Nutritional Tips for Managing High Blood Pressure Effectively
Discover effective dietary approaches to manage high blood pressure, including sodium reduction, potassium-rich foods, healthy oils, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish. Incorporating these foods into your routine can help control hypertension and improve overall cardiovascular health.

Strategies for Controlling Hypertension Through Diet
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a long-term condition marked by elevated arterial pressure levels. Often asymptomatic, if left unmanaged, it can lead to severe complications such as cardiovascular diseases, strokes, kidney damage, and vision problems. Implementing specific dietary practices is essential in mitigating these risks.
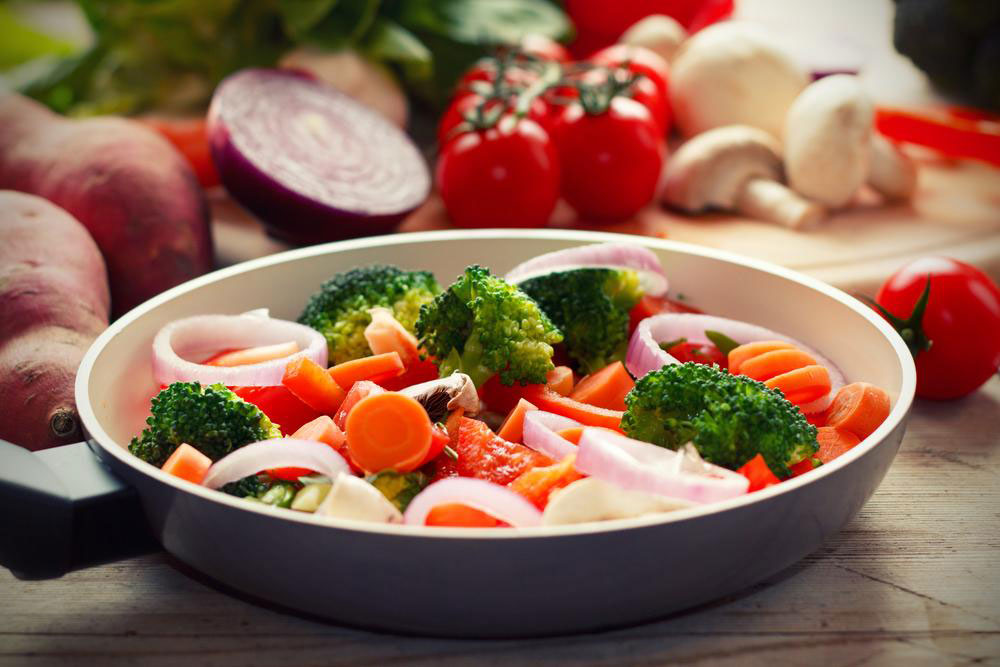
A key cause of hypertension is high sodium intake, which promotes fluid retention and increases pressure. A diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars is advised. Increasing intake of potassium-rich foods like sweet potatoes, white beans, winter squash, and low-fat yogurt helps maintain proper sodium balance. Incorporating flax seeds, which contain beneficial components like alpha-linolenic acid and lignans, can also assist in lowering blood pressure.
Dark chocolate or cocoa products, rich in flavanols, help relax blood vessels and enhance circulation. Using olive oil for cooking, known for its antioxidant polyphenols, supports vascular health. Unsalted pistachios may also aid in vessel relaxation, though further studies are ongoing.
Eating fatty fish such as salmon three times a week offers omega-3 fatty acids that can help reduce blood pressure within several months. Adopting the DASH diet, focused on heart-friendly foods, can be highly beneficial—consult your healthcare provider to customize dietary plans suited to your condition.