Effective Strategies for Monitoring Your Blood Glucose Levels
Learn effective methods to monitor your blood glucose levels. This guide covers testing frequencies for different types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Stay informed on best practices to manage your condition, prevent complications, and optimize your treatment plan with modern testing devices and professional advice.
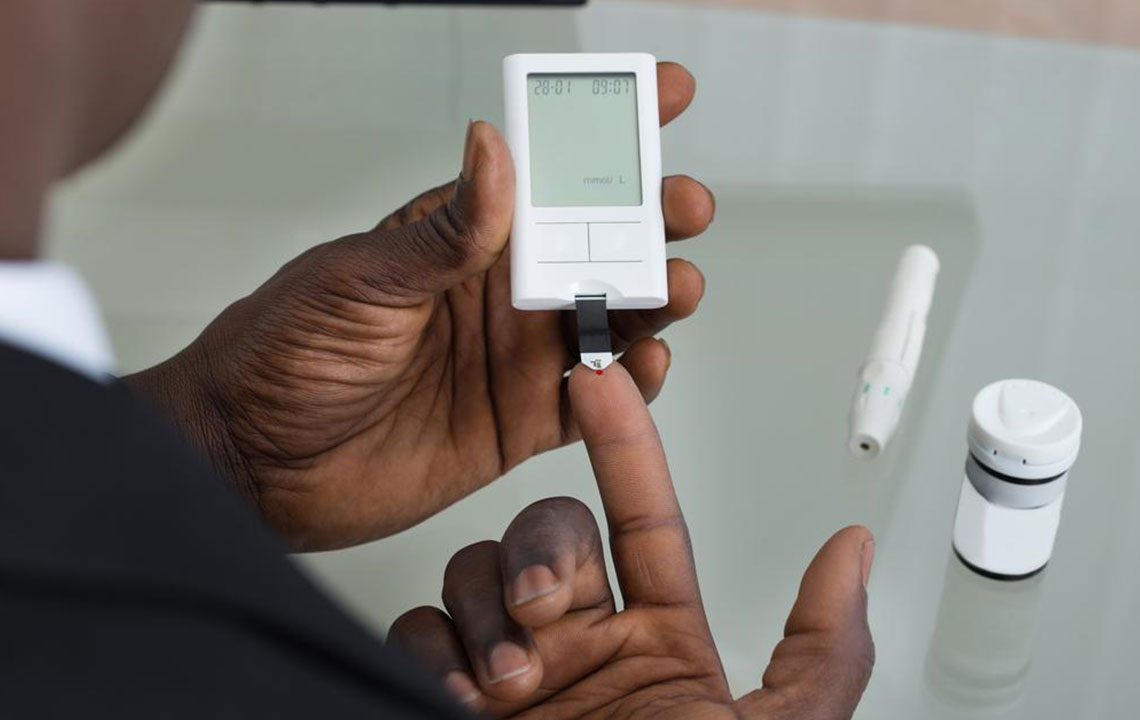
How Often Should You Check Your Blood Sugar?
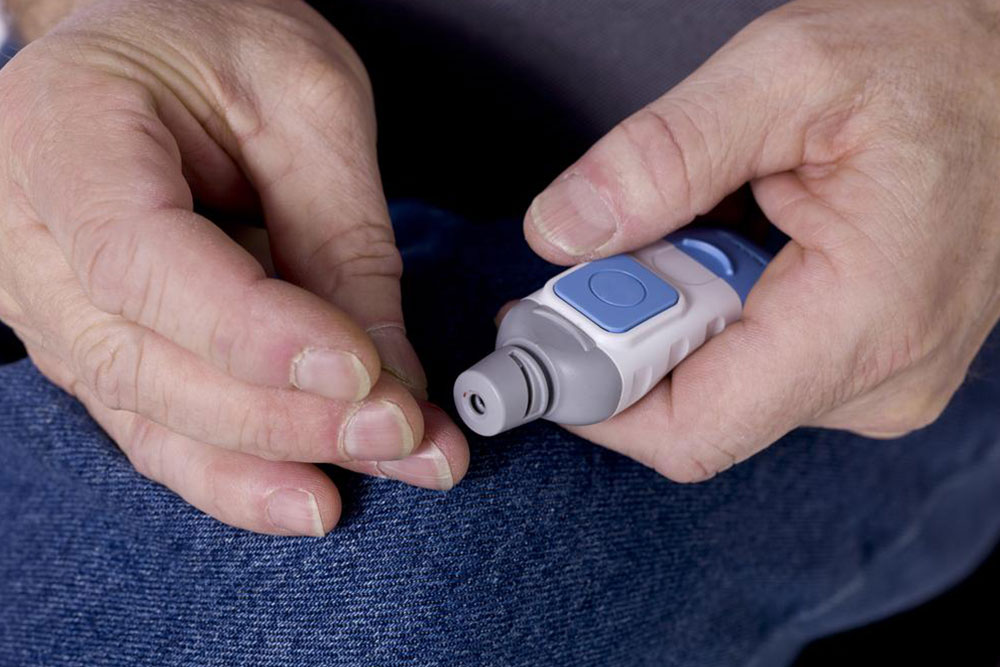
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for comprehensive diabetes care. With modern electronic devices, testing has become quick and simple. Consistent measurement helps control blood glucose, prevent complications, and tailor treatments. The testing frequency varies based on the type of diabetes and individual health factors. Following an appropriate testing routine allows patients to maintain blood sugar within target ranges and make necessary lifestyle or medication adjustments.
When is blood sugar testing necessary? The need for frequent checks depends on your diabetes type. Different conditions require personalized testing schedules to ensure optimal management.
People with type 1 diabetes often need to check their blood glucose five to seven times daily. Tests are typically done before and after meals, exercise, and daily activities, enabling better management through self-monitoring devices.
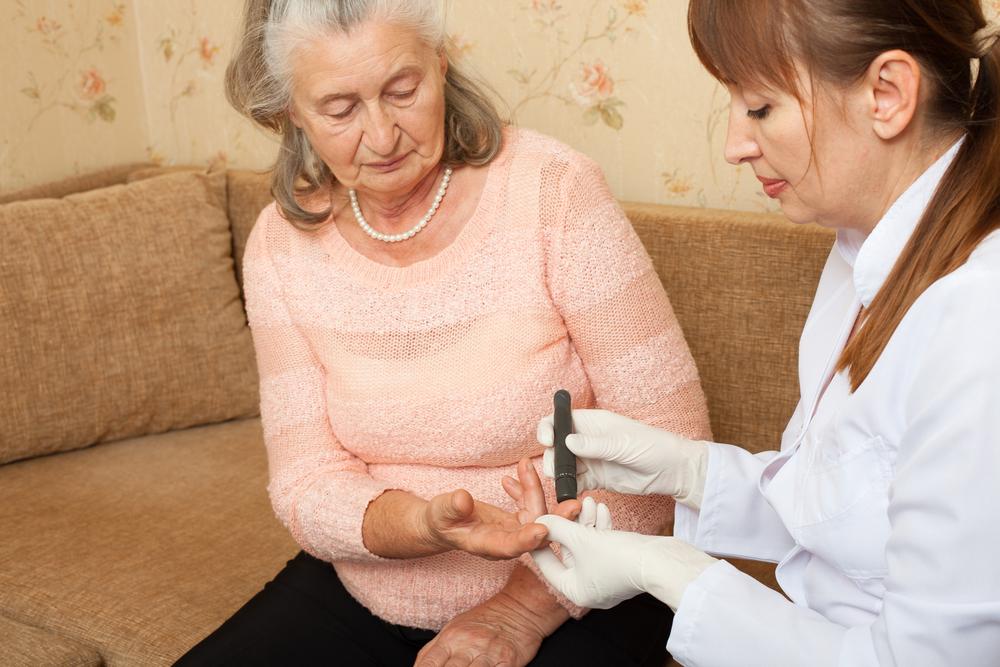
Those with insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes are usually advised to perform tests at least twice daily, such as before and after meals, based on their treatment plan and healthcare advice.
The frequency for type 2 diabetics can vary, especially depending on disease control and age. Patients not using insulin might test less frequently. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes follow specific testing routines, mainly checking blood sugar levels around meal times, with individual needs taken into account.
Important Reminder:
This content offers general insights into blood sugar monitoring, symptoms, and management. It is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Always seek advice from qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment decisions.