Understanding Common Bacterial Skin Infections and Their Management
This article provides an overview of common bacterial skin infections such as folliculitis, cellulitis, impetigo, and boils. It discusses their causes, symptoms, and effective prevention and treatment strategies. Emphasizing the importance of hygiene and timely medical intervention, the content aims to educate readers on managing skin infections to avoid serious health issues.
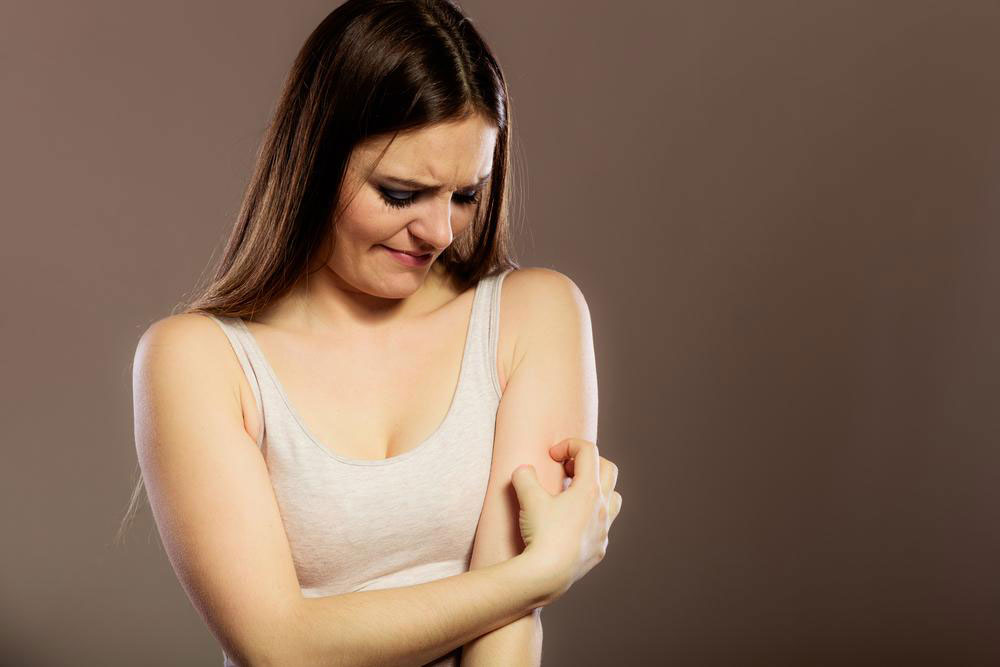

Understanding Common Bacterial Skin Infections and Their Management
Infections caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are leading contributors to skin ailments. Key bacterial skin infections include:
Folliculitis: An infection of hair follicles causing red, inflamed bumps similar to acne, often linked to contaminated pools or hot tubs.
Cellulitis: Usually affecting the legs, this infection causes redness, swelling, and tenderness in the skin, which can develop anywhere on the body.
Impetigo: A highly contagious condition with two forms—larger blisters (bullous) and crusted yellow sores (non-bullous), commonly affecting young children with oozing lesions.
Boils are bacterial infections originating from hair follicles that extend into deeper layers, appearing as tender, red lumps that enlarge and fill with pus. Skin injuries, such as cuts or sunburns, increase the risk of infection. Good hygiene, proper wound cleaning, and covering injuries with sterile dressings are key preventive steps. Mild infections may resolve with minimal intervention, but severe cases need medical treatment, including drainage and antibiotics. Prompt care and wound management are essential to avoid complications.