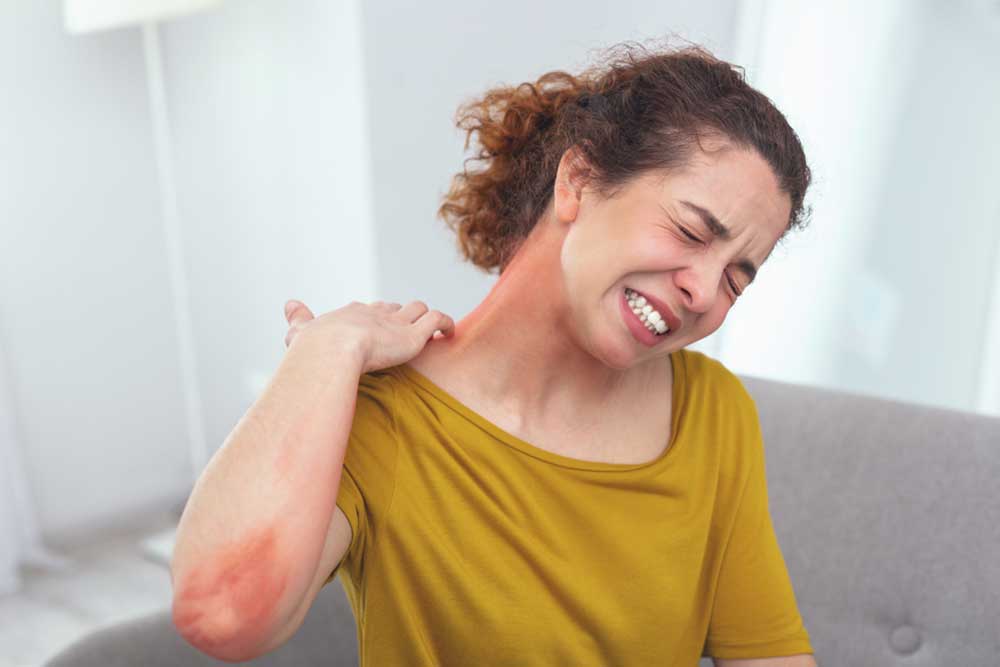
Ringworm is a widespread fungal infection affecting the skin, presenting as distinct circular rashes that can appear anywhere on the body. It spreads easily through contact with contaminated items like clothing, bedding, and surfaces, as well as through contact with infected animals. While children are more prone, anyone can contract this infection. The causative fungi feed on dead skin cells, hair, and nails. Transmission occurs via direct skin contact, touching contaminated objects, or interacting with infected animals or soil. Contributing factors include poor hygiene, tight clothing, compromised immunity, and participation in contact sports. Symptoms include itchy, red, ring-shaped patches that grow outward over time. Diagnosis involves skin examinations and lab tests. Treatment options range from over-the-counter antifungal creams to prescription oral medications, especially for scalp infections. Prevention involves maintaining proper hygiene, not sharing personal items, keeping skin dry, and wearing protective footwear in public areas. It’s important to seek medical advice before using steroid creams, as improper use can worsen the condition. Good hygiene practices and awareness are essential for reducing the risk of infection.