Understanding Pneumococcal Lung Infections: Prevention and Insights
This article explores pneumococcal lung infections, highlighting their causes, symptoms, high-risk groups, and prevention strategies. Vaccination, good nutrition, and early diagnosis are key in reducing disease impact. Ongoing research into vaccines and diagnostics aims to improve control measures, especially amid rising antibiotic resistance. Understanding these aspects helps protect vulnerable populations and promotes healthier communities.
Understanding Pneumococcal Lung Infections: Prevention and Insights
Overview of Pneumococcal Respiratory Illness
Pneumococcal diseases, including pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, are major health concerns, especially for children under five. These infections can target the lungs, bloodstream, middle ear, and nervous system. Vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk. Prevention strategies like vaccination, proper nutrition, and early detection are vital in decreasing disease incidence and saving lives.

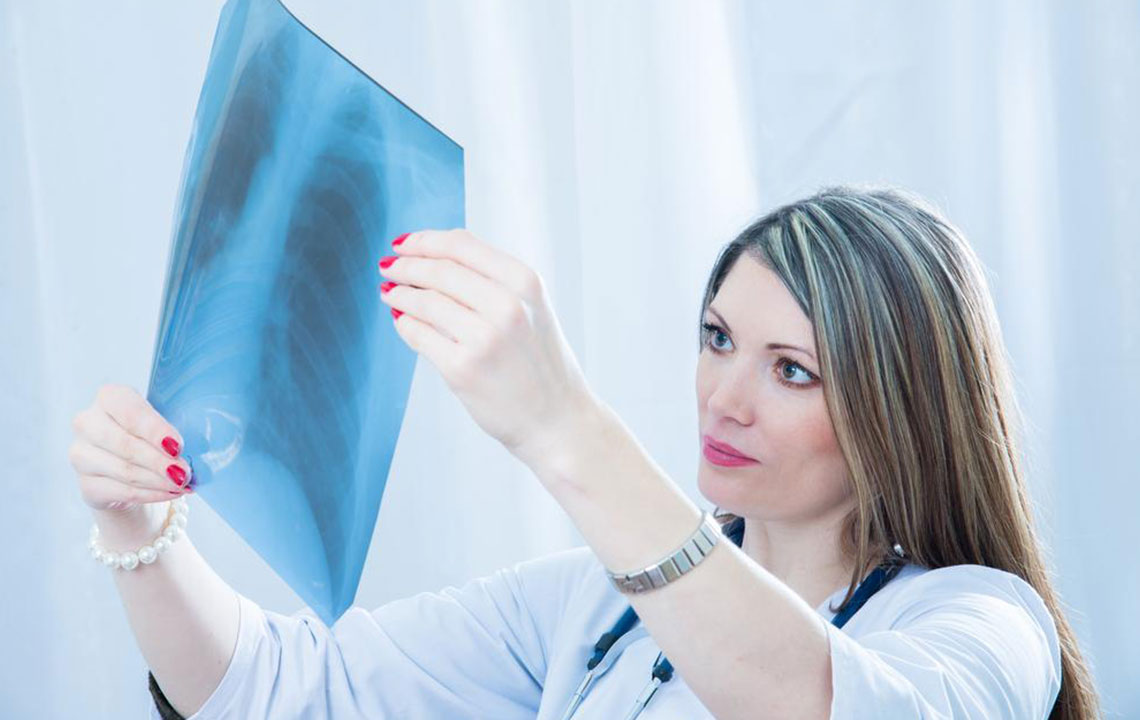
What is pneumococcal pneumonia?
Pneumococcal pneumonia is a bacterial lung infection caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. It affects the respiratory system and can spread to the bloodstream, ears, and nervous system. High-risk groups include young children, the elderly, and individuals with health issues like heart or lung diseases or weakened immunity. Symptoms present as fever, cough, chest discomfort, quick breathing, and exhaustion. Diagnosis involves clinical exams, blood tests, and chest scans.
Preventative measures involve:
Eating a balanced diet to strengthen defenses.
Breastfeeding infants during the first six months to enhance immune development.
Receiving pneumococcal vaccinations, especially for at-risk groups such as older adults and immunocompromised individuals.
Vaccination reduces the chances of infection substantially and decreases antibiotic dependence. Given rising antibiotic resistance, prevention remains crucial. Research continues into improved vaccines and diagnostic methods, with organizations like NIAID leading efforts to control pneumococcal diseases.
Note:
This article provides insights into pneumococcal infections based on current research. For medical concerns, always consult healthcare professionals. Our content aims to inform, not replace professional advice, and we are not responsible for external discrepancies or services.