Effective Strategies for Managing and Treating Knee Pain
This guide explores common causes of knee pain like ligament injuries, cartilage tears, and arthritis. It emphasizes early diagnosis and treatments, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery, to restore mobility. Recognizing symptoms promptly can prevent progression and improve quality of life.

Knee discomfort affects many individuals at some point, often caused by sports, exercise, or everyday activities. Common issues include tendinitis, muscle strains, and damage to cartilage or ligaments. While mild pain can hinder daily activity, severe discomfort may limit mobility. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing further issues and restoring function.
Common Causes of Knee Discomfort
Ligament Damage
Ligaments connect the thigh to the lower leg, ensuring stability. Injuries such as ACL, PCL, or MCL tears, frequently seen in athletes, can cause intense pain and may require surgical repair.
Cartilage Damage
Damage to the knee’s cartilage, especially the menisci, can occur during trauma. Such injuries often cause significant pain and may need surgical treatment to repair or remove damaged tissue.
Knee Arthritis
Arthritis causes persistent pain and may lead to joint stiffness or disability. Types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. Symptoms often involve swelling, limited movement, and stiffness.
Autoimmune and Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, inflames joint tissues and can damage cartilage. Post-traumatic arthritis develops after injuries like ligament tears or fractures, resulting in joint degeneration over time.
Osteoarthritis
The most common form, resulting from cartilage wear and tear due to aging, injuries, or genetics. It presents with pain, swelling, and reduced mobility, especially in individuals over 50.
Severe Injuries: Dislocation and Fractures
Dislocating the knee is a medical emergency that can disrupt blood flow. Fractures from direct impacts require urgent treatment due to extreme pain and potential complications.
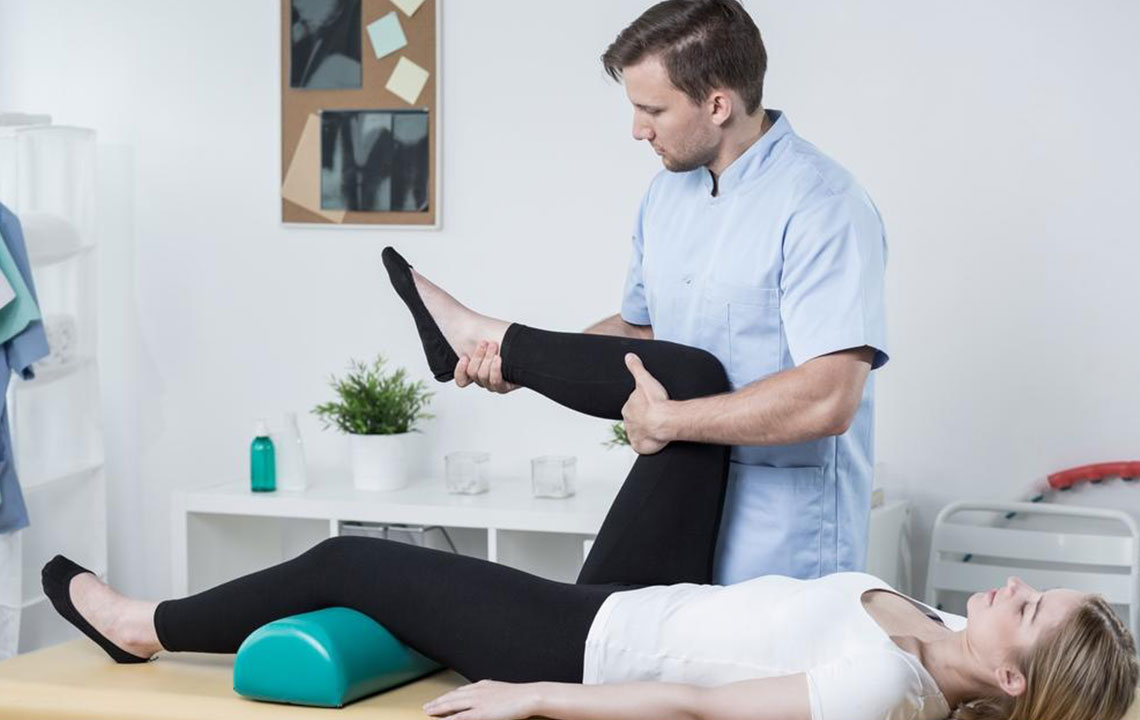
Diagnosing Knee Problems
Medical evaluation involves physical exams, X-rays, and specialized tests to identify the cause of pain, assess joint function, and detect conditions like arthritis or trauma.
Managing Kneeg Pain from Arthritis
Treatment includes exercises to strengthen muscles, weight loss, pain medications like NSAIDs, and supportive devices. Severe cases may benefit from surgical options such as partial or total knee replacement. Consulting a specialist ensures optimal care.