Recognizing and Understanding Narcissistic Personality Disorder
This article provides an in-depth overview of Narcissistic Personality Disorder, covering its key traits, symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understanding this disorder helps in recognizing warning signs and seeking appropriate help. The content emphasizes the importance of early intervention and professional diagnosis to manage the condition effectively.

Recognizing and Understanding Narcissistic Personality Disorder
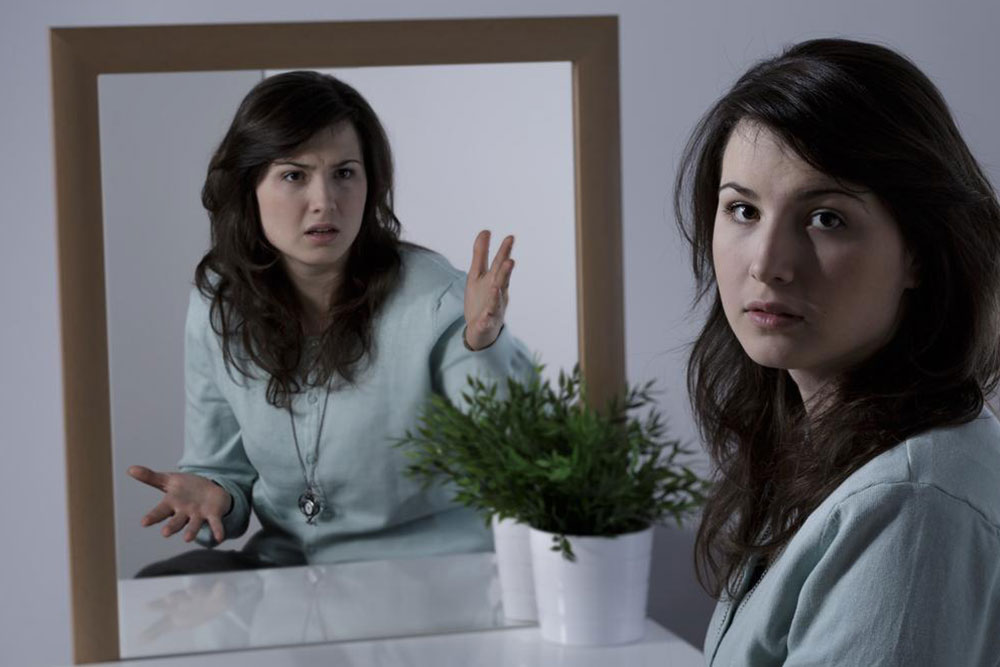
While some believe narcissism is transient, it often signifies a deeper psychological issue. Excessive self-love beyond healthy boundaries leads individuals to see themselves as extraordinary or above others. Approximately 6% of individuals experience this condition at some point, with men more frequently affected. If you notice narcissistic behaviors in someone, continue reading to explore the traits and signs of this personality disorder.
Overview
Narcissistic individuals typically lack empathy and struggle to understand others’ emotions, often feeling insecure beneath their inflated self-image. They crave attention and validation, which can annoy others or lead to criticism. These traits can cause difficulties in social interactions and emotional wellbeing for both the individual and those around them.
Identifying Traits
Common indicators of narcissistic tendencies include:
Overinflated view of personal importance and accomplishments.
Fixation on fantasies of power, celebrity, or attractiveness.
Belief in being special or unique.
Constant need for admiration.
Expecting exclusive privileges.
Using others for personal advantage.
Little empathy for others’ feelings.
Feelings of envy towards others.
Arrogant or condescending behavior.
Such behaviors often lead to feelings of frustration or depression, especially when others respond negatively. Narcissists may also be patronizing and quick to criticize minor flaws in those around them.
Diagnosis and Identification
Since no biological tests exist for this disorder, mental health professionals rely on behavioral assessments. Many individuals are unaware of their traits and might only seek help when their behaviors create significant social or emotional problems.
Origins and Causes
The exact causes remain uncertain, but factors like genetics, upbringing, social environment, and psychological influences play roles. Family dynamics, peer interactions, and environmental stresses may contribute, and the disorder can sometimes be inherited from parents with narcissistic traits.
Impact and Treatment Options
Narcissism exists on a spectrum from mild egocentricity to severe impairment. Mild cases might not disrupt daily routines, but more serious forms can cause workplace conflicts, relationship failures, or risky behaviors. Severe cases may necessitate intensive therapy or hospitalization. Early detection and intervention are vital; consulting a mental health professional is recommended if you notice narcissistic behaviors.