Innovative Approaches to Shingles Management and Recovery with Proper Care and Nutrition
Discover effective strategies to manage and recover from shingles through early medical treatment, proper skin care, natural remedies, and a nutritious diet. These methods can help alleviate pain, promote healing, and support immune health for a smoother recovery process.

Innovative Approaches to Shingles Management and Recovery with Proper Care and Nutrition
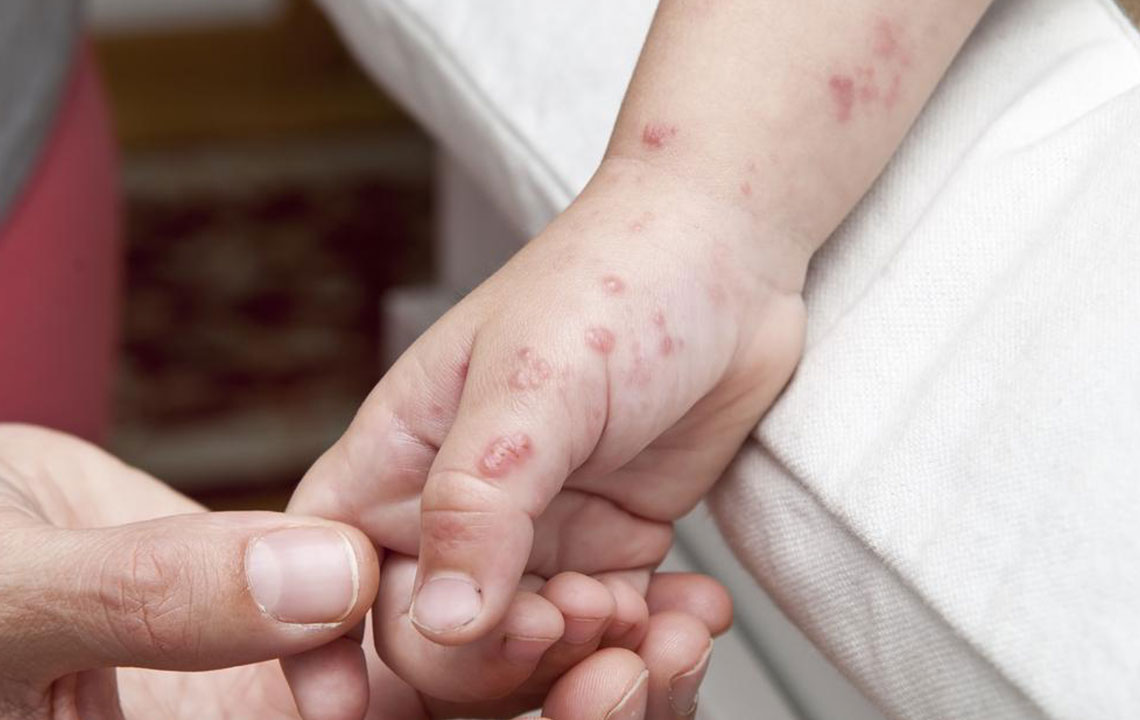
Timely medical intervention is crucial once shingles symptoms emerge to effectively control the virus. Starting antiviral medications early can speed up blister healing and reduce discomfort.
Avoid scratching or touching the affected area. Popping blisters may cause bacterial infections, scarring, and increase the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Daily Care Tips:
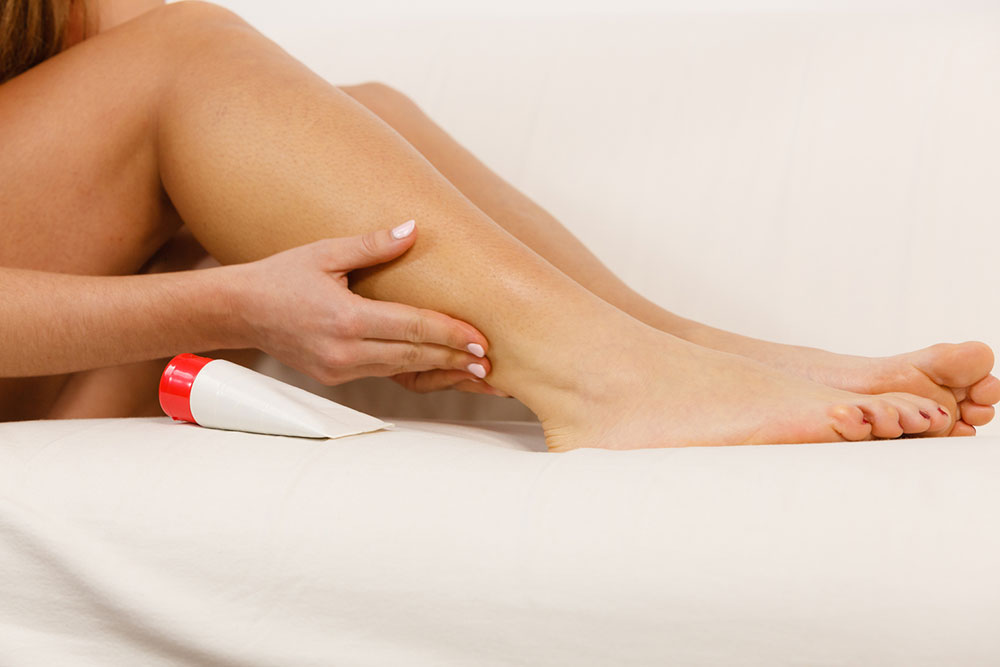
Gently cleanse the affected skin with mild soap and water, avoiding harsh chemicals and strong fragrances.
Use cold compresses several times daily to soothe pain and reduce itchiness, while keeping the skin moist.
Apply petroleum jelly and calamine lotion to maintain skin hydration.
Use a homemade cornstarch paste (two parts cornstarch to one part water) for 10-15 minutes daily to relieve itching.
Wear loose, breathable clothing to promote faster drying and comfort.
Alternative Healing Methods:
Applying manuka or clover honey may help alleviate pain and support healing.
Mixtures of raw honey, leek juice, and aloe vera can have soothing effects.
Essential oils like tea tree, lemongrass, peppermint, and geranium may reduce pain; always perform a patch test and dilute with a carrier oil before use. Diffusing these oils is also beneficial.
Acupuncture has shown potential in alleviating shingles-related pain.
Dietary Recommendations for Shingles Recovery:
Stay well-hydrated to aid healing and maintain health.
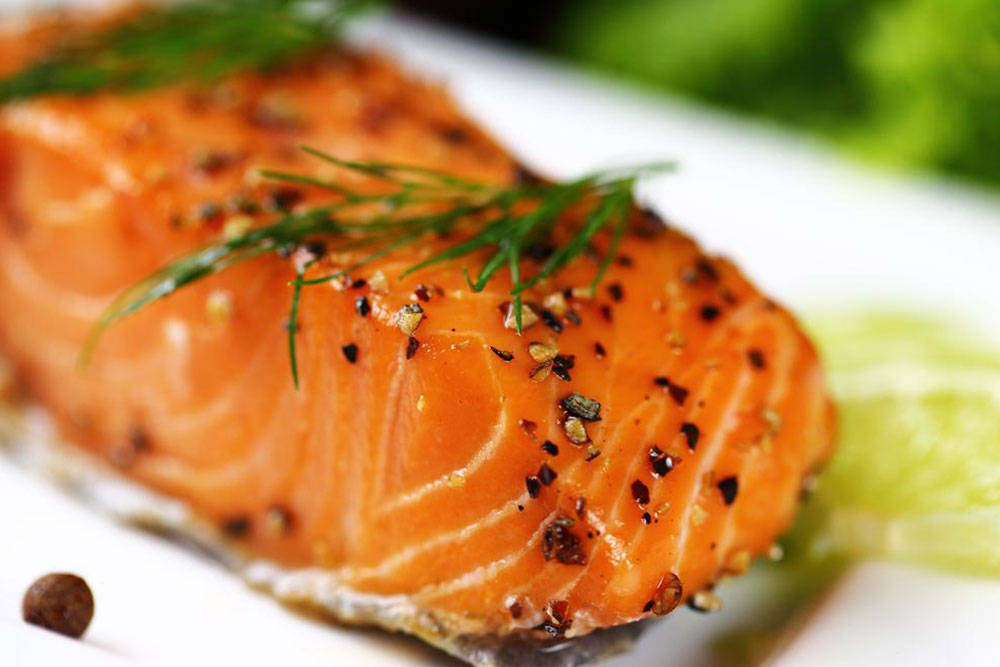
Enhance immune function with foods high in Vitamin B, such as low-fat dairy, eggs, organic poultry, and wild-caught fish.
Include raw garlic and onions in your meals.
Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables rich in Vitamin C.
Add leafy greens to your diet for added nutrients.
Note: These complementary approaches support recovery but consult your healthcare provider before making changes or combining therapies. Proper medical guidance remains essential.