Thyroid Autoimmune Disorder: Dietary and Lifestyle Approaches to Management
This article offers practical dietary and lifestyle tips for managing Graves' disease effectively. Emphasizing nutrition, stress management, exercise, avoiding toxins, and organic choices, it helps individuals support their thyroid health naturally alongside medical treatments.

Effective Strategies for Managing Graves' Disease with Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Graves' disease is a common autoimmune condition impacting the thyroid gland, resulting in excessive hormone production. It affects metabolism, sleep quality, mood, and appetite. Early diagnosis and proactive management are vital.
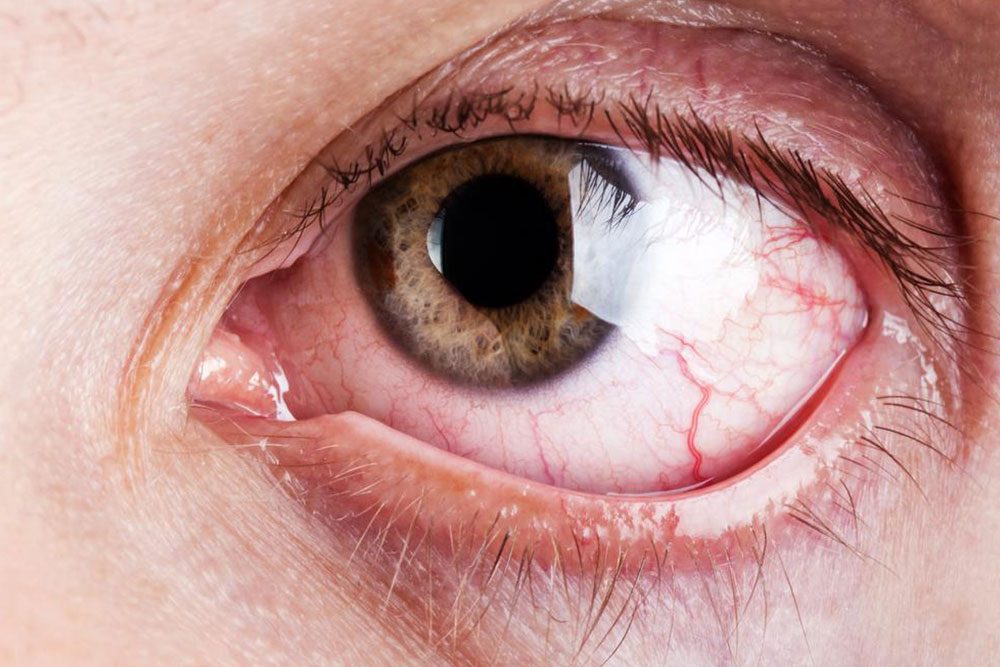
Symptoms include excessive sweating, weight loss, sleep disturbances, anxiety, fatigue, digestive problems, mood swings, enlarged thyroid (goiter), sensitivity to heat, irregular heartbeat, menstrual irregularities, erectile issues, and hand tremors. Less frequent signs include eye protrusion (Graves' ophthalmopathy) and skin thickening (Graves' dermopathy).
Key Tips for Managing Graves' Disease Naturally
While medical treatment is crucial, lifestyle modifications and self-care significantly help control symptoms.
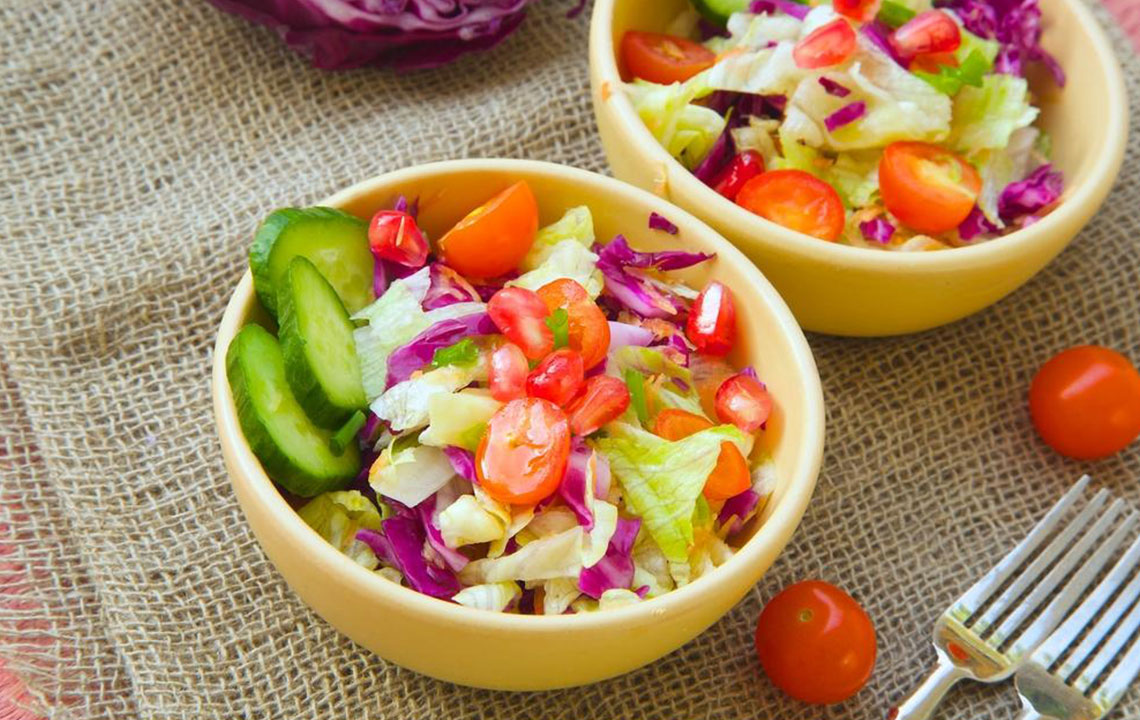
Follow a Balanced and Nutritious Diet Focus on consuming fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, spices, healthy fats, and probiotic-rich foods. This combination supports immune function and reduces inflammation linked to Graves' disease.
Reduce Stress Effectively High stress levels can aggravate symptoms. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, gentle exercise, massage therapy, or engaging in hobbies. Quality time with loved ones can also help lower stress.
Stay Active Regularly Engaging in physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, decrease inflammation, and boost overall health. Suitable options include yoga, swimming, cycling, and aerobics.
Avoid Smoking Smoking introduces toxins that promote inflammation and impair thyroid health, worsening Graves' symptoms.
Opt for Organic Goods Reduce chemical exposure by choosing organic products for cosmetics, personal hygiene, and food. This minimizes toxin intake and promotes better health.
Disclaimer: This blog shares educational health information. While the tips are supported by research, please consult healthcare providers for personalized medical advice. We are not responsible for any inaccuracies or outdated content.