Restorative Surgical Options for Eyelid Drooping
Discover effective surgical options to address drooping eyelids, including external, sling, and internal techniques. Learn about costs, recovery tips, and how these procedures can restore vision and appearance, offering reliable solutions for eyelid ptosis. Suitable for various muscle strengths and severity levels, these treatments improve both function and aesthetics, ensuring a significant enhancement in quality of life for patients suffering from eyelid drooping.
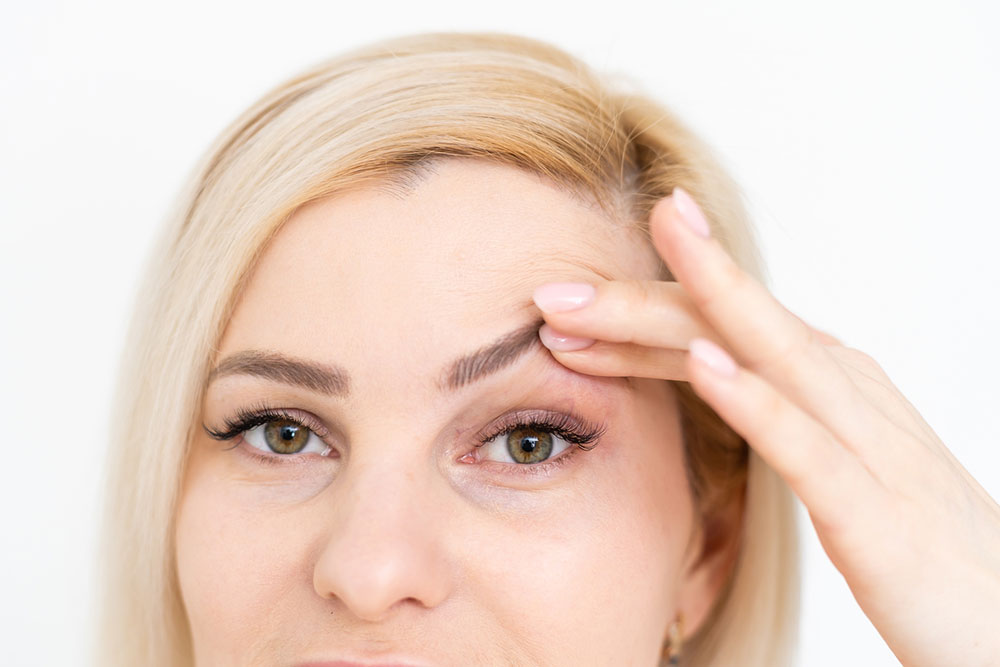

Effective Approaches to Correct Sagging Eyelids
Ptosis, or eyelid drooping, can be present from birth or develop later due to muscle weakening. Approximately 11.5% of adults experience this condition, yet many are unaware of available corrective procedures. Surgeries currently provide reliable solutions, especially for adults, restoring vision and enhancing appearance. Here's what you should know about droopy eyelids and how surgical options can help:
What Causes Drooping Eyelids
This condition results when eyelid muscles, mainly the levator muscles, weaken or malfunction, causing eyelids to sag over the eyes. It can involve one or both eyes, with severity varying. When acquired over time, muscle weakening leads to drooping.
Several surgical techniques are available to correct eyelid drooping, each suited for different muscle strengths and severity levels. The main procedures include:
External Method
Ideal for patients with strong levator muscles.
Steps involved include:
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia helps keep the patient relaxed and pain-free.
Incision: A cut is made along the natural eyelid crease.
Muscle Positioning: The levator muscle is sutured to the eyelid’s connective tissue, lifting the eyelid for better vision.
The surgeon may check eyelid positioning during the operation. The scar usually remains hidden within the eyelid fold.Frontalis Sling Technique
Used when levator muscles are too weak or other methods are unsuitable.
Anesthesia: Typically performed under general anesthesia for comfort.
Procedure: The eyelid connects to the frontalis muscle above the eyebrow, often through a silicone rod, allowing forehead muscles to assist in lifting the eyelid.
Patients may temporarily have difficulty closing their eyes fully; this usually resolves within 2-3 months. Using lubricating drops or ointments helps prevent dryness during recovery.Internal (Transconjunctival) Technique
Suitable for those with sufficient muscle strength, involving shortening eyelid muscles from within.
Anesthesia: Can be local or general.
Procedure: The surgeon flips the eyelid inward and shortens muscles like Muller’s or levator to lift the eyelid.
Cost Details
Prices typically range from $3,000 to $6,000 per eyelid, depending on the surgical method and the extent of correction. Treating both eyelids can cost $6,000 to over $12,000. Although substantial, most find the results worth the investment, making proper planning essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
Post-Operative Care & Tips
Swelling and bruising are common initially.
Keep eyes away from soaps, shampoos, and irritants immediately after surgery.
Avoid rubbing eyes and limit screen time to aid healing.