Comprehensive Guide to Effective Diabetes Management
This article provides vital information on diabetes types, diagnosis methods, and prevention tips. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise in managing and preventing the disease. Understanding these aspects helps individuals take proactive steps toward better health and diabetes control.
Comprehensive Guide to Effective Diabetes Management
The pancreas is vital in regulating blood sugar by producing insulin, which transports glucose into cells for energy. Insufficient insulin production causes elevated blood sugar levels, resulting in diabetes—a condition that can damage organs over time.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of this disease.
Type 1 Diabetes
Typically identified in children and teenagers but can occur at any age. It involves little to no insulin production and requires daily insulin injections to maintain blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
Comprising approximately 90% of diabetes cases, it mostly affects adults. It happens when the body stops responding properly to insulin, but lifestyle modifications can often control it. Advanced cases may need medication.
Gestational Diabetes
Diagnosis Methods
Multiple tests confirm type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
A1C Test
Measures average blood sugar over three months; levels over 6.5% suggest diabetes.
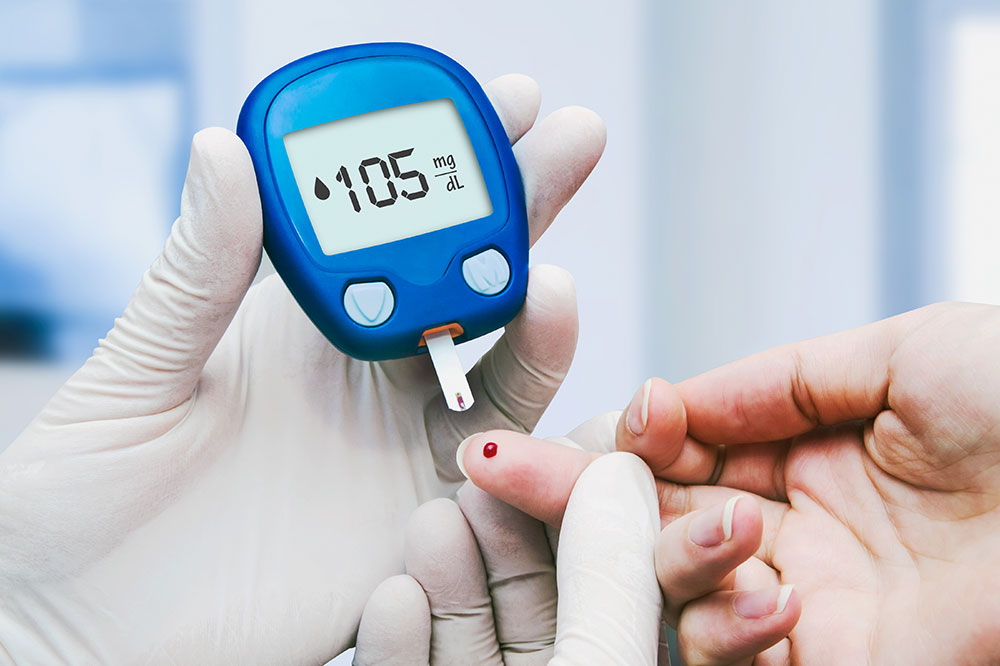
Random Blood Sugar Test
Checks blood sugar at any time for high levels.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Assesses body’s response to sugar after fasting and drinking a sugary solution.
Gestational diabetes involves specific screening like glucose tolerance tests.
Prevention Strategies
Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented via lifestyle changes. Key steps include reducing refined carbohydrate and sugar intake, maintaining regular physical activity, staying well-hydrated, and reaching a healthy weight. Quitting smoking and limiting processed foods further reduces risk. These habits enable proactive health management.
Effective control of type 2 diabetes largely depends on healthy lifestyle choices. Adopting better routines can significantly improve outcomes.