Kidney Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Approaches
This article explores kidney failure, its key causes like diabetes and hypertension, early symptoms such as swelling and fatigue, and treatment options including dialysis and transplants. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle adjustments like diet and exercise, and highlights the need for timely medical intervention to improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by kidney issues.
Kidney Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Approaches
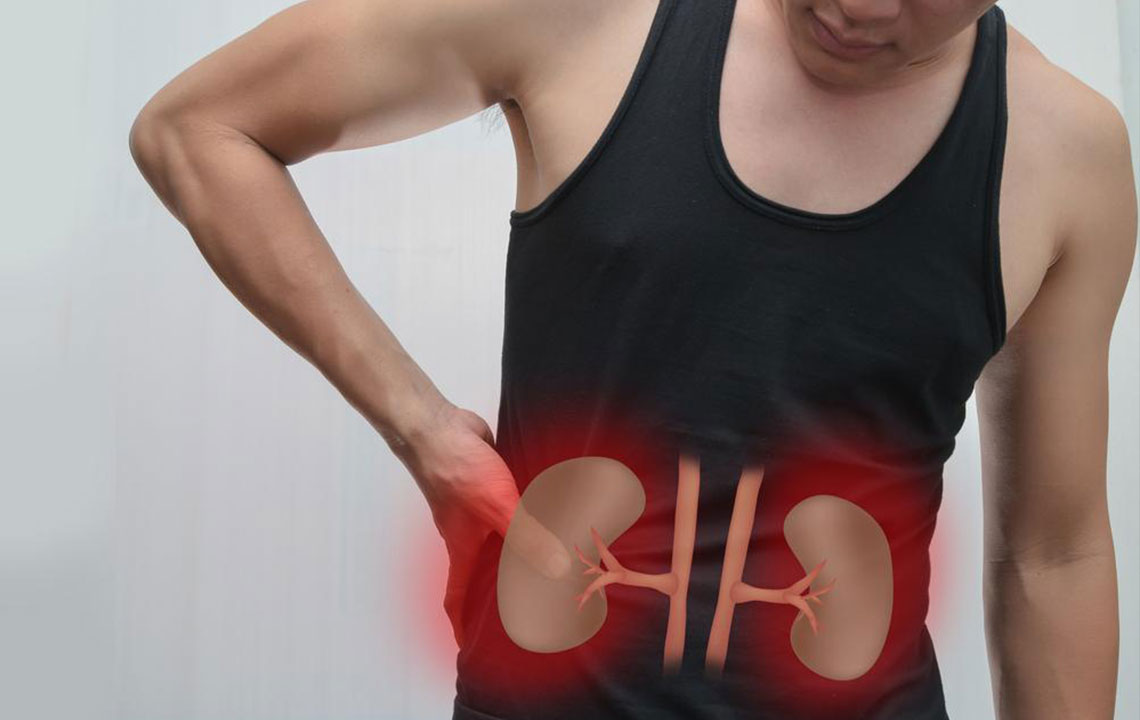
The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood. About one in seven adults face kidney health problems, which may develop into complete renal failure if not addressed. Early detection of urinary issues and understanding their causes are vital for effective treatment. Modern medical treatments offer promising options to prevent serious kidney damage. Recognizing early signs and knowing the root causes can lead to timely intervention, enhancing health outcomes and life quality.
Major Causes of Kidney Failure
1. Diabetes Mellitus
Chronic high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their filtering capacity. Without proper management, this can result in failure.
2. Hypertension
Long-standing high blood pressure causes narrowing of renal blood vessels, reducing blood flow and damaging kidney tissue, potentially culminating in failure.
3. Polycystic Kidney Disease
An inherited condition involving cyst formation, leading to enlarged kidneys and deteriorating function over time.
4. Autoimmune Disorders like Lupus
The immune system may mistakenly attack kidney tissues, leading to inflammation and damage.
5. Glomerular Diseases
Damage to tiny filtering units inside the kidneys hampers waste removal, increasing failure risk.
Signs and Symptoms
1. Decreased Urine Production
A significant drop in urine volume signals possible kidney issues, requiring medical attention.
2. Swelling in Legs and Feet
Fluid buildup due to impaired waste removal causes edema in lower limbs.
3. Fatigue and Weakness
Toxin accumulation in the blood leads to exhaustion, difficulty concentrating, and overall weakness.
4. Dry, Itchy Skin
Imbalances in minerals from kidney malfunction often cause skin irritation.
5. Blood in Urine
Leaking blood due to damaged filters indicates advanced renal problems.
6. Puffy Eyes
Loss of proteins causes facial swelling around the eyes.
7. Increased Urination
Kidney damage can elevate urination frequency, while infections may produce similar symptoms. Seeking medical advice is recommended.
Treatment Options
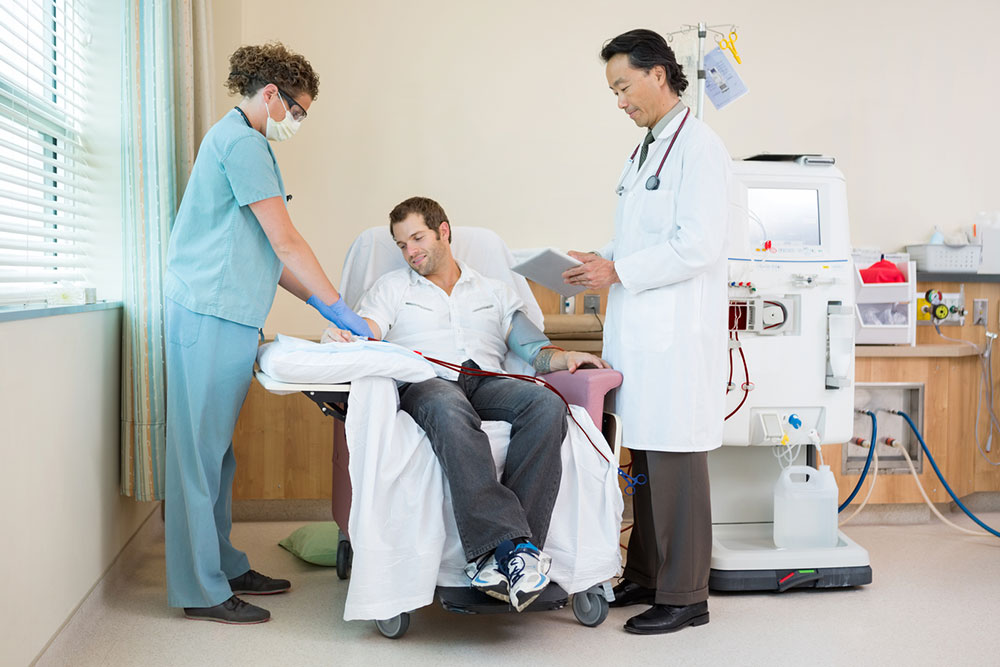
1. Dialysis
An artificial method to eliminate excess fluids and toxins. Types include peritoneal dialysis, which uses the abdominal cavity, and hemodialysis, which filters blood externally. Patients typically require multiple sessions weekly.
2. Kidney Transplantation
Replacing diseased kidneys with healthy donor organs provides a long-lasting treatment, with medication to prevent rejection necessary.
Lifestyle Modifications
1. Reduce Salt Intake
Limiting salt helps control blood pressure and decrease fluid retention.
2. Adopt Heart-Healthy Eating Habits
Focus on consuming greens, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to support kidney and heart health.
3. Maintain Adequate Hydration
Drinking sufficient fluids helps overall kidney function; include nutritious options like broth and fresh juices.
4. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity can regulate blood pressure and cholesterol, safeguarding renal health. Walking and jogging are ideal choices.
5. Seek Medical Guidance and Support
Managing kidney disease involves lifestyle changes and professional support from healthcare providers, family, and friends. Being aware of the seriousness is essential.