Comprehensive Guide to Insulin Therapy for Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide covers essential insulin administration techniques for diabetes management. It details the use of insulin in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, exploring various delivery methods like injections, pens, and pumps. Tailored to individual needs, this information helps patients choose suitable options for effective blood sugar control and improved quality of life. Always seek professional medical advice for personalized treatment plans.
Understanding Insulin Therapy for Effective Diabetes Control
Proper insulin management is crucial for people living with diabetes. Correct administration techniques and schedules are essential daily practices. While insulin therapy is most common among type 1 diabetics, many with type 2 also require it for optimal health.
Healthcare providers customize insulin regimens based on individual needs, as diabetes varies widely among patients. This article explores various methods of insulin delivery to help you choose the best fit for your lifestyle.
Insulin Usage in Type 1 Diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes generally follow a routine of daily insulin injections, starting with two doses per day and increasing to three or four based on blood glucose monitoring. Multiple insulin types are available to help achieve consistent blood sugar levels. Regular insulin administration minimizes the risk of complications such as stroke, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Insulin Needs for Type 2 Diabetes
Most type 2 diabetics end up needing insulin therapy at some stage, often combining it with oral medications and lifestyle changes. Some may initially require only one evening injection, but if oral treatments lose effectiveness, additional insulin doses may be needed.
Various Ways to Administer Insulin
While injections are common, other delivery methods exist to suit different preferences:
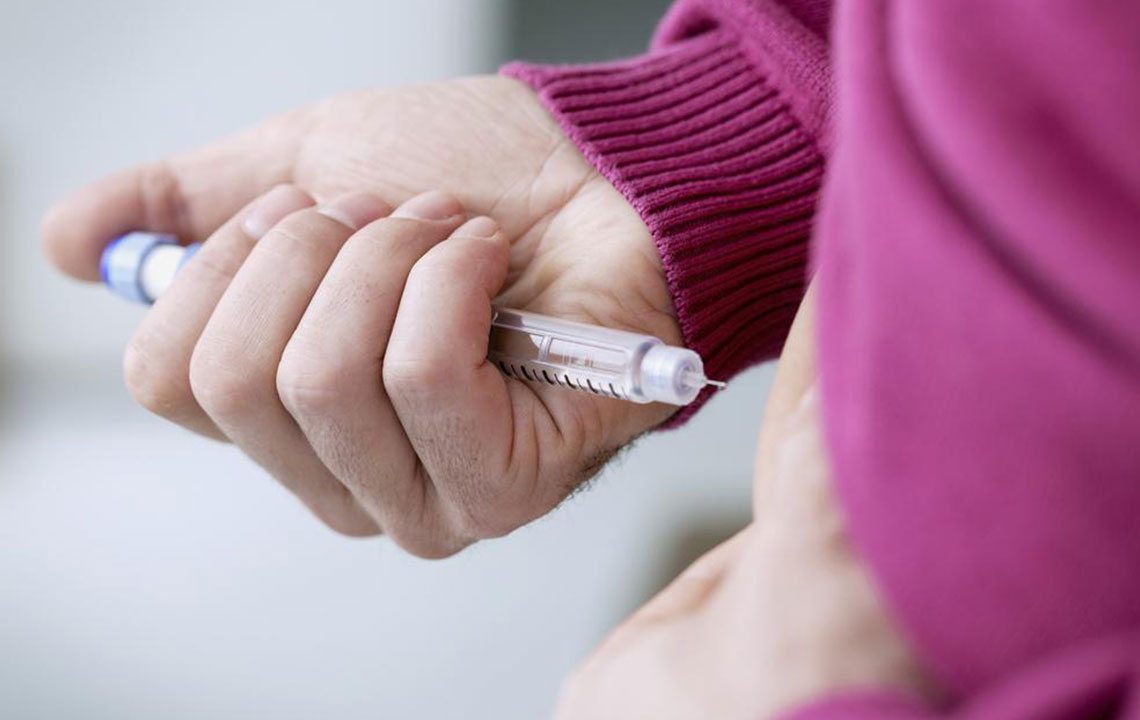
Syringe with magnifier: Helps those with impaired vision inject insulin safely by stabilizing the needle.
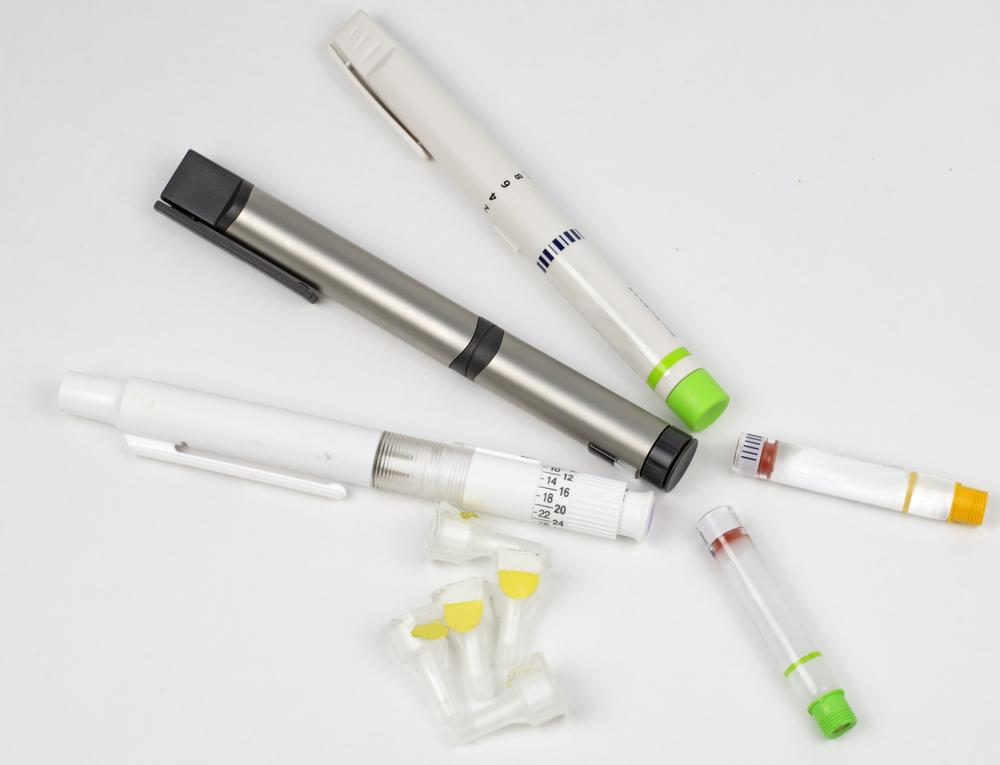
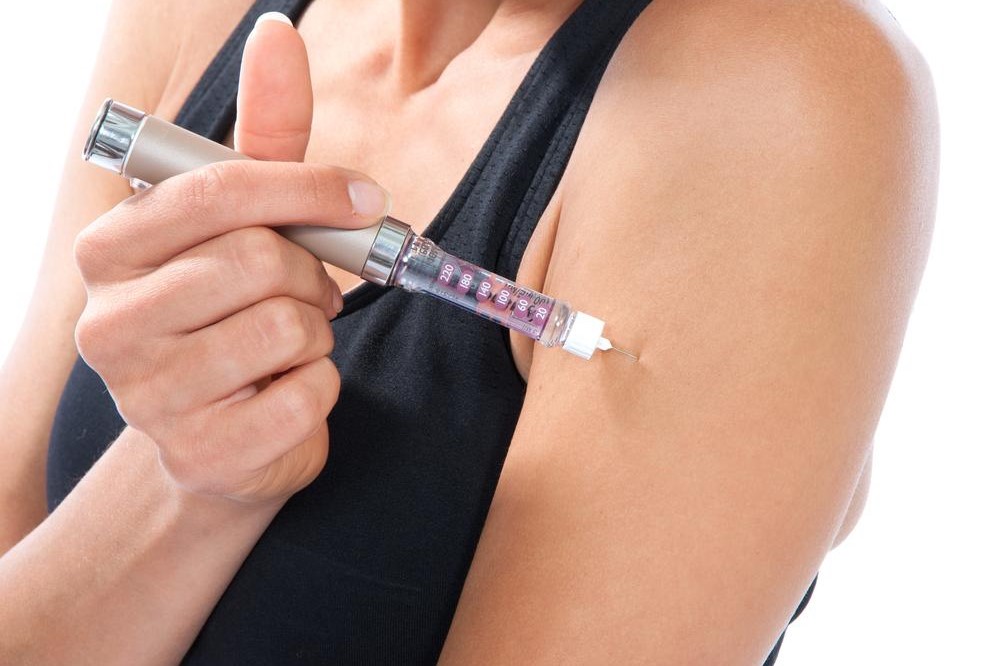
Reusable insulin pen: Looks like a large pen, releasing insulin via a pre-filled cartridge—simple to operate by pressing a button.
Insulin pump: A portable device worn on the body, delivering continuous insulin through a small tube inserted into the abdomen, adjustable for personalized dosing.
Insulin patch pump: A modern, less invasive system using an adhesive patch placed on the skin to administer insulin without needles or tubing.
Choosing the most suitable method depends on your lifestyle and comfort. These options provide flexibility for effective diabetes management with minimal hassle.
Important Reminder:
This overview offers general information about symptoms, treatments, and side effects. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance tailored to your condition.