Proven Methods to Relieve Back Muscle Discomfort
Discover effective strategies for relieving back muscle discomfort. This guide covers medication options, physical therapy, and preventative measures to manage and prevent back pain, ensuring better musculoskeletal health and quality of life.

Proven Methods to Relieve Back Muscle Discomfort
Back muscle soreness, characterized by sudden, intense pain, impacts individuals of all ages. This common problem often stems from sedentary habits, such as prolonged sitting, or injuries from activities like heavy lifting. Various factors contribute to severe back muscle pain, making treatment complex. Several healthcare organizations suggest personalized therapies based on the cause and severity, which can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Choosing the right approach depends on individual needs. Options include:
Over-the-counter drugs: NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) offer quick relief but should be used cautiously under medical supervision.
Muscle relaxants: Prescribed for persistent pain, these may cause drowsiness, so use carefully.
Topical agents: Creams or gels applied directly can temporarily numb pain but do not treat underlying issues.
Opioids: Short-term use of medications such as hydrocodone may be necessary for severe pain, with caution due to addiction risks.
Antidepressants: Low-dose medications like amitriptyline can help manage chronic pain.
Injections: Cortisone shots reduce inflammation temporarily, especially for radiating pain.
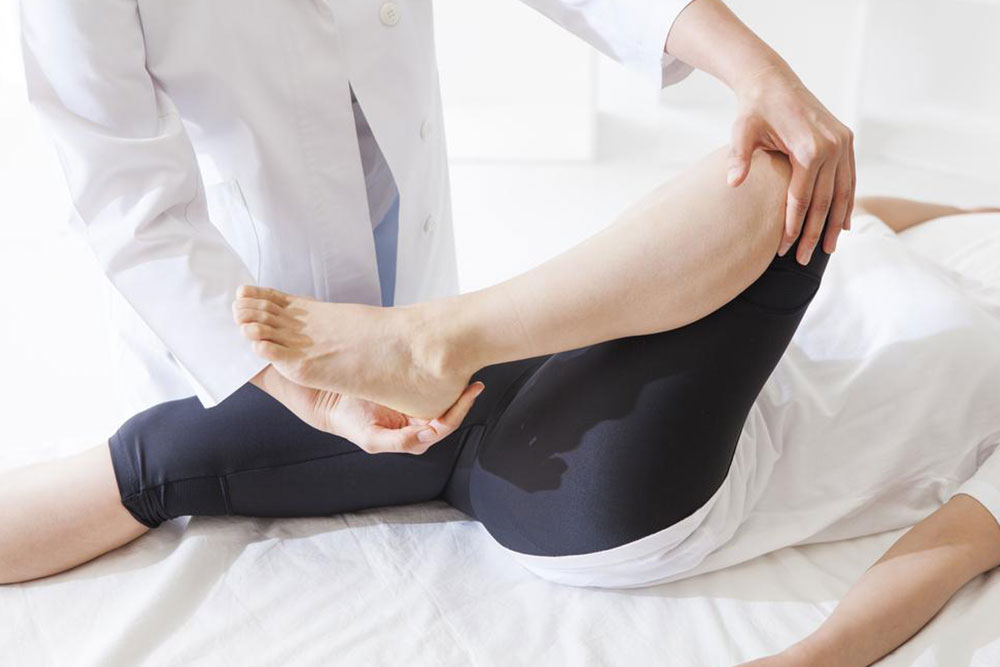
Physical therapy: Therapists can guide exercises and therapies like ultrasound and heat to prevent future episodes.
Surgical procedures: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be required if other treatments fail.
Maintaining an active lifestyle, proper ergonomics, and weight management are essential for prevention. Regular exercises like walking strengthen back muscles and reduce discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional for persistent issues to ensure safe and effective treatment.