Hernia Essentials: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Learn about hernias, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understand how lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures can effectively manage hernia conditions. Early detection is key to preventing serious complications.
Hernia Essentials: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
A hernia happens when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weakness in the surrounding muscles or connective tissue, commonly in the abdomen or groin area. This often results in a visible bump accompanied by discomfort or pain. Types include inguinal, hiatal, umbilical, and incisional hernias. Although usually not life-threatening, hernias do not resolve on their own and may require surgery to prevent complications. Several effective treatments are available to manage hernias promptly and effectively.
Causes of Hernias
Weakness in the abdominal muscles combined with strain can lead to hernia formation. Contributing factors include genetic predisposition, chronic coughing, heavy lifting, aging, previous abdominal surgeries, pregnancy, increased internal pressure due to conditions like constipation or chronic cough, and sudden weight gain.
Recognizing Symptoms
The earliest sign is often a visible lump or bulge that becomes more noticeable with exertion, coughing, or standing. In infants, crying can reveal the hernia. Other symptoms include dull or sharp pain in the lower abdomen that worsens with movement, a sense of heaviness or pressure, burning sensations at the bulge site, acid reflux, or swallowing difficulties. Sometimes, hernias are asymptomatic and discovered during medical exams.
Diagnosis involves physical examinations to detect bulges, especially when standing or coughing. Imaging tests like endoscopy or X-rays identify hiatal hernias, while ultrasounds are useful in detecting umbilical hernias in infants. Treatment varies based on the hernia's size and severity, ranging from observation and lifestyle changes to surgical intervention.
Managing Symptoms with Lifestyle Changes
While hernias typically require surgical repair for complete cure, symptom relief can be achieved through diet and activity modifications. Avoid large meals, prevent bending or lying down right after eating, and maintain a healthy weight. Gentle abdominal exercises can strengthen muscles but should be performed under medical guidance. Avoid trigger foods such as spicy dishes and tomatoes to reduce acid reflux discomfort.
Medications for Hernia Relief
Medications like proton pump inhibitors, H-2 blockers, and antacids help reduce stomach acid, alleviating associated symptoms such as heartburn and indigestion.
Surgical Treatments
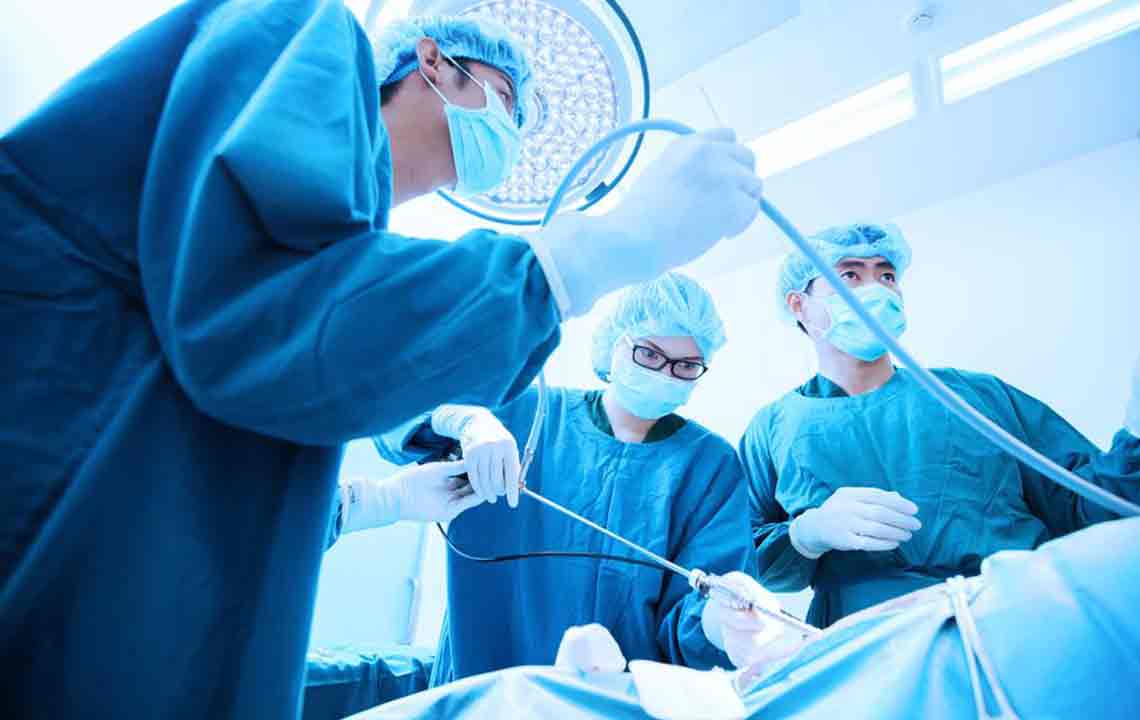
Hernias that grow rapidly or cause pain often require surgery. The procedure involves closing the hernia opening, usually with surgical mesh. Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery uses small incisions and a camera, while open surgery involves a larger cut with a longer recovery period. Surgery is crucial to prevent serious complications like tissue strangulation or damage.
Quick recognition and treatment of hernia symptoms are vital, as neglect can lead to life-threatening issues. Early medical intervention ensures effective management and reduces health risks.