Monitoring Heart Rate: Recognize Warning Signs and Stay Healthy
Learn essential insights into heart rate management, recognizing abnormal rhythms, and tips to maintain cardiovascular health. This guide helps identify when to seek medical help based on heart rate patterns, offering practical advice for a healthy heart. Understanding these signs can prevent serious health issues and promote long-term well-being.

Monitoring Heart Rate: Recognize Warning Signs and Stay Healthy
How to Monitor Your Heart Rate and When to Seek Medical Help
Maintaining a stable heart rate is crucial for overall wellness, similar to how a vehicle requires smooth operation. An ideal rhythm reflects good health, but factors such as stress and lifestyle can impact it. Paying attention to early signs like irregular beats can prevent serious issues. Detecting abnormal heart rates early can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved quality of life.
The heart's proper function is essential for circulating blood effectively, ensuring oxygen and nutrients reach all tissues. Disruptions can hinder daily functioning and health. Let's delve into what constitutes a normal heart rate, variations, and indicators needing medical attention.
What is considered a normal resting heart rate?
Typically, a resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 BPM. Values below 60 BPM are called bradycardia, while above 100 BPM is labeled tachycardia.
Many health experts find that a resting rate between 50 and 70 BPM is optimal.
Age and physical activity influence individual normal ranges for heart rate.
A heart rate less than 60 BPM suggests bradycardia.
Active, healthy people may have slower heart rates due to fitness, medications, or sleep patterns.
Slow heart rates might also indicate underlying conditions like heart problems, infections, electrolyte imbalances, or thyroid disorders.
A rate over 100 BPM indicates tachycardia.
Factors such as exercise, stress, caffeine, or drug use can cause rapid heartbeats.
Persistent high heart rate may be linked to anemia, lung issues, hormonal changes, or cardiac diseases.
How to estimate your safe maximum exercise heart rate?
Use age-based formulas; for example, subtract age from 220. For age 40, that results in 180 BPM. Then, multiply by 0.7 and 0.8 to get a target range: 126 to 144 BPM.
Exceeding this range indicates a vigorous workout.
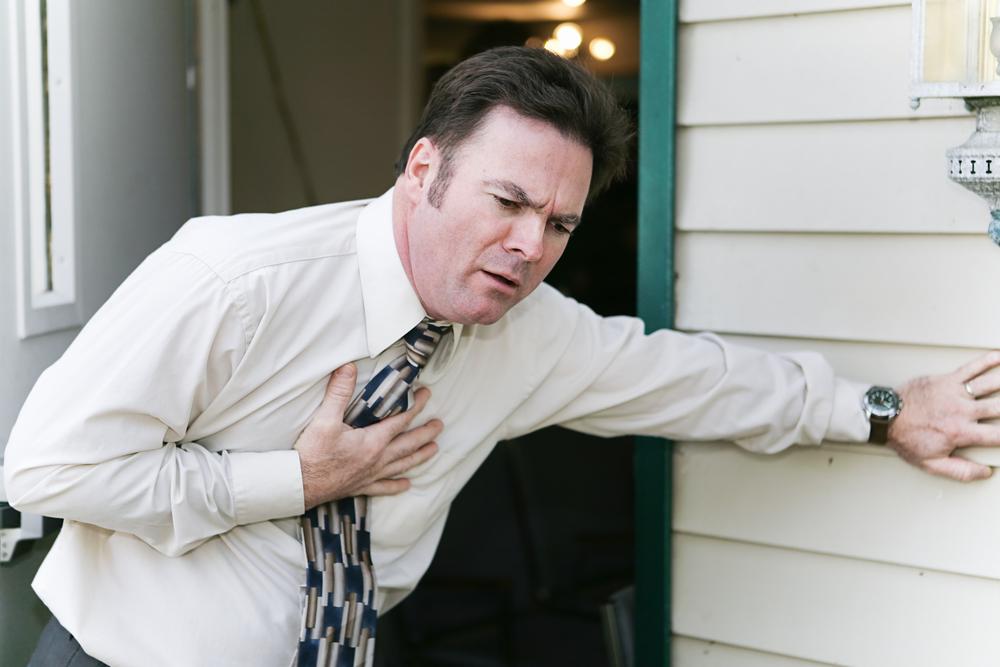
Warning signs including irregular heart rhythms and symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations warrant consultation with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Tips for maintaining heart health include eating nutritious foods, avoiding smoking and excess alcohol, managing cholesterol and calorie intake, and regular exercise like walking, swimming, or sports activities.